“Resynthesizing reality: driving vivid virtual environments from sensor networks” by Haddad, Dublon, Mayton, Russell, Xiao, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Entry Number: 51
Title:
- Resynthesizing reality: driving vivid virtual environments from sensor networks
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
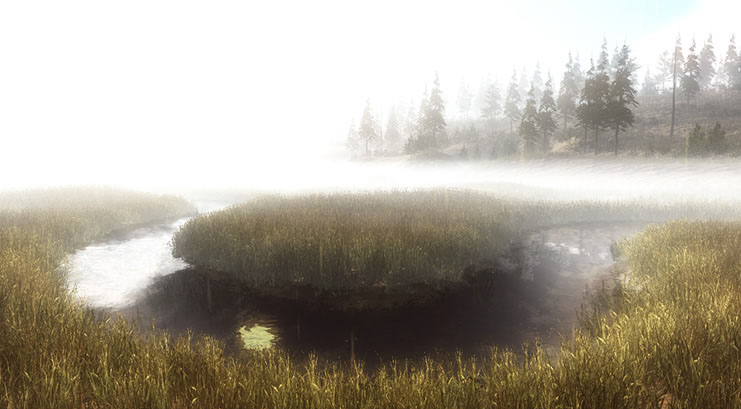
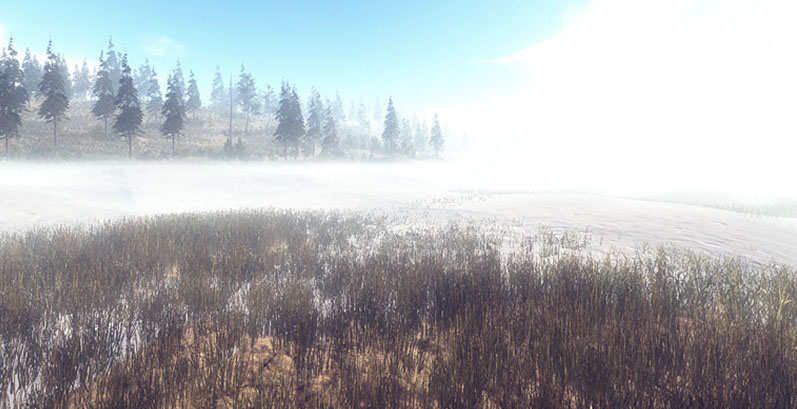
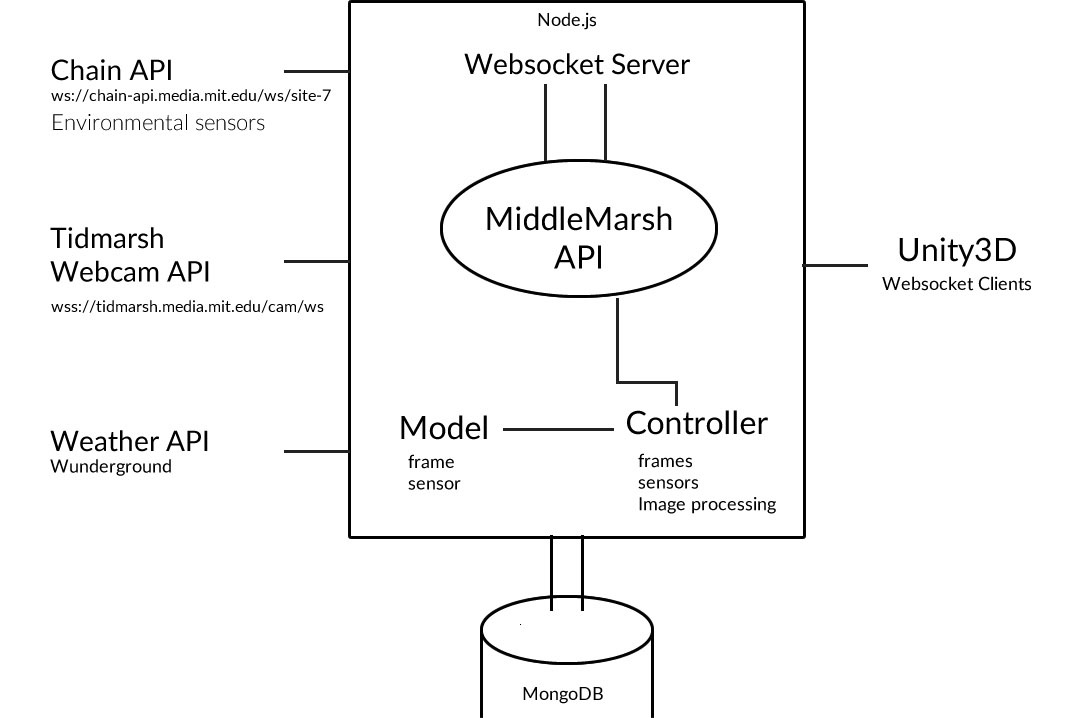
The rise of ubiquitous sensing enables the harvesting of massive amounts of data from the physical world. This data is often used to drive the behavior of devices, and when presented to users, it is most commonly visualized quantitatively, as graphs and charts. Another approach for the representation of sensor network data presents the data within a rich, virtual environment. These scenes can be generated based on the physical environment, and their appearance can change based on the state of sensor nodes. By freely exploring these environments, users gain a vivid, multi-modal, and experiential perspective into large, multi-dimensional datasets. This paper presents the concept of “Resynthesizing Reality” through a case study we have created based on a network of environmental sensors deployed at a large-scale wetland restoration site. We describe the technical implementation of our system, present techniques to visualize sensor data within the virtual environment, and discuss potential applications for such Resynthesized Realities.
References:
Gershon Dublon, Laurel S Pardue, Brian Mayton, Noah Swartz, Nicholas Joliat, Patrick Hurst, and Joseph A Paradiso. 2011. Doppellab: Tools for exploring and harnessing multimodal sensor network data. In Proc. IEEE Sensors 2011. 1612–1615.Google ScholarCross Ref
Joshua Lifton, Mark Feldmeier, Yasuhiro Ono, Cameron Lewis, and Joseph A Paradiso. 2007. A platform for ubiquitous sensor deployment in occupational and domestic environments. In IPSN2007. ACM, 119–127.Google Scholar
Joshua Lifton, Mathew Laibowitz, Drew Harry, Nan-Wei Gong, Manas Mittal, and Joseph A Paradiso. 2009. Metaphor and manifestation cross-reality with ubiquitous sensor/actuator networks. IEEE Pervasive Computing 8, 3 (2009). Google ScholarDigital Library
Evan Lynch and Joseph Paradiso. 2016. Sensorchimes: Musical mapping for sensor networks. In NIME 2016.Google Scholar
Brian Mayton, Gershon Dublon, Spencer Russell, Evan F. Lynch, Don Derek Haddad, Vasant Ramasubramanian, Clement Duhart, Glorianna Davenport, and Joseph A. Paradiso. 2017. The Networked Sensory Landscape: Capturing and Experiencing Ecological Change Across Scales. to appear in Presence (2017).Google Scholar
Spencer Russell and Joseph A Paradiso. 2014. Hypermedia APIs for sensor data: a pragmatic approach to the web of things. In Mobiquitous 2014. 30–39.