“Leo: a system for cost effective 3D shaded graphics” by Deering and Nelson
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Leo: a system for cost effective 3D shaded graphics
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
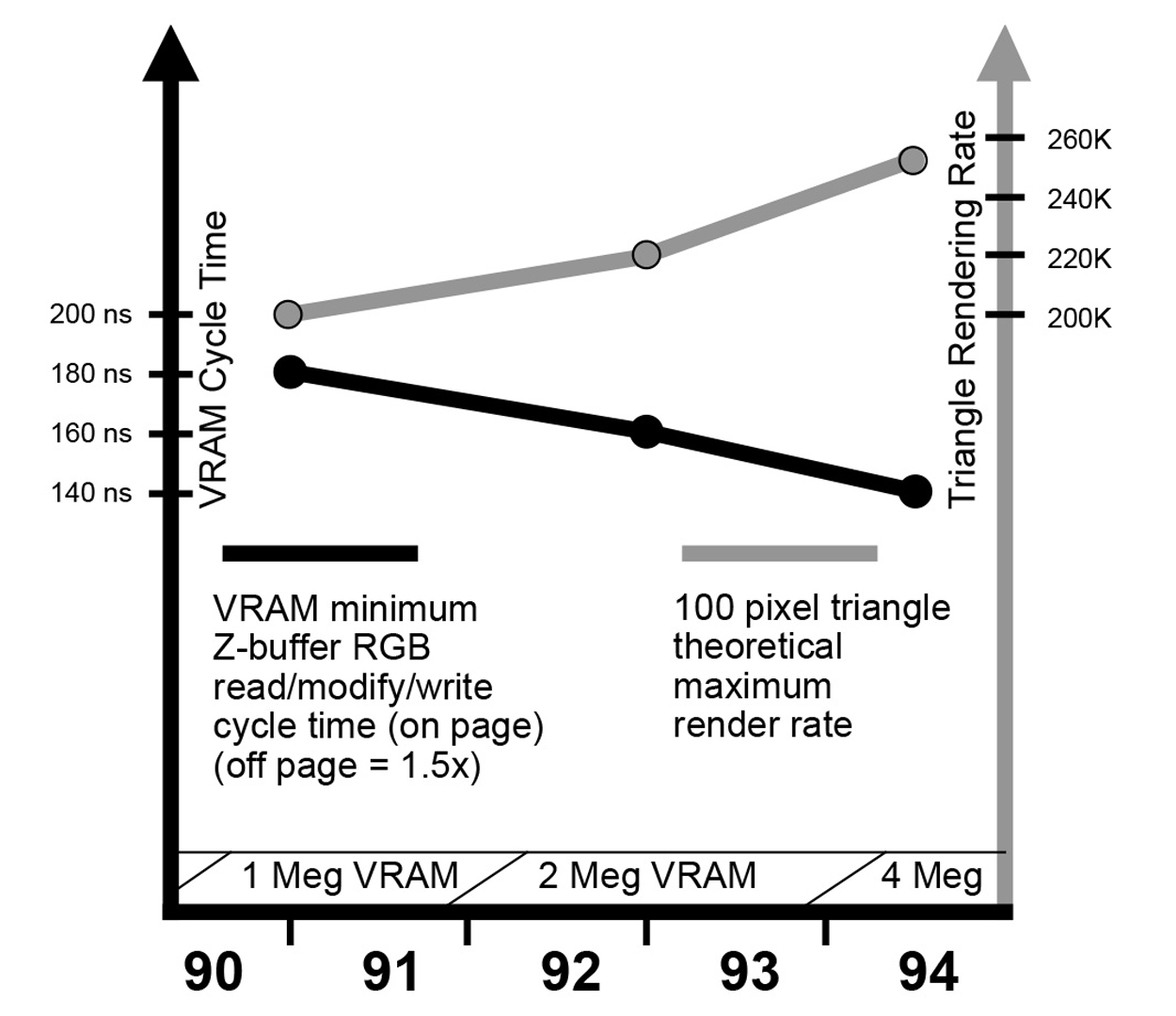
A physically compact, low cost, high performance 3D graphics accelerator is presented. It supports shaded rendering of triangles and antialiased lines into a double-buffered 24-bit true color frame buffer with a 24-bit Z-buffer. Nearly the only chips used besides standard memory parts are 11 ASICs (of four types). Special geometry data reformatting hardware on one ASIC greatly speeds and simplifies the data input pipeline. Floating-point performance is enhanced by another ASIC: a custom graphics microprocessor, with specialized graphics instructions and features. Screen primitive rasterization is carried out in parallel by five drawing ASICs, employing a new partitioning of the back-end rendering task. For typical rendering cases, the only system performance bottleneck is that intrinsically imposed by VRAM.
References:
1. Abi-Ezzi, Salim, and L. Shirman. Tessellation of Curved Surfaces under Highly Varying Transformations. Proc. Eurographics ’91 (Vienna, Austria, September 1991), 385-397.
2. Akeley, Kurt and T. Jermoluk. High-Performance Polygon Rendering, Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’88 (Atlanta, GA, Aug 1-5, 1988). In Computer Graphics 22, 4 (July 1988), 239-246.
3. Anido, M., D. Allerton and E. Zaluska. MIGS – A Multiprocessor Image Generation System using RISC-like Microprocessors. Proceedings of CGI ’89 (Leeds, UK, June 1989), Springer Verlag 1990.
4. Deering, Michael, S. Winner, B. Schediwy, C. Dully and N. Hunt. The Triangle Processor and Normal Vector Shader: A VLSI system for High Performance Graphics. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’88 (Atlanta, GA, Aug 1-5, 1988). In Computer Graphics 22, 4 (July 1988), 21-30.
5. Deering, Michael. High Resolution Virtual Reality. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’92 (Chicago, IL, July 26-31, 1992). In Computer Graphics 26, 2 (July 1992), 195-202.
6. Dunnett, Graham, M. White, P. Lister and R. Grimsdale. The Image Chip for High Performance 3D Rendering. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications 12, 6 (November 1992), 41-52.
7. Foley, James, A. van Dam, S. Feiner and J Hughes. Computer Graphics: Principles and Practice, 2nd ed., Addison- Wesley, 1990.
8. Kelley, Michael, S. Winner, K. Gould. A Scalable Hardware Render Accelerator using a Modified Scanline Algorithm. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’92 (Chicago, IL, July 26-31, 1992). In Computer Graphics 26, 2 (July 1992), 241-248.
9. Kirk, David, and D. Voorhies. The Rendering Architecture of the DN10000VS. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’90 (Dallas, TX, August 6-10, 1990). In Computer Graphics 24, 4 (August 1990), 299-307.
10. Molnar, Steven, J. Eyles, J. Poulton. PixelFlow: High-Speed Rendering Using Image Composition. Proceedings of SIG- GRAPH ’92 (Chicago, IL, July 26-31, 1992). In Computer Graphics 26, 2 (July 1992), 231-240.
11. Nelson, Scott. GPC Line Quality Benchmark Test. GPC Test Suite, NCGA GPC committee 1991.
12. Torborg, John. A Parallel Processor Architecture for Graphics Arithmetic Operations. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’87 (Anaheim, CA, July 27-31, 1987). In Computer Graphics 21, 4 (July 1987), 197-204.