“Rigid core particle: stabilization technique in large time step fluid simulation” by Hamano, Tsumura, Nakaguchi and Miyake
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Rigid core particle: stabilization technique in large time step fluid simulation
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
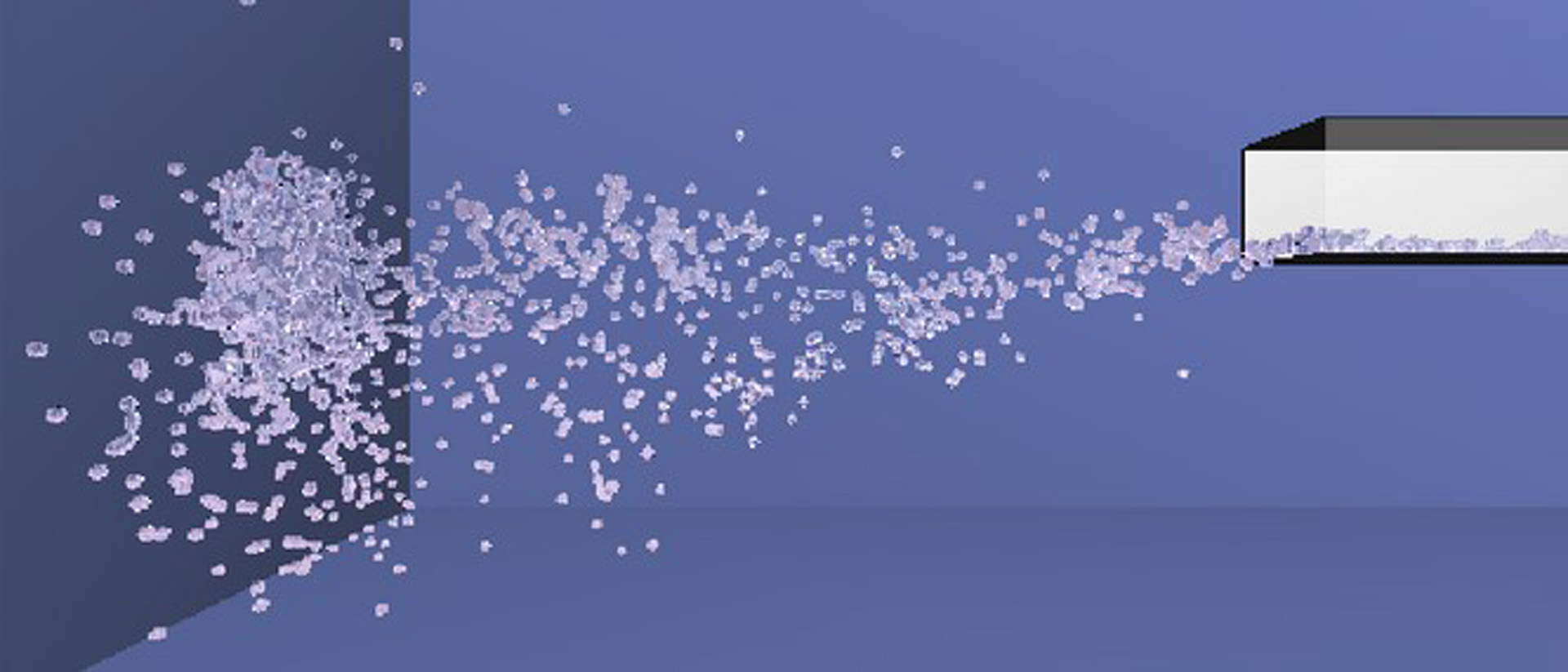
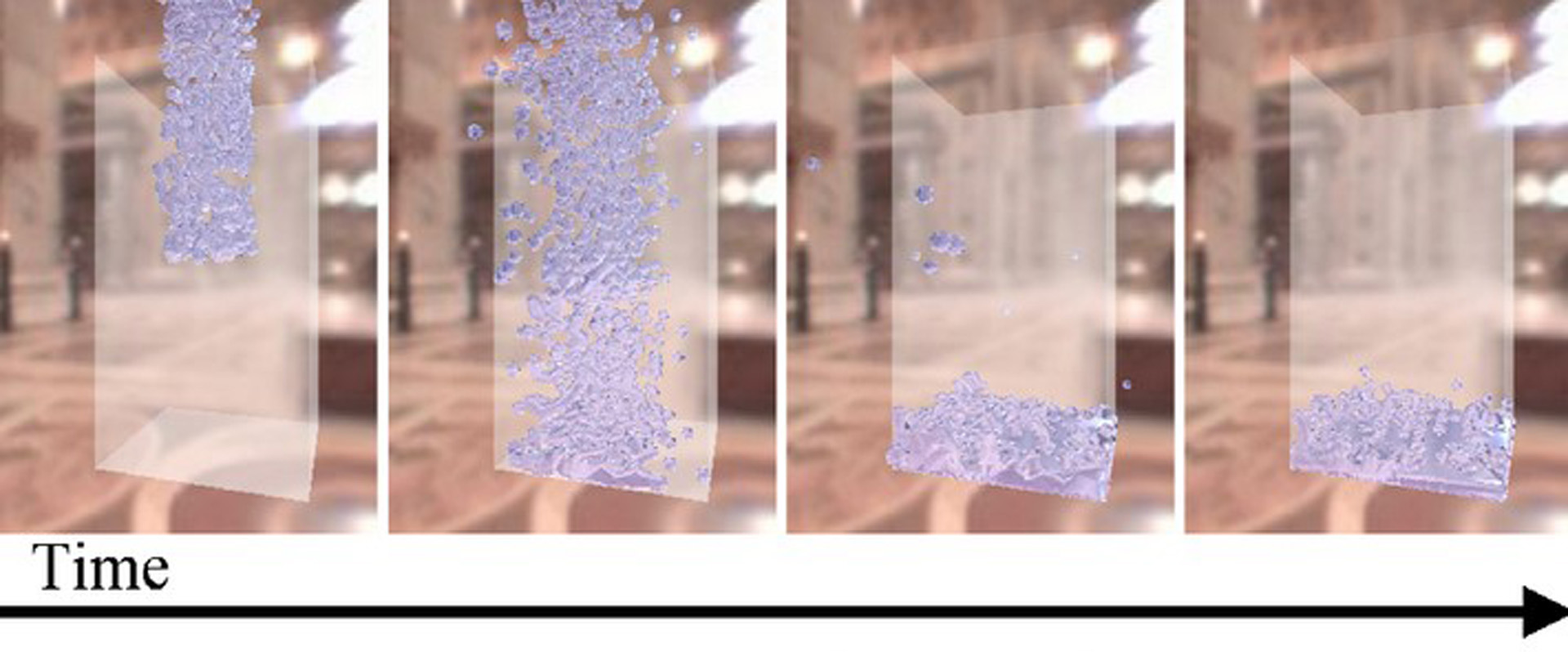
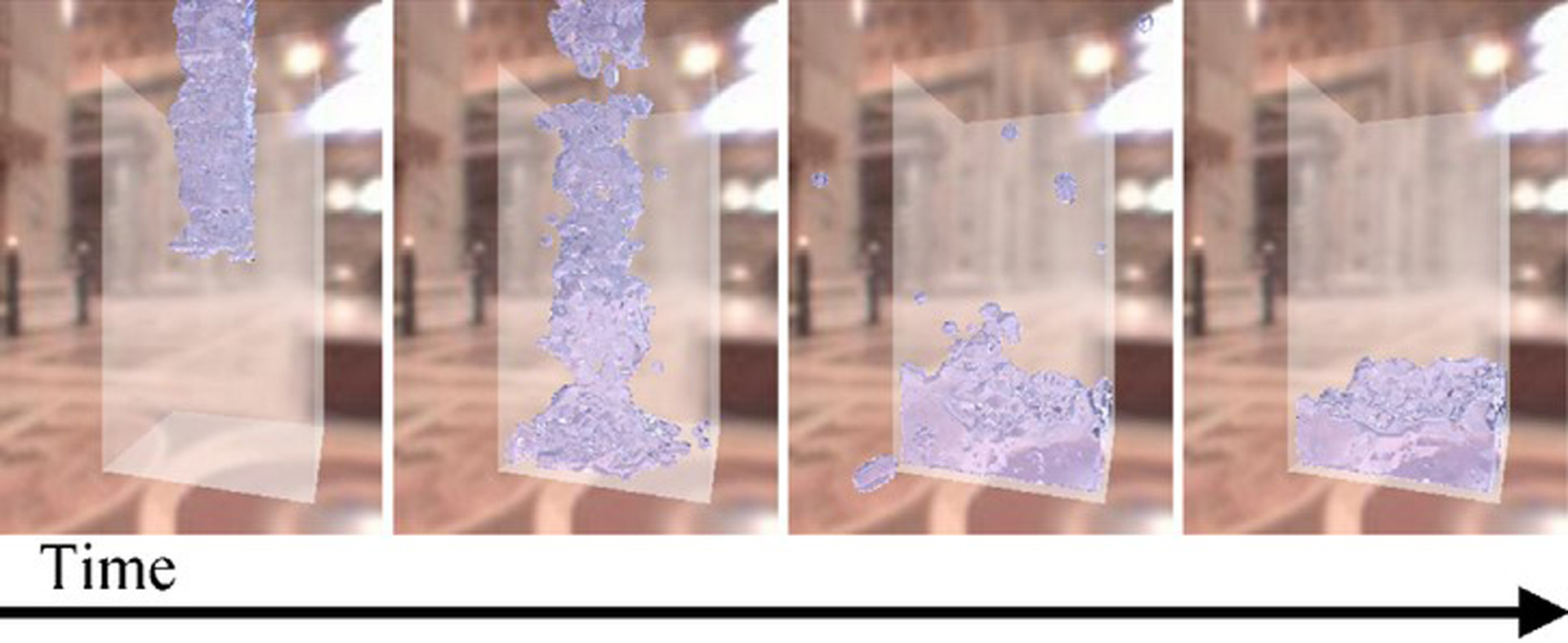
One of the most serious bottle-necks in fluid simulation occurs because the time step must be set to a small value to avoid numerical instability. To overcome this problem, this paper introduces a rigid core for the particles to maintain stability in particle-based fluid simulations. The fluid dynamics is calculated using the particle-based method with smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) [Müller et al. 2003]. By using continuous collision detection (CCD) [Redon et al. 2001] among the rigid cores, unnatural compression and expansion can be prevented in large time step simulations. The calculation cost of CCD is negligible compared to that of small time step simulations, since CCD can be accelerated by a physics processing unit (PPU). Furthermore, this paper proposes a new real-time surface visualization technique that can also be assisted by a PPU. This technique generates large-scale high-resolution meshes compared to those generated by conventional lattice-based methods.
References:
1. Müller, M. et al. “Particle-based fluid simulation for interactive applications”, Proceedings of 2003 ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 154–159, 2003
2. Redon, Stephane et al. “CONTACT: Arbitrary in-between motions for collision detection”, Proceedings of IEEE International Workshop on Robot-Human Communication, pp. 106–111, 2001.
Additional Images: