“Embroidery Modeling and Rendering in Real Time” by Chen, McCool and Kitamoto
Conference:
- SIGGRAPH 2011
-
More from SIGGRAPH 2011:


Type(s):
Title:
- Embroidery Modeling and Rendering in Real Time
Presenter(s):
Description:
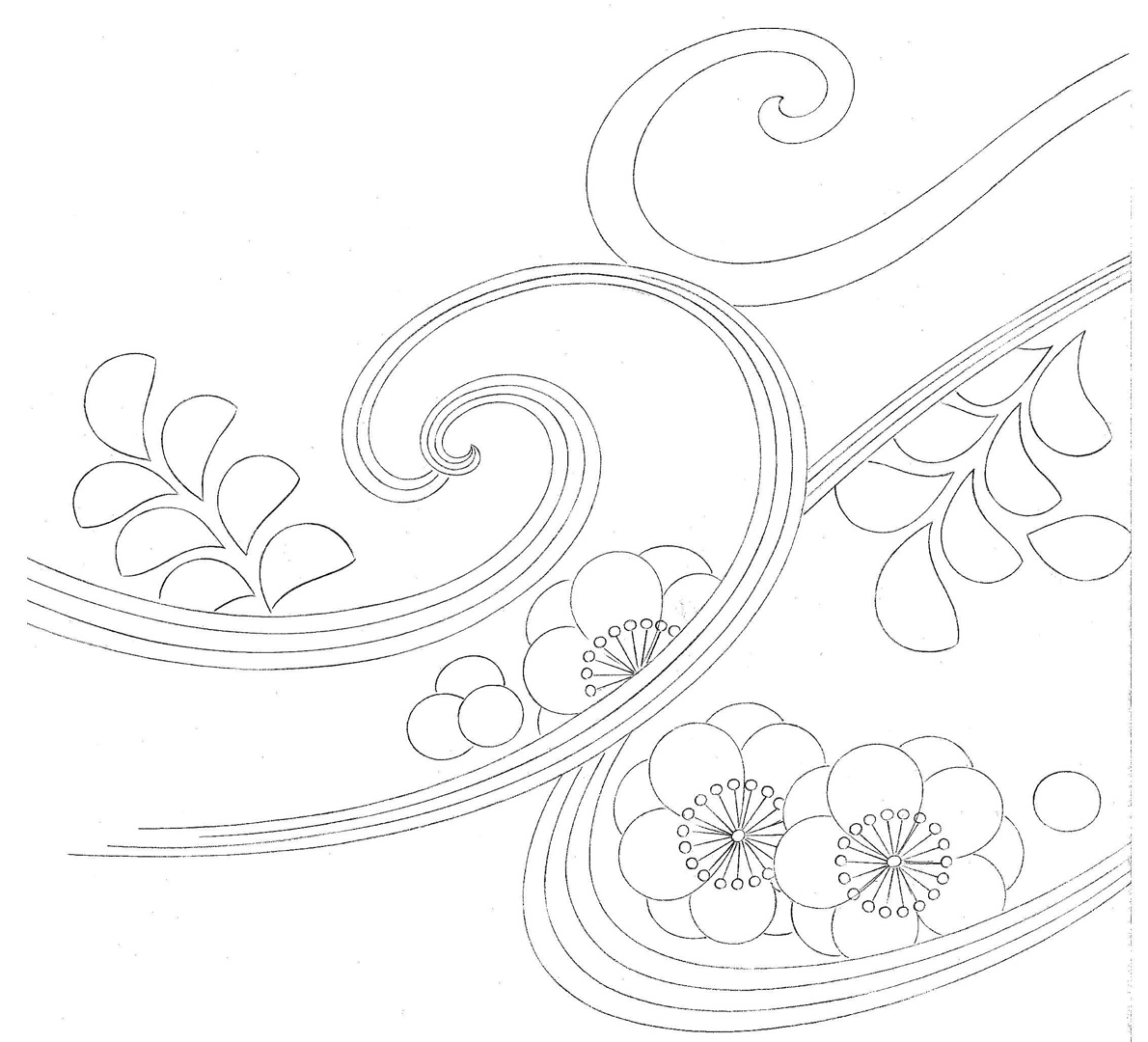
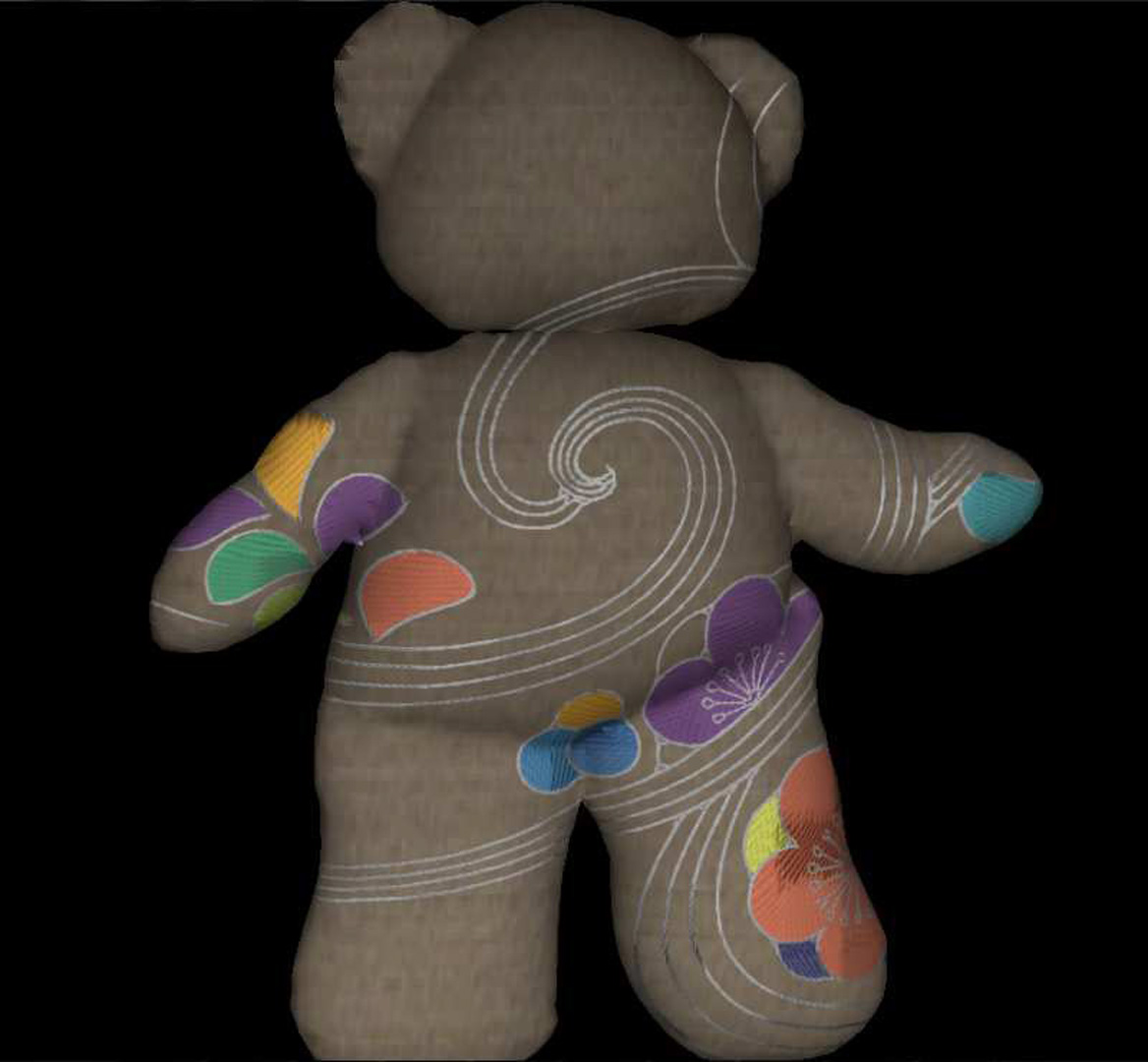
Many non-photorealistic rendering algorithms have been developed recently that simulate different traditional artistic styles including painting, mosaics, and stippling. However, there is at least one more traditional approach to rendering images non-photorealistically: embroidery. Embroidery creates images by stitching threads of different colours into a base cloth. In free hand embroidery, many different stitch styles are possible and stitches can be placed relatively freely on the surface.
There is no previous work dealing specifically with stitch placement to simulate embroidery, but there are some applicable techniques. For example, based on Lloyd’s Method, a common iterative technique to place samples by relaxation, Hausner [Hausner 2001] developed an algorithm to distribute small square tiles to form synthetic mosaics. The stippling algorithm presented by Secord successfully produces attractive results in a natural way by using a weighted variant of Lloyd’s method [Secord 2002].
Embroidery also has a set of traditional patterns. As a reference, we have been studying the book Traditional Japanese Patterns [Kurenai-Kai 2005] which defines a set of sewing techniques used in Japanese free embroidery.
The goal of our work is to transform a traditional embroidery pattern (typically consisting mainly of region outlines) into a high-quality embroidery image generated in real time. Real time rendering enables the user to navigate around the image and manipulate it. We also want to be able to place the embroidery on deforming objects and use dynamic lighting models for the threads.