“Verifocal: a Platform for Vision Correction and Accommodation in Head-Mounted Displays” by Laont, Hasnain, Guillemet, Wirajaya, Khoo, et al. …
Notice: Pod Template PHP code has been deprecated, please use WP Templates instead of embedding PHP. has been deprecated since Pods version 2.3 with no alternative available. in /data/siggraph/websites/history/wp-content/plugins/pods/includes/general.php on line 518
Conference:
- SIGGRAPH 2018
-
More from SIGGRAPH 2018:
Notice: Array to string conversion in /data/siggraph/websites/history/wp-content/plugins/siggraph-archive-plugin/src/next_previous/source.php on line 345

Notice: Array to string conversion in /data/siggraph/websites/history/wp-content/plugins/siggraph-archive-plugin/src/next_previous/source.php on line 345

Type(s):
Entry Number: 22
Title:
- Verifocal: a Platform for Vision Correction and Accommodation in Head-Mounted Displays
Presenter(s):
Description:
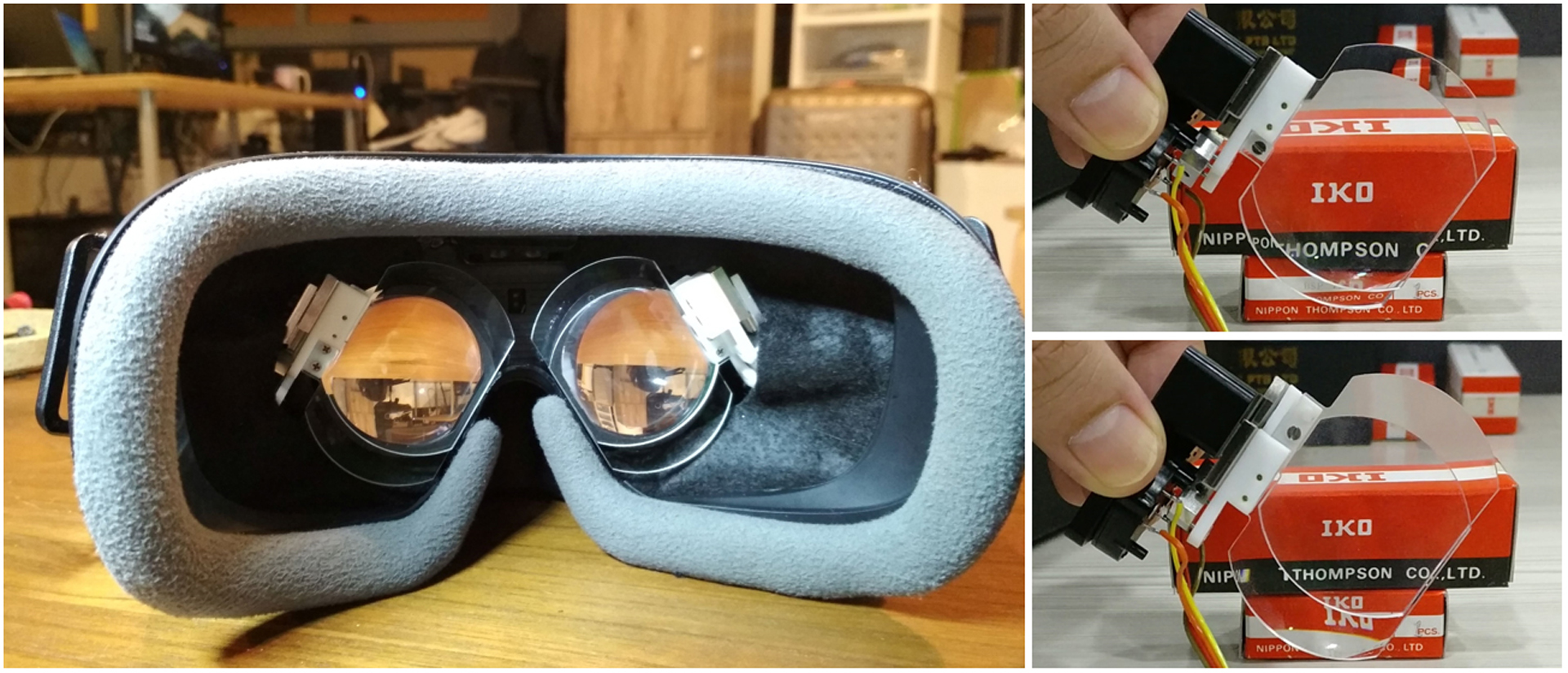
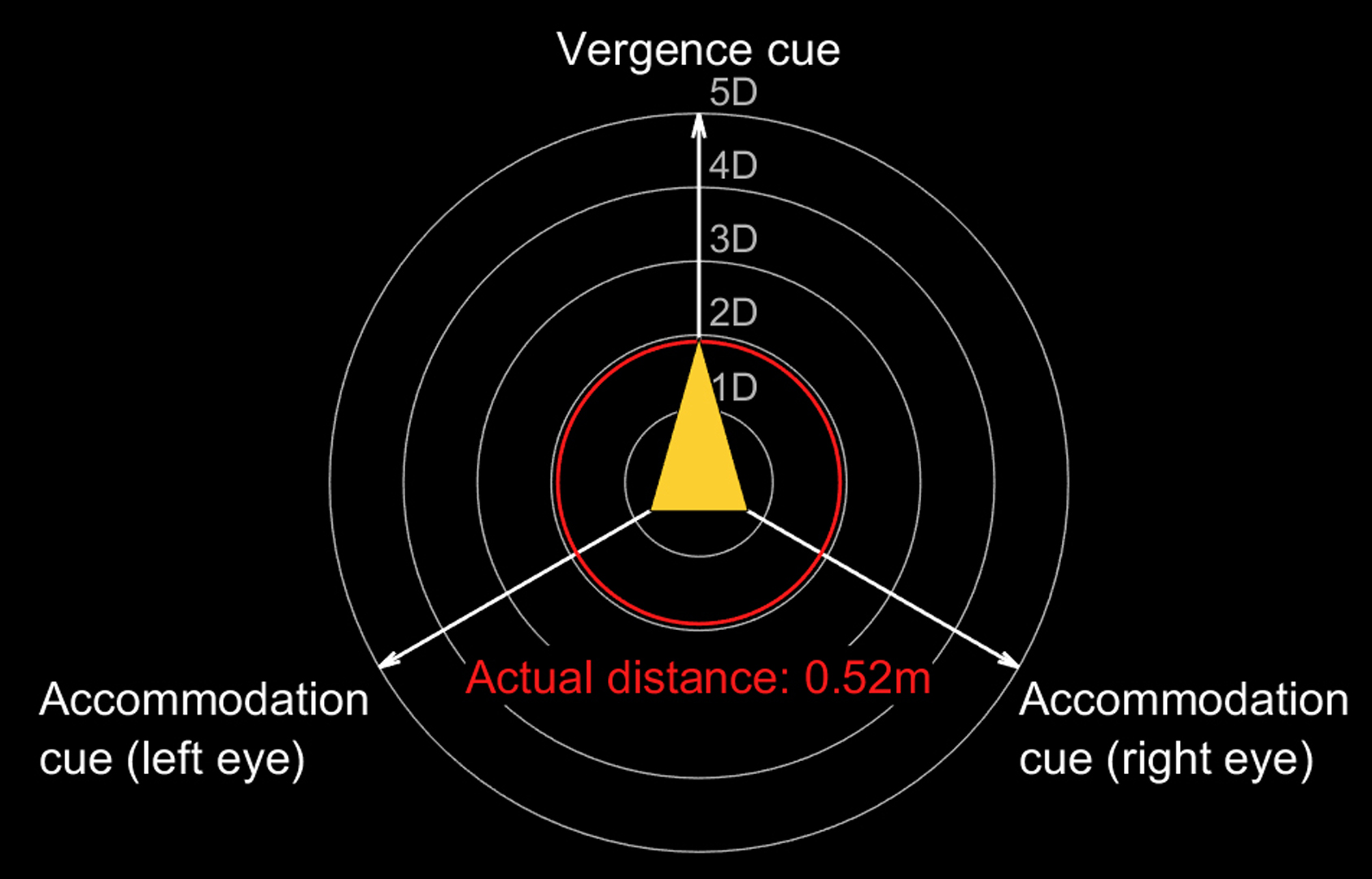
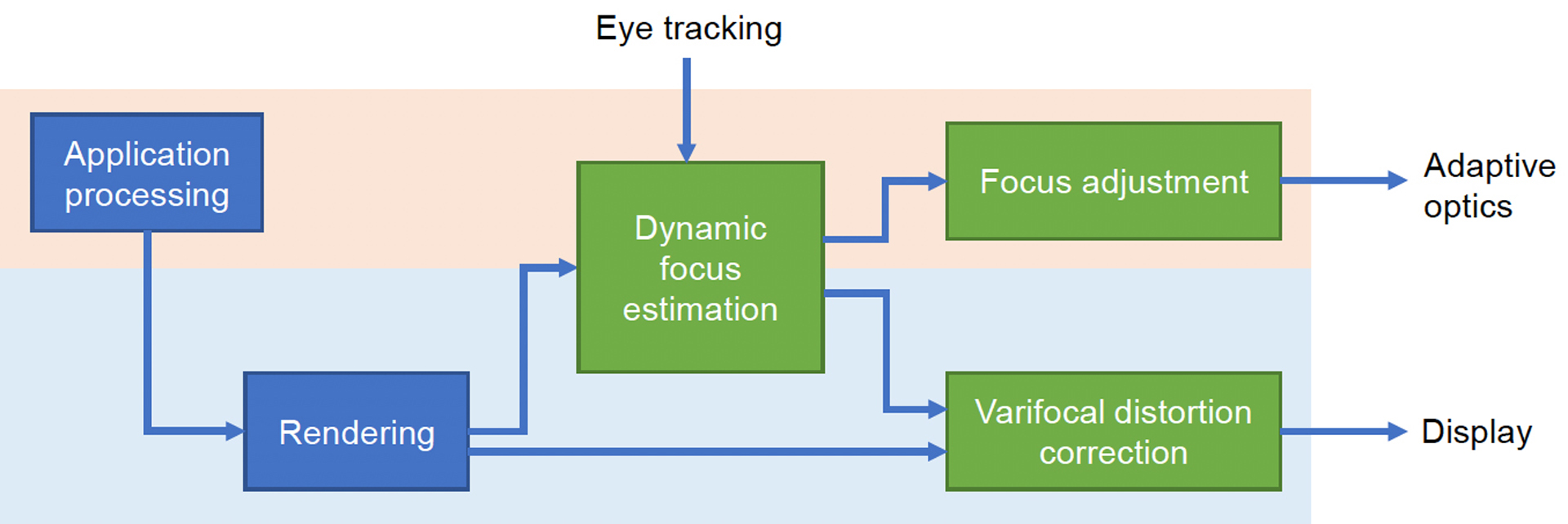
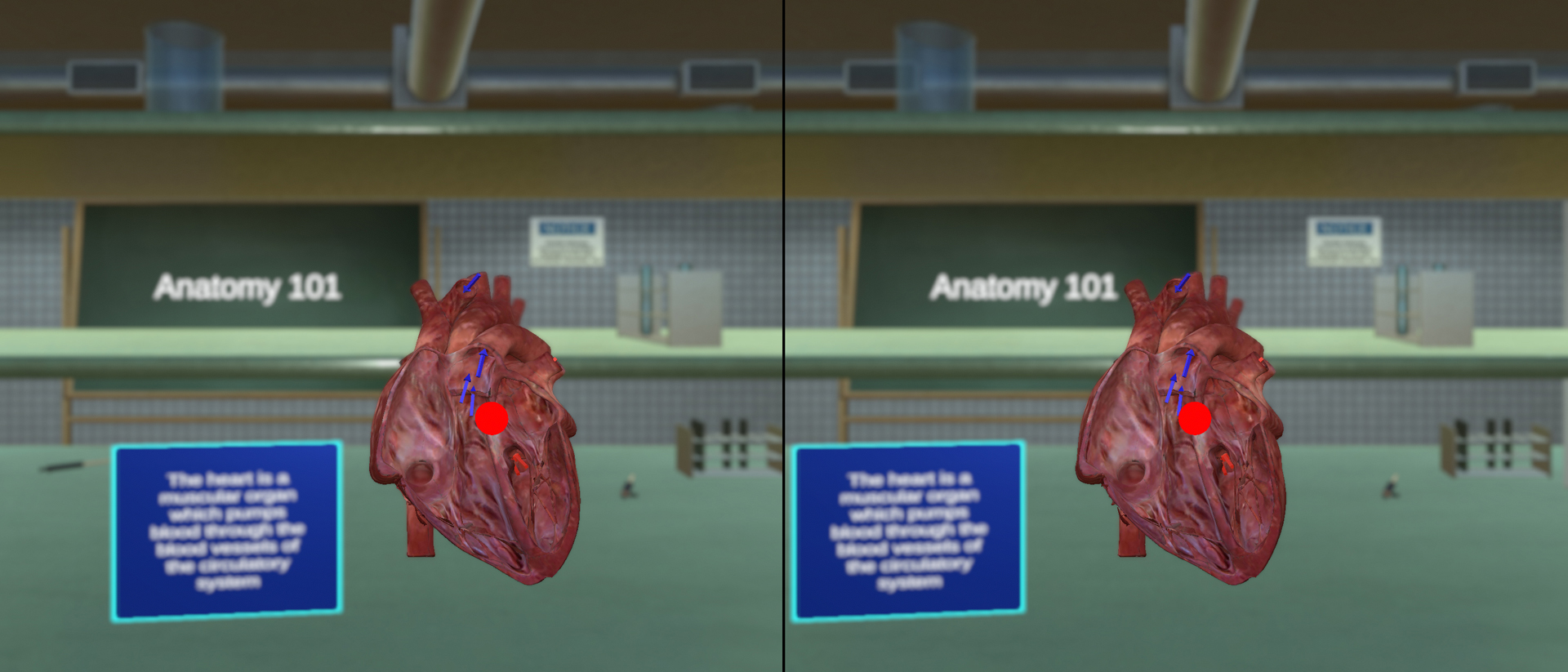
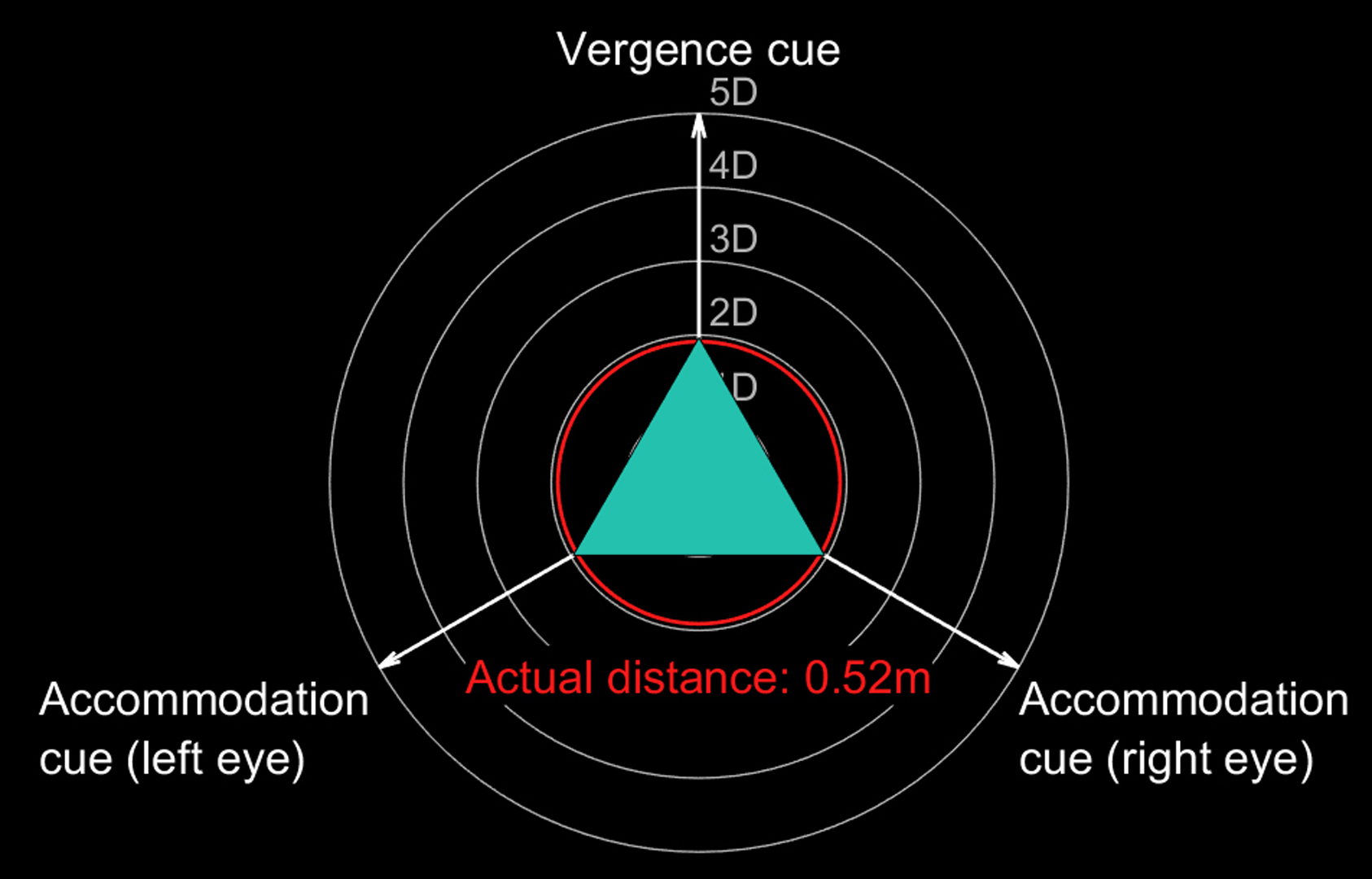
The vergence-accommodation conflict is a fundamental cause of discomfort in today’s Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR). We present a novel software platform and hardware for varifocal headmounted displays (HMDs) to generate consistent accommodation cues and account for the user’s prescription. We investigate multiple varifocal optical systems and propose the world’s first varifocal mobile HMD based on Alvarez lenses. We also introduce a varifocal rendering pipeline, which corrects for distortion introduced by the optical focus adjustment, approximates retinal blur, incorporates eye tracking and leverages on rendered content to correct noisy eye tracking results. We demonstrate the platform running in compact VR headsets and present initial results in video pass-through AR.
References:
K. Aksit, W. Lopes, J. Kim, P. Shirley, and D. Luebke. 2017. Near-eye varifocal augmented reality display using see-through screens. ACM Trans. Graph. 6 (2017).
L.W. Alvarez. 1967. Two-element variable-power spherical lens. (1967). US Patent 3,305,294.
D. Dunn, C. Tippets, K. Torell, P. Kellnhofer, Akșit K, P. Didyk, K. Myszkowski, D. Luebke, and H. Fuchs. 2017. Wide €eld of view varifocal near-eye display using see-through deformable membrane mirrors. TVCG 23, 4 (2017).
D. Hoffman, A. Girshick, K. Akeley, and M. Banks. 2008. Vergence-accommodation conflicts hinder visual performance and cause visual fatigue. Journal of Vision 8, 3 (2008).
H. Hua. 2017. Enabling focus cues in head-mounted displays. Proc. IEEE 105 (2017).
R. Konrad, E. Cooper, and G. Wetzstein. 2016. Novel optical configurations for virtual reality: evaluating user preference and performance with focus-tunable and monovision near-eye displays. In CHI.
G. Koulieris, B. Bui, M. Banks, and G. Drettakis. 2017. Accommodation and comfort in head-mounted displays. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (2017), 87:1–87:11.
G. Kramida. 2016. Resolving the vergence-accommodation conflict in head-mounted displays. IEEE TVCG 22, 7 (2016), 1912–1931.
P.-Y. Laffont and A. Hasnain. 2017. Adaptive dynamic refocusing: toward solving discomfort in virtual reality. In SIGGRAPH’17, Emerging Technologies.
N. Padmanaban, R. Konrad, T. Stramer, E.A. Cooper, and G.Wetzstein. 2017. Optimizing virtual reality for all users through gaze-contingent and adaptive focus displays. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2017).
R. E. Stevens, D. Rhodes, A. Hasnain, and P.-Y. Laffont. 2018. Varifocal technologies providing prescription and VAC mitigation in HMDs using Alvarez lenses. (2018).
C. Vienne, L. Sorin, L. Blondé, Q. Huynh-.u, and P. Mamassian. 2014. Effect of the accommodation-vergence conflict on vergence eye movements. Vision Research 100 (2014), 124–133.
Keyword(s):
- varifocal
- vision correction
- vergence-accommodation conict
Additional Images: