“Multiple Scattering using Machine Learning”
Conference:
Type(s):
Entry Number: 70
Title:
- Multiple Scattering using Machine Learning
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
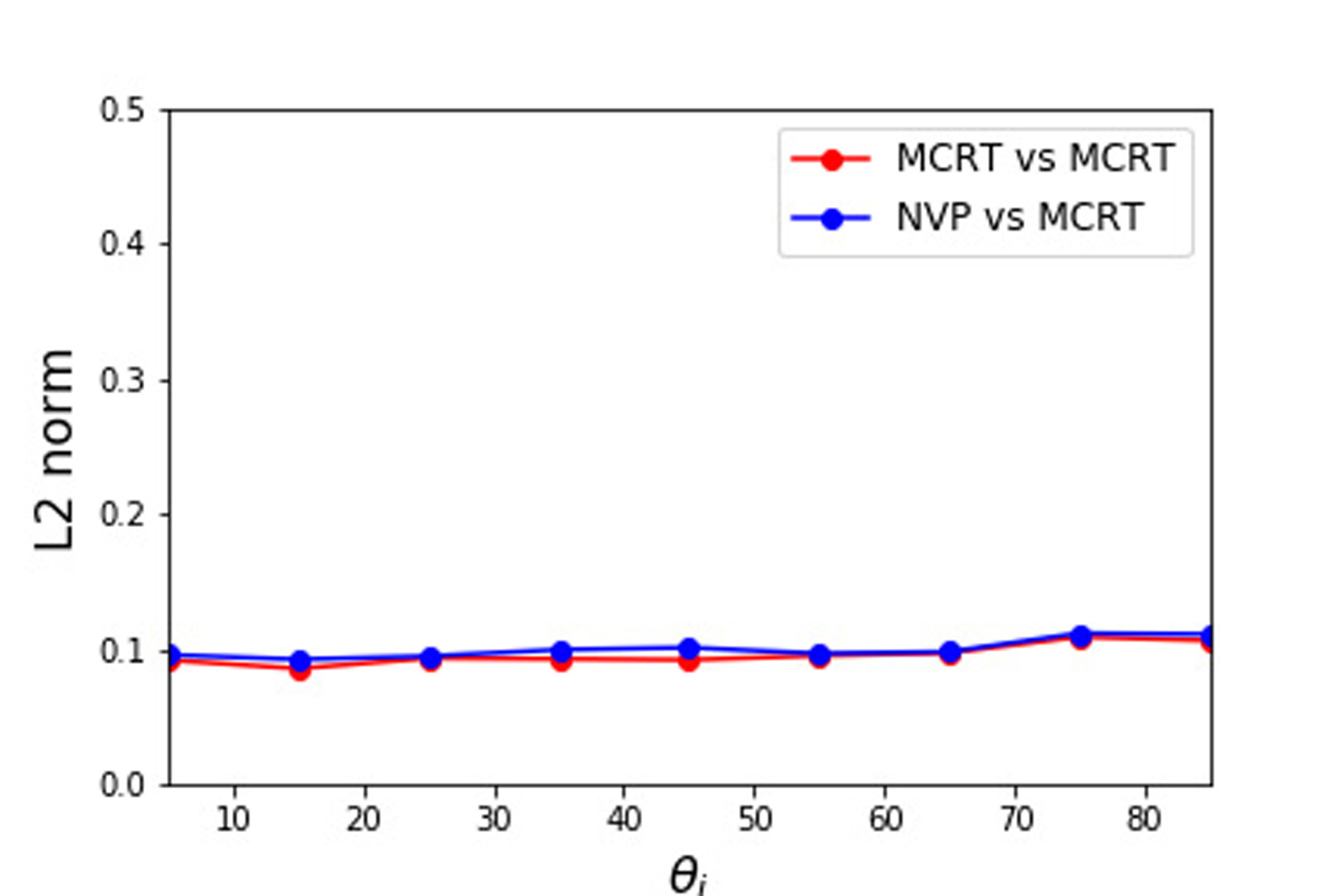
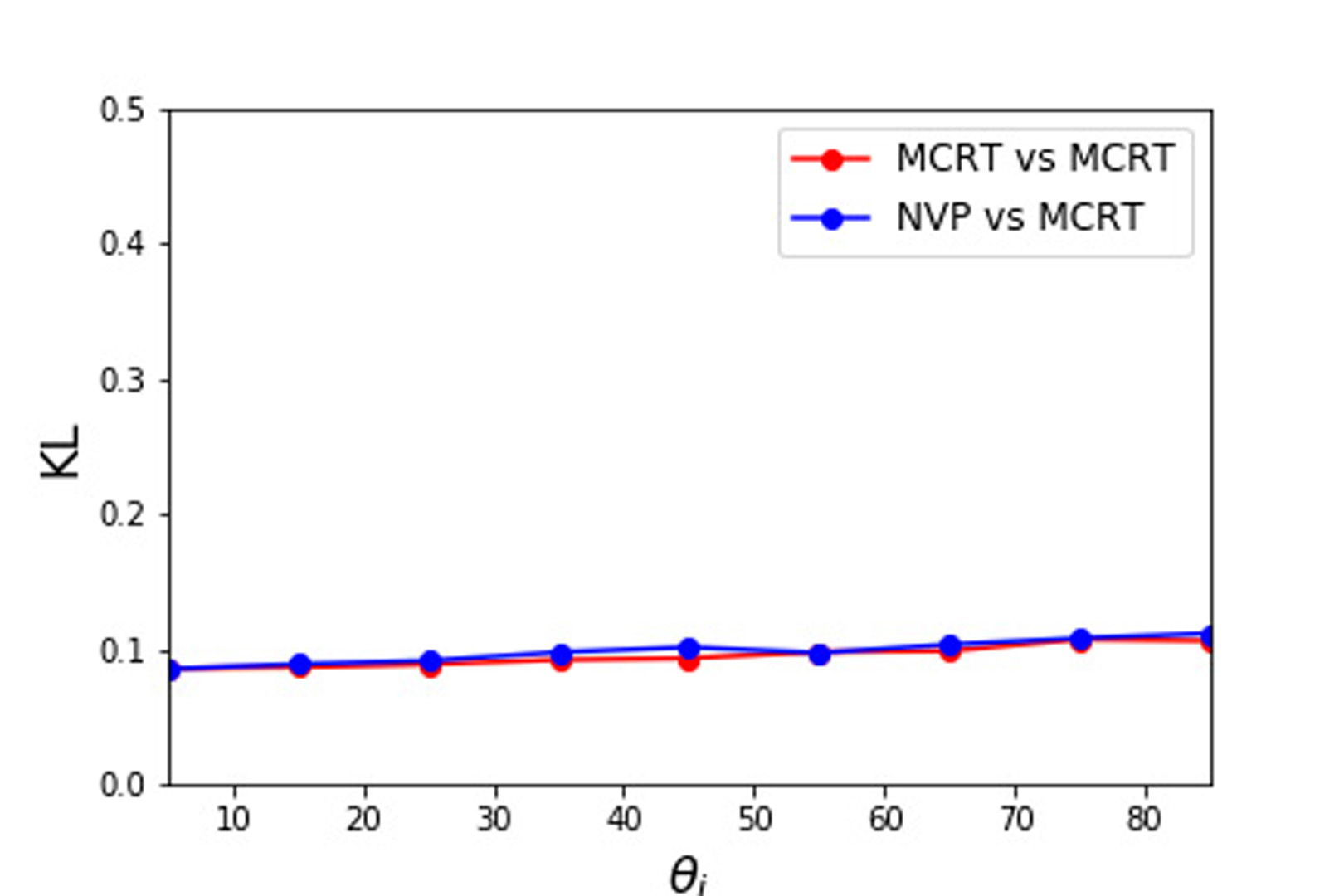
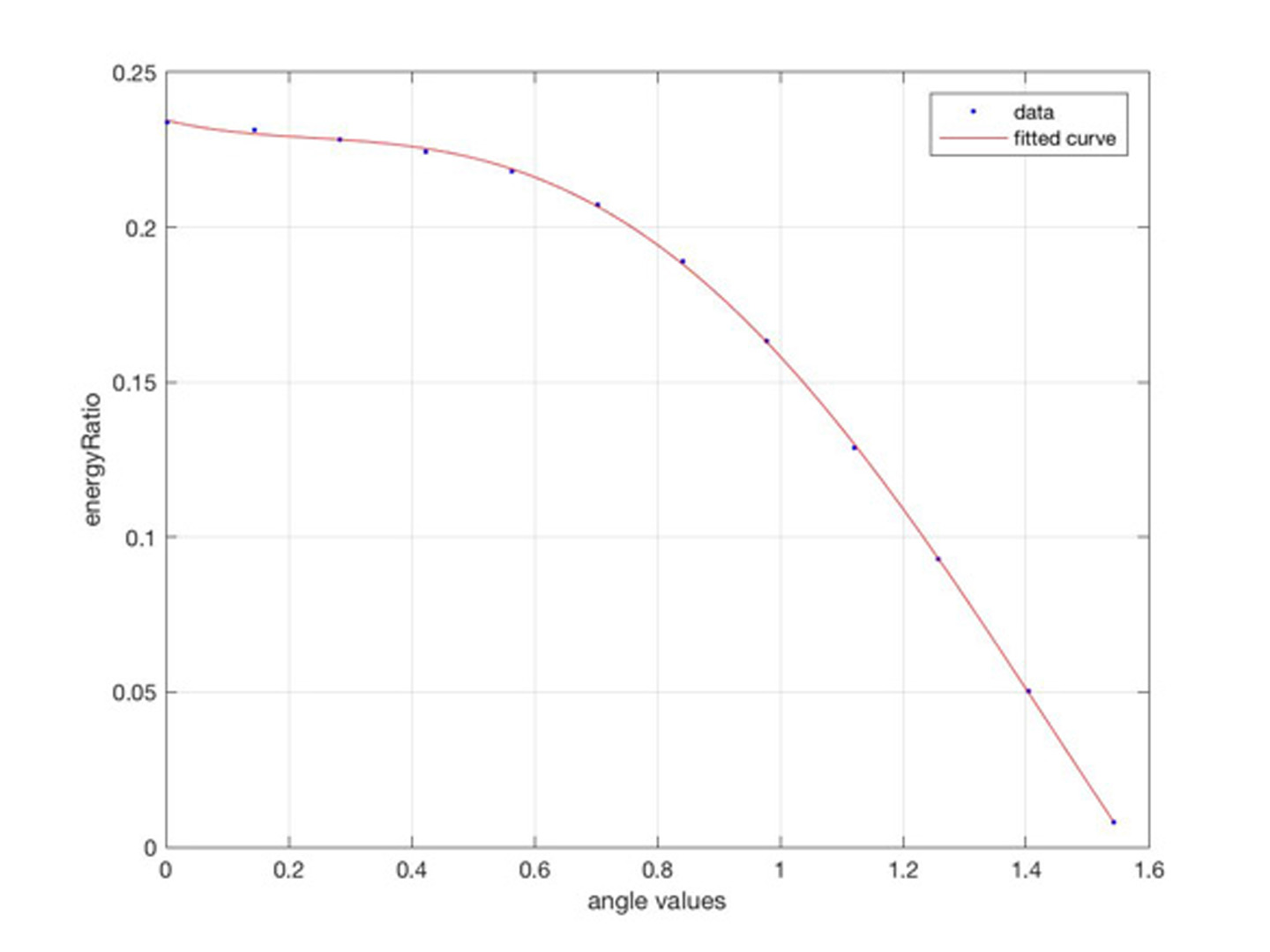
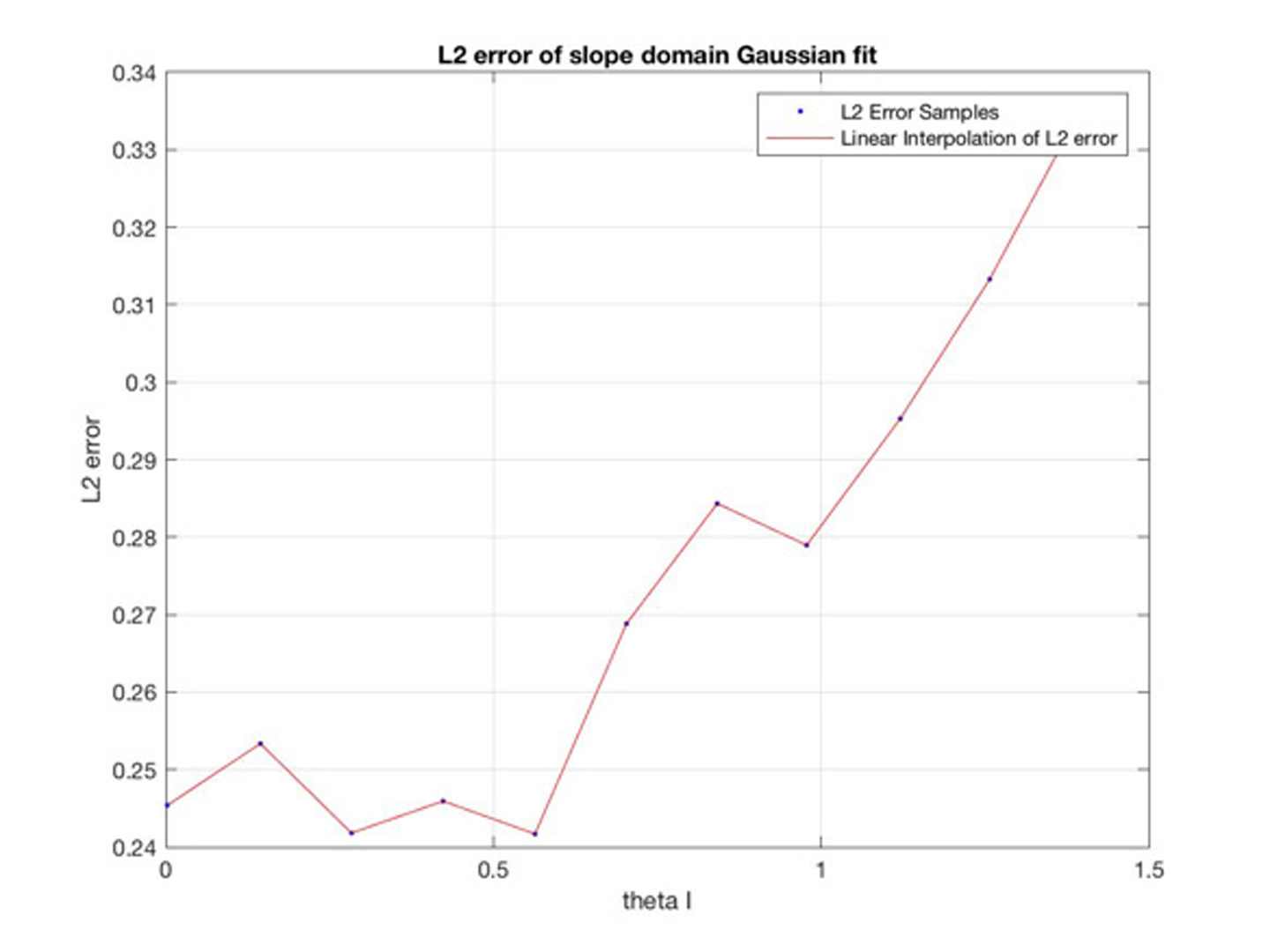
Microfacet-based reflection models are widely used in visual effects applications ranging from computer games to animation and feature film rendering. However, the standard microfacet BRDF supports single scattering only. Light that is scattered more than once is not accounted for, which can lead to significant energy loss. As physically based rendering becoming more prevalent in production, the lack of energy preservation has become problematic. This has lead to several recent works on multiple scattering. Heitz et al. [2016] presented a volumetric approach to model multiple scattering accurately but its stochastic evaluation increases variance. Xie and Hanrahan [2018] presented an analytical multiple scattering model that is efficient but has a singularity in the direction of mirror reflection.
References:
A. P. Dempster, N. M. Laird, and D. B. Rubin. 1977. Maximum Likelihood from Incomplete Data via the EM Algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological) 39, 1 (1977), 1–38. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2984875
Laurent Dinh, Jascha Sohl-Dickstein, and Samy Bengio. 2016. Density estimation using Real NVP. CoRR abs/1605.08803 (2016). arXiv:1605.08803 http://arxiv.org/abs/1605.08803
Eric Heitz, Johannes Hanika, Eugene d’Eon, and Carsten Dachsbacher. 2016. Multiple-scattering Microfacet BSDFs with the Smith Model. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 4, Article 58 (July 2016), 14 pages.