“CHICAP: Low-cost hand motion capture device using 3D magnetic sensors for manipulation of virtual objects” by Lee, Kim, Kim and Lee
Conference:
Experience Type(s):
Title:
- CHICAP: Low-cost hand motion capture device using 3D magnetic sensors for manipulation of virtual objects
Entry Number: 04
Organizer(s)/Presenter(s):
Description:
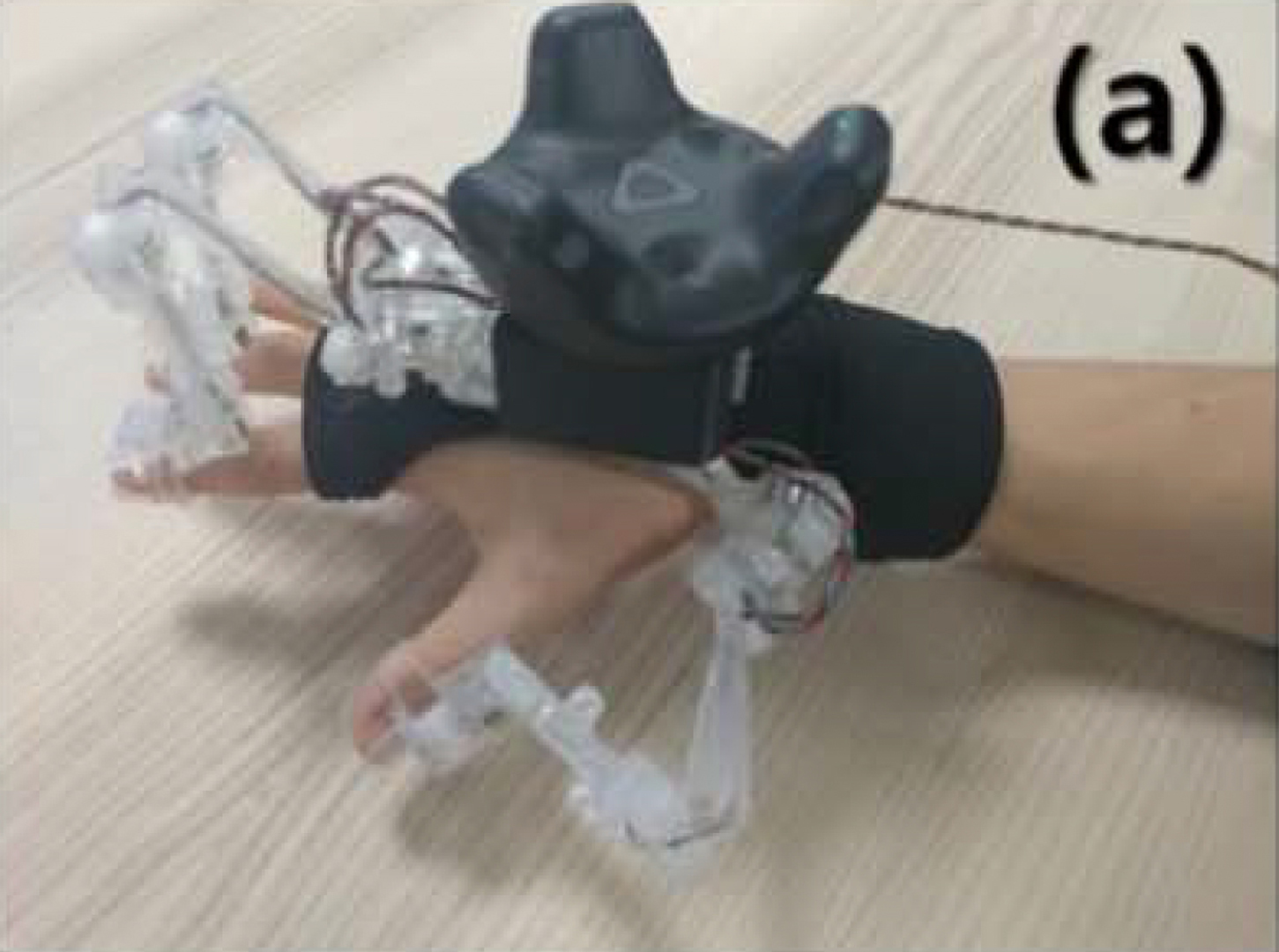
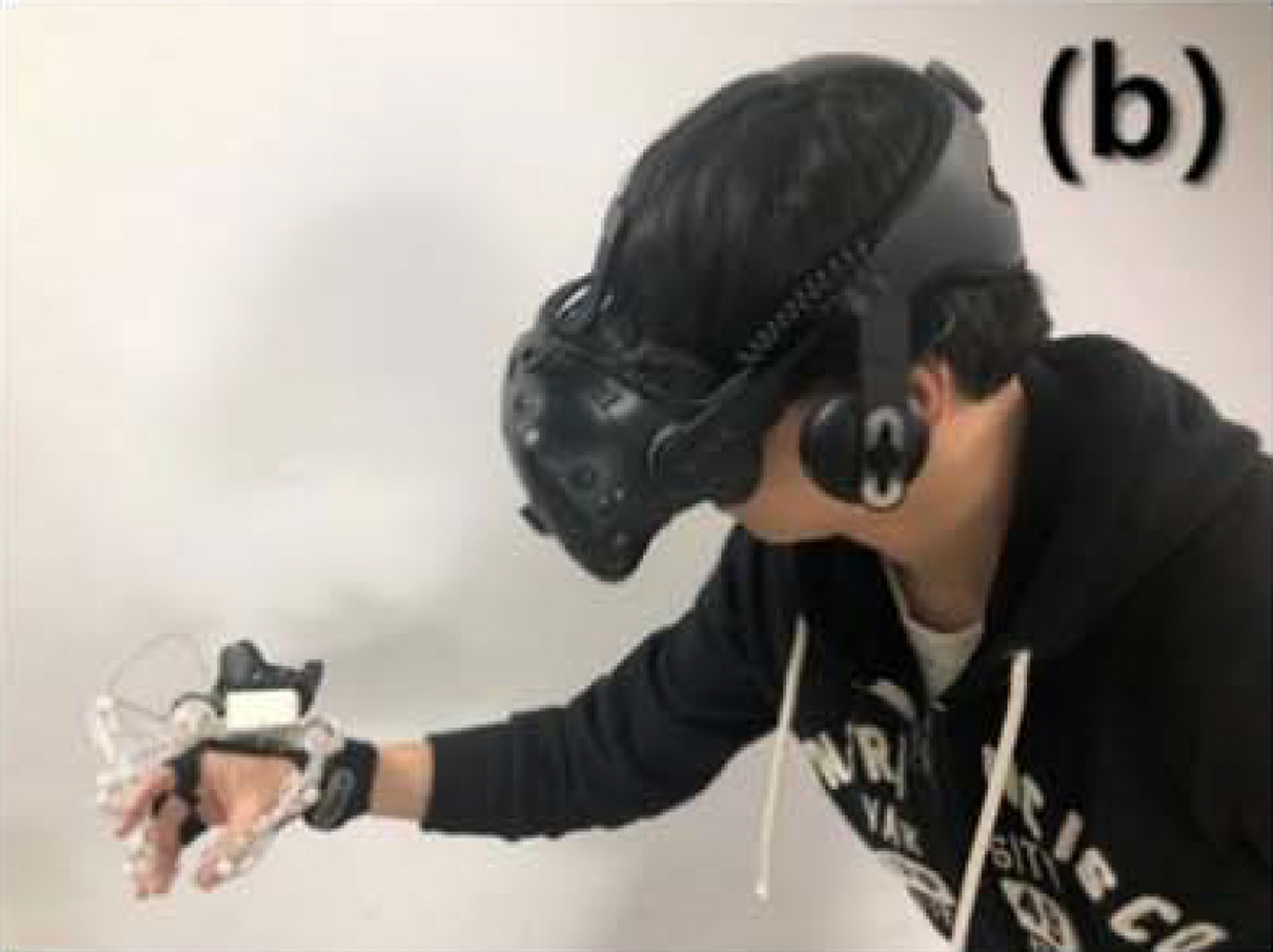
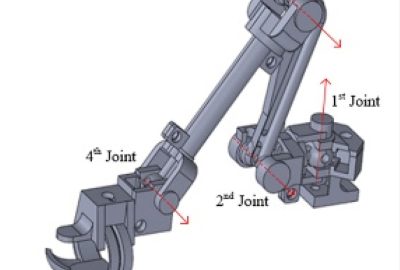
In the research, we propose a cost-effective 3-finger exoskeleton hand motion-capturing device and a physics engine-based hand interaction module for immersive experience in manipulation of virtual objects. The developed device provides 12 DOFs data of finger motion by a unique bevel-gear structure as well as the use of six 3D magnetic sensors. It shows a small error in relative distance between two fingertips less than 2 mm and allows the user to reproduce precise hand motion while processing the complex joint data in real-time. We synchronize hand motion with a physics engine-based interaction framework that includes a grasp interpreter and multi-modal feedback operation in virtual reality to minimize penetration of a hand into an object. The system enables feasibility of object manipulation as far as the needs go in various tasks in virtual environment.
References:
Engelhard, N., Endres, F., Hess, J., Sturm, J., & Burgard, W. 2011. Real-time 3D visual SLAM with a hand-held RGB-D camera. In Proc. of the RGB-D Workshop on 3D Perception in Robotics at the European Robotics Forum, Vasteras, Sweden(Vol. 180, pp. 1-15).
Gu, X., Zhang, Y., Sun, W., Bian, Y., Zhou, D., & Kristensson, P. O. 2016. Dexmo: An inexpensive and lightweight mechanical exoskeleton for motion capture and force feedback in VR. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1991-1995). ACM.
Valtin, M., Salchow, C., Seel, T., Laidig, D., & Schauer, T. 2017. Modular finger and hand motion capturing system based on inertial and magnetic sensors. Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering, 3(1), 19-23.
Kim, J. S., & Park, J. M. 2016. Direct and realistic handover of a virtual object. In Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on (pp. 994-999). IEEE.
Keyword(s):
- Exoskeleton hand MoCap
- Object manipulation
- virtual reality
- 2018 ETech Lee: CHICAP: Low-cost hand motion capture device using 3D magnetic sensors for manipulation of virtual objects
- 2018 ETech Lee: CHICAP: Low-cost hand motion capture device using 3D magnetic sensors for manipulation of virtual objects
- 2018 ETech Lee: CHICAP: Low-cost hand motion capture device using 3D magnetic sensors for manipulation of virtual objects
- 2018 ETech Lee: CHICAP: Low-cost hand motion capture device using 3D magnetic sensors for manipulation of virtual objects
- 2018 ETech Lee: CHICAP: Low-cost hand motion capture device using 3D magnetic sensors for manipulation of virtual objects
Additional Images:
Acknowledgements:
This work was supported by the Global Frontier R&D Program on Human-centered Interaction for Coexistence funded by a National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning in Korean Government (NRF-2010-0029759).