“Spectral compression of mesh geometry” by Karni and Gotsman
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Spectral compression of mesh geometry
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
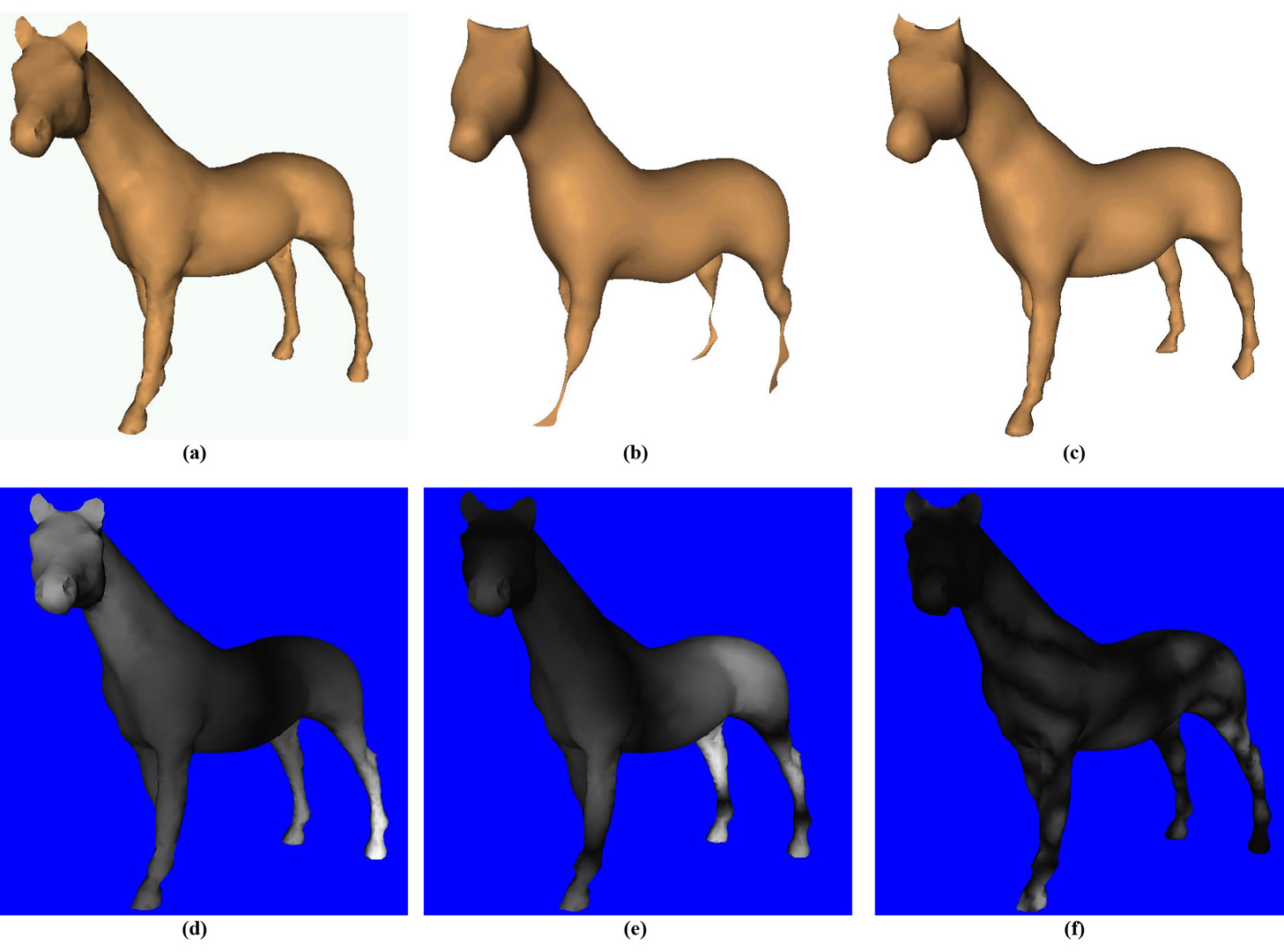
We show how spectral methods may be applied to 3D mesh data to obtain compact representations. This is achieved by projecting the mesh geometry onto an orthonormal basis derived from the mesh topology. To reduce complexity, the mesh is partitioned into a number of balanced submeshes with minimal interaction, each of which are compressed independently. Our methods may be used for compression and progressive transmission of 3D content, and are shown to be vastly superior to existing methods using spatial techniques, if slight loss can be tolerated.
References:
1. V. Bajaj, V. Pascucci and G. Zhuang. Single resolution compression of arbitrary triangular meshes with properties. Proceedings of the Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, 1999.
2. N. Biggs. Alegbraic Graph Theory (2nd Ed.). Cambridge University Press, 1993.
3. M. Chow. Geometry compression for real-time graphics. Proceedings of Visualization ’97, IEEE, 1997.
4. D. Cohen-Or, O. Remez, and D. Levin, Progressive compression of arbitrary triangular meshes. Proceedings of Visualization ’99, IEEE, 1999.
5. M. Deering, Geometry compression, Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’95, pp. 13-20, ACM, 1995.
6. M. Desbrun, M. Meyer, P. Schroeder and A. Barr. Implicit fairing of irregular meshes using diffusion and curvature flow. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’99, pp. 317-324, ACM, 1999.
7. M. Garey and D. Johnson, Computers and intractability: A guide to the theory of NP-completeness, Addison-Wesley, 1978.
8. S. Gumhold and W. Strasser. Real time compression of triangle mesh connectivity. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’98, pp. 133-140, ACM, 1998.
9. I. Guskov, W. Sweldens and P. Schroeder. Multiresolution signal processing for meshes. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’99, pp. 325-334, ACM, 1999.
10. M. Isenburg and J. Snoeyink. Mesh collapse compression. Proceedings of SIBGRAPHI’99- 12th Brazilian Symposium on Computer Graphics and Image Processing, pp.27- 28, 1999.
11. M. Isenberg and J. Snoeyink. FaceFixer: Compressing polygon meshes with properties. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 2000.
12. A. Khodakovsky, P. Schroeder and W. Sweldens. Progressive geometry compression. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 2000.
13. D. King and J. Rossignac. Guaranteed 3.67v bit encoding of planar triangle graphs. In Proceedings of 1 lth Canadian Conference on Computation Geometry, pp.146-149, 1999.
14. G. Karypis and V. Kumar. MeTiS: A software package for partitioning unstructured graphs, partitioning meshes, and computing fill-reducing orderings of sparse matrices. Version 4.0, Univ. of Minnesota, Dept. of Computer Science, 1998. Available at http://wwwusers.cs.umn.edu/Nkarypis/metis/metis.html
15. L. Kobbelt, S. Campanga, J. Vorsatz and H.-P. Seidel. Interactive multi-resolution modeling on arbitrary meshes. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’98, pp. 105-114, ACM, 1998.
16. P. Lancaster and M. Tismenetsky. The theory of matrices. (2nd Ed.), Academic Press, 1985.
17. J. Li and C.-C. Kuo, A dual graph approach to 3D triangular mesh compression, In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Chicago, 1998.
18. J. Rossignac. Edgebreaker: Connectivity compression for triangle meshes. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 5(1), 1999.
19. D. Salomon. Data compression: The complete reference. Springer Verlag, 1998.
20. G. Taubin. A signal processing approach to fair surface design. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’95, pp. 351-358, ACM, 1995.
21. G. Taubin and J. Rossignac. Geometric compression through topological surgery. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 17(2):84-115, 1998.
22. C. Touma and C. Gotsman. Triangle mesh compression. In Proceedings of Graphics Interface ’98, pp. 26-34, 1998.