“Image-based lighting with a piecewise-constant importance function” by Cohen
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Image-based lighting with a piecewise-constant importance function
Session/Category Title: Global Illumination
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
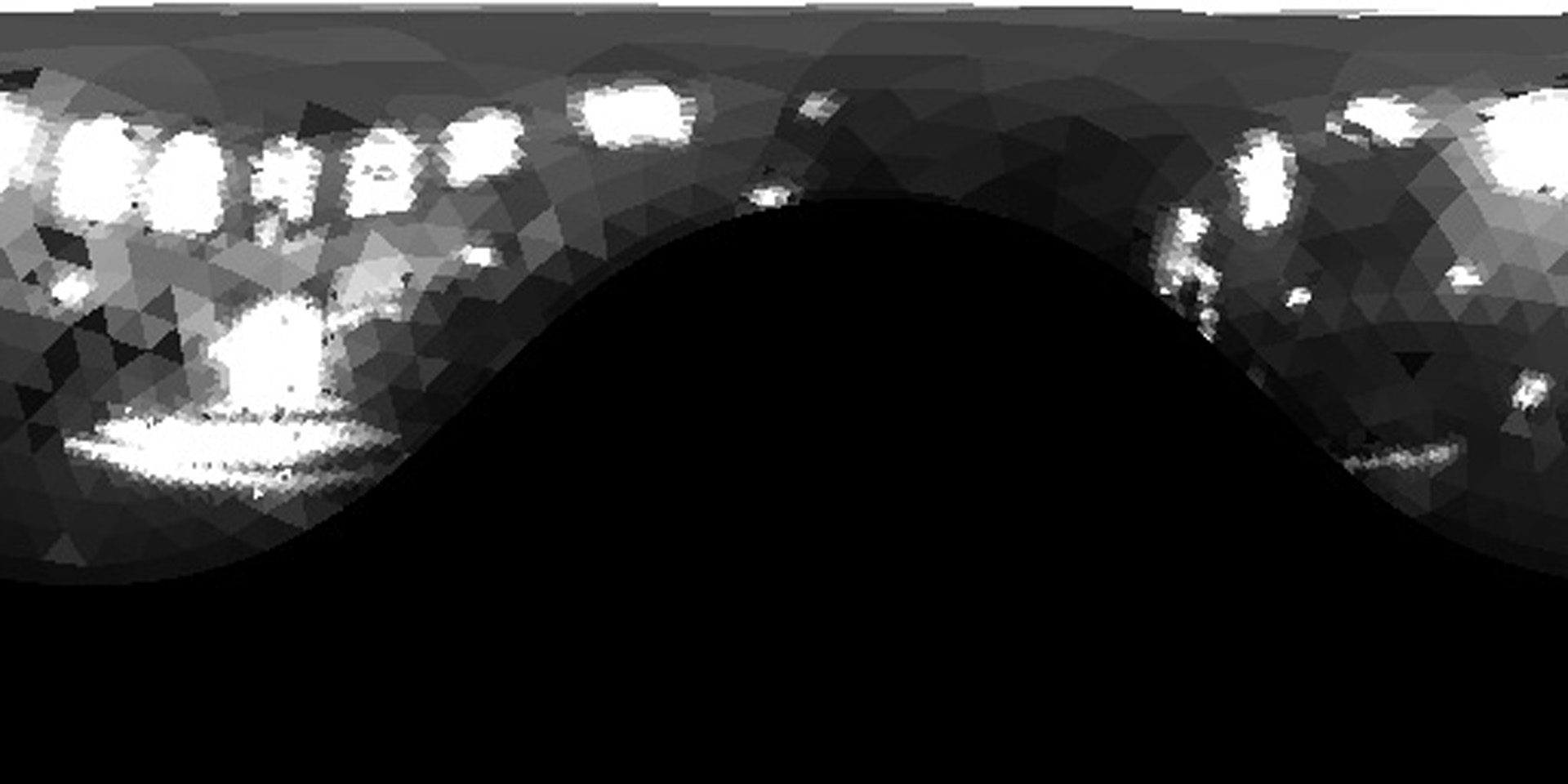
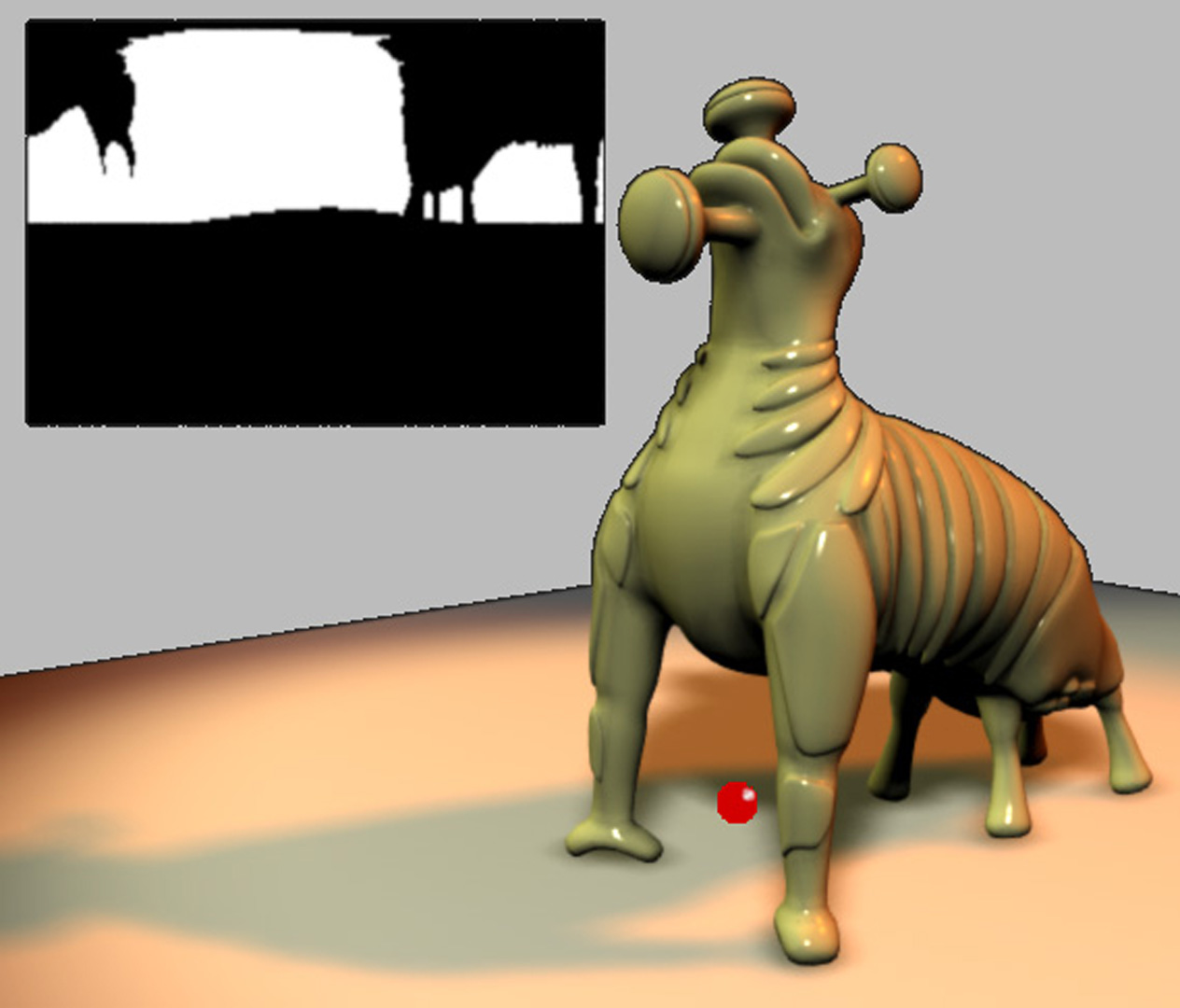
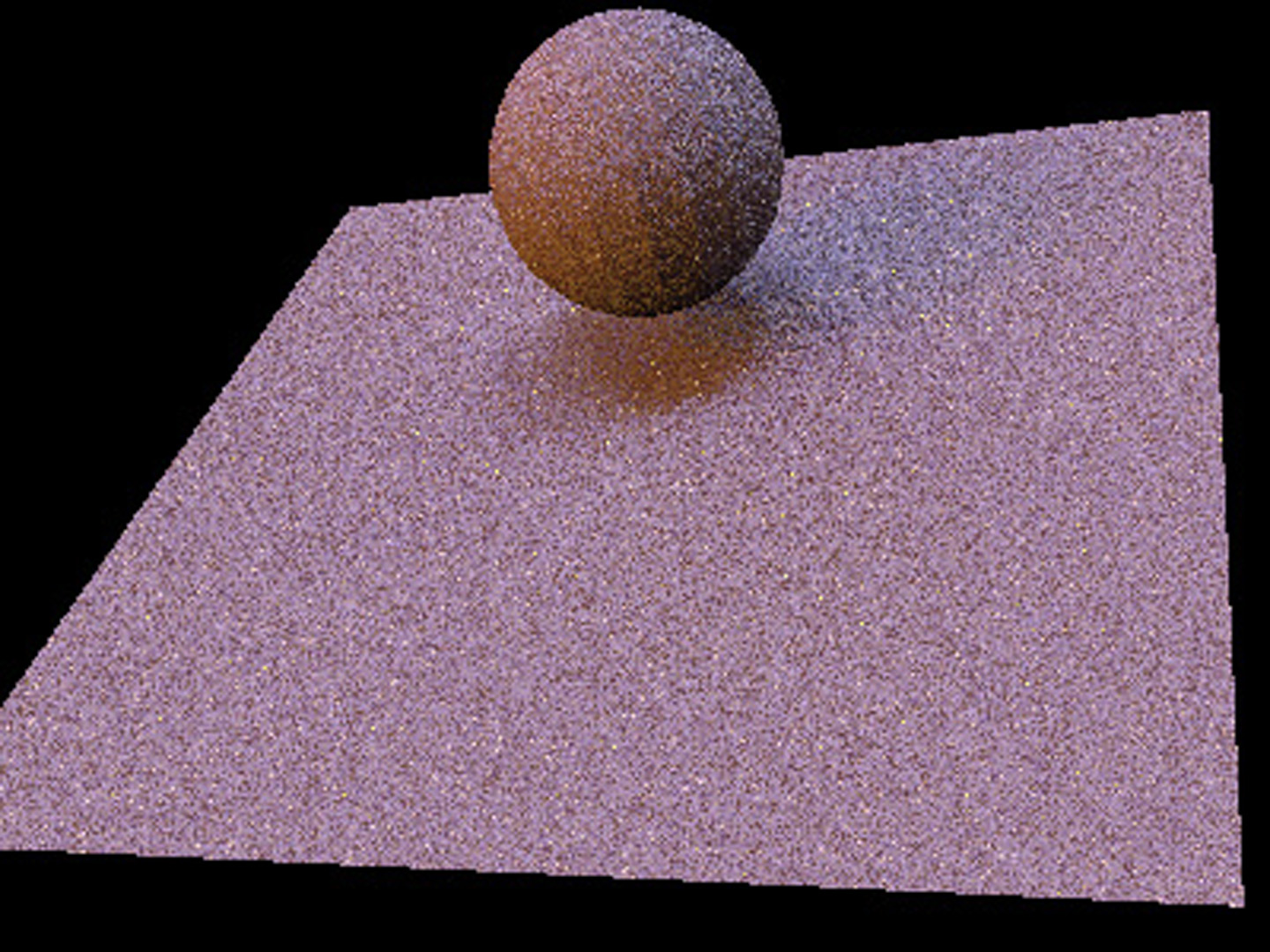
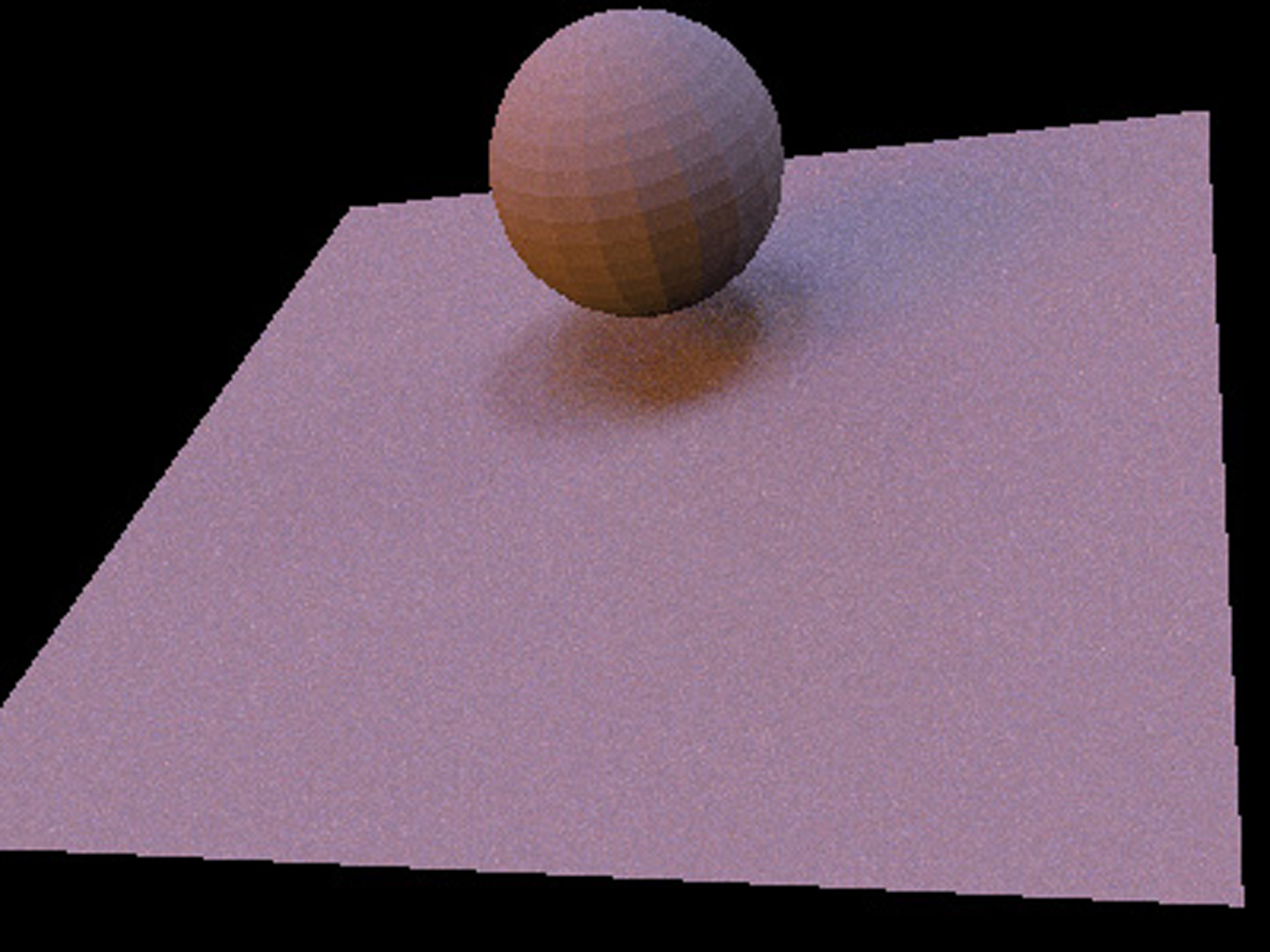
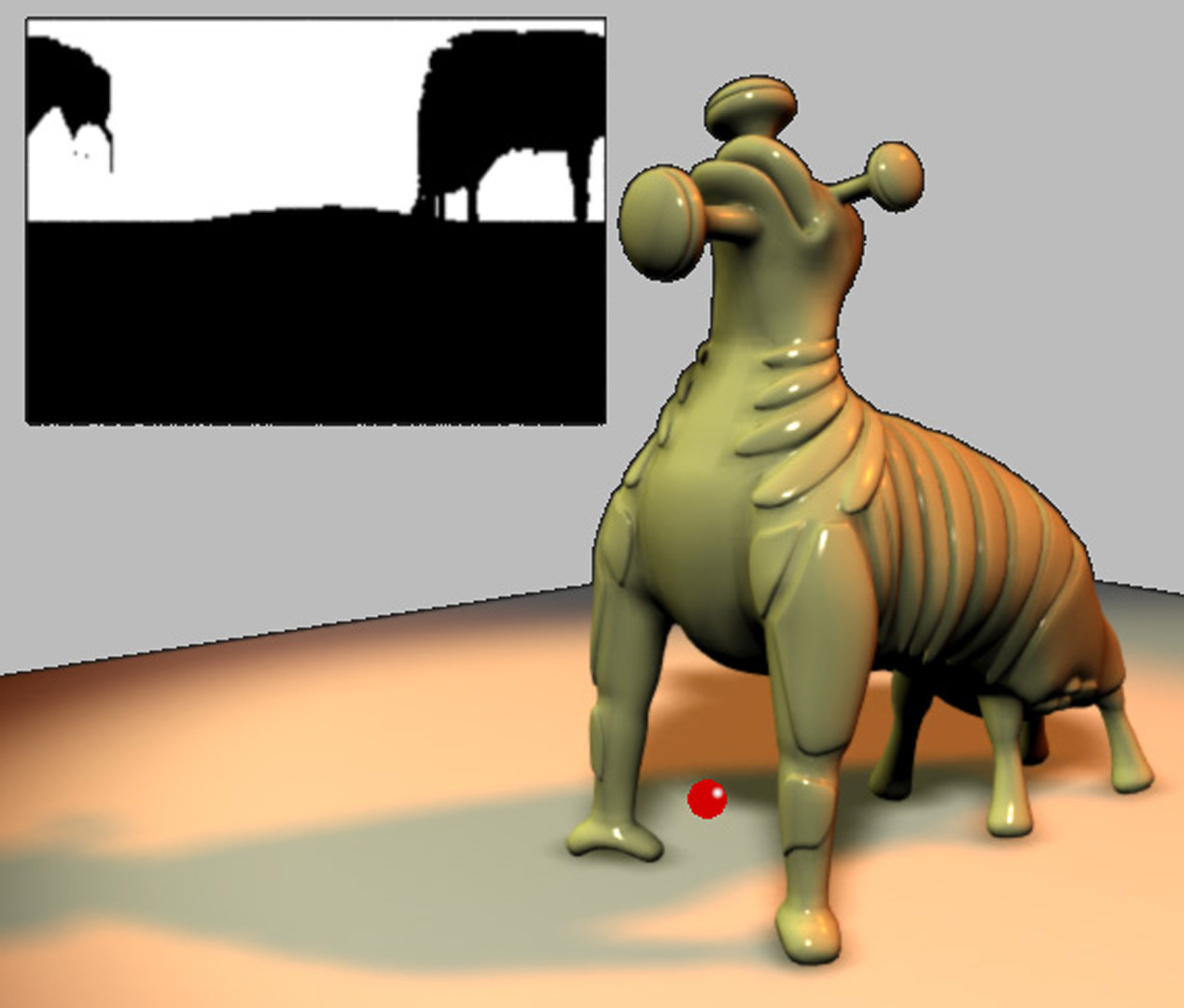
A common rendering task in visual effects is to integrate computer- generated elements with a live action background. The CG models range from organic characters animated via complex physical models to static objects like buildings or vehicles. Often, all of the light in the scene emanates from outside the object, and the object passively reflects incident radiance toward the camera. In the technique of Image-based lighting (IBL), the light from the real world is recorded and used to render the virtual object.
To handle these situations realistically, global illumination algorithms (such as [Agarwal et al. 2003] and [Kollig and Keller 2003])]) computeat a surface point, the radiance reflected toward the cam- era due to direct illumination (i.e., photons that have traveled directly from the light source to the surface, without having been reflected in between). We present an unbiased Monte Carlo technique for estimating this value efficiently. We use an importance sampling estimator with a novel piecewise-constant importance function that effectively concentrates ray samples where energy is likely to be found.
References:
Agarwal, S., Ramamoorthi, R., Belongie, S., and Jensen, H. W. 2003. Structured importance sampling of environment maps. ACM Transactions on Graphics 22, 3 (July), 605–612.
Kollig, T., and Keller, A. 2003. Efficient illumination by high dynamic range images. In Eurographics Symposium on Rendering: 14th Eurographics Workshop on Rendering, 45–51.