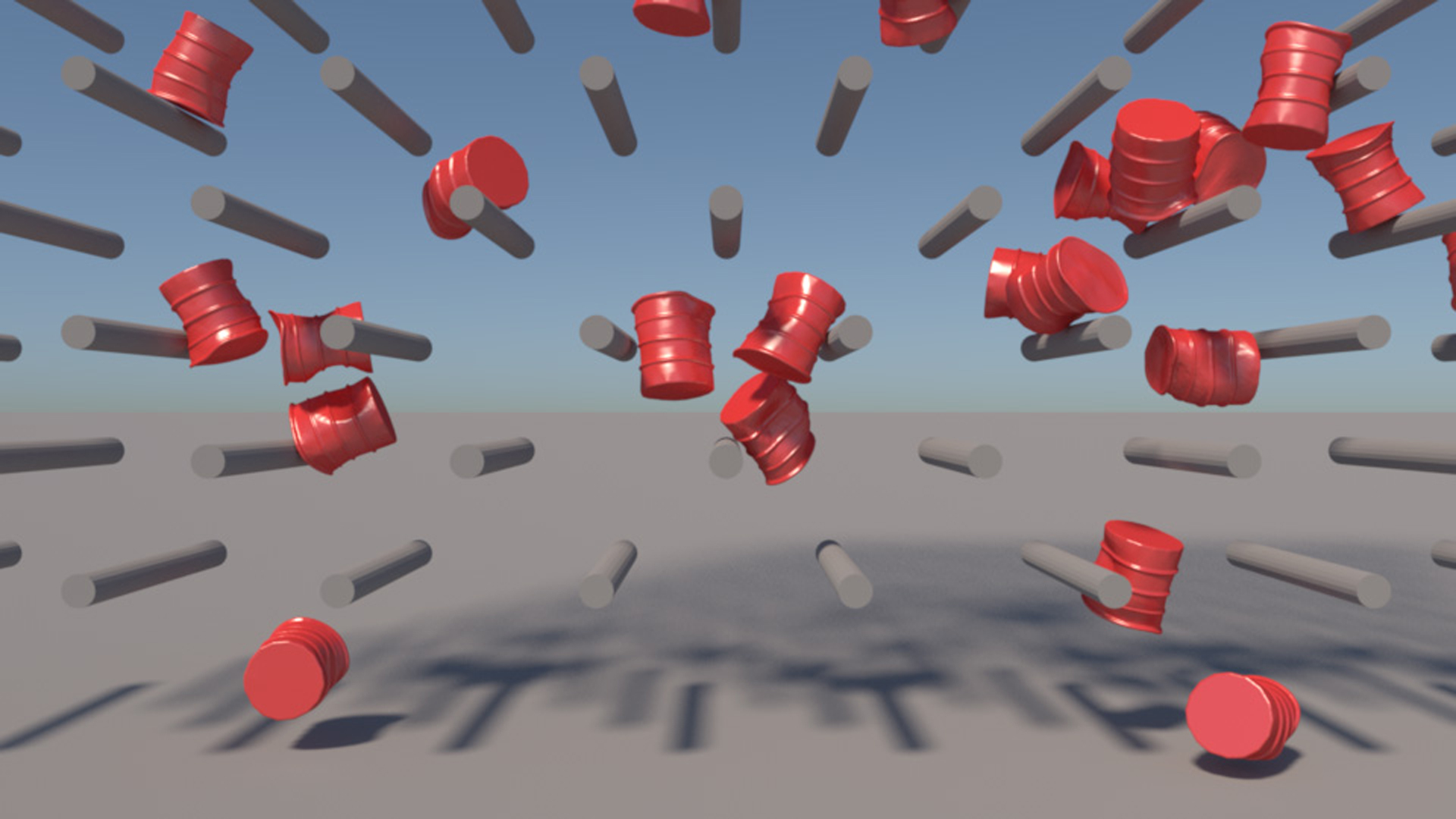
“Example-based plastic deformation of rigid bodies” by Thuerey
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Example-based plastic deformation of rigid bodies
Session/Category Title: RIGGING & SKINNING
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
Physics-based animation is often used to animate scenes containing destruction of near-rigid, man-made materials. For these applications, the most important visual features are plastic deformation and fracture. Methods based on continuum mechanics model these materials as elastoplastic, and must perform expensive elasticity computations even though elastic deformations are imperceptibly small for rigid materials. We introduce an example-based plasticity model based on linear blend skinning that allows artists to author simulation objects using familiar tools. Dynamics are computed using an unmodified rigid body simulator, making our method computationally efficient and easy to integrate into existing pipelines. We introduce a flexible technique for mapping impulses computed by the rigid body solver to local, example-based deformations. For completeness, our method also supports prescoring based fracture. We demonstrate the practicality of our method by animating a variety of destructive scenes.
References:
1. Abe, Y., and Popović, J. 2006. Interactive animation of dynamic manipulation. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, 195–204. Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Bao, Z., Hong, J.-M., Teran, J., and Fedkiw, R. 2007. Fracturing rigid materials. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 13, 2 (Mar.), 370–378. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Barbič, J., and James, D. L. 2005. Real-time subspace integration for St. Venant-Kirchhoff deformable models. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3, 982–990. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Bargteil, A. W., Wojtan, C., Hodgins, J. K., and Turk, G. 2007. A finite element method for animating large viscoplastic flow. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3, 16. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. BeamNG, 2016. http://www.beamng.com. accessed January 19, 2016.Google Scholar
6. Bouaziz, S., Martin, S., Liu, T., Kavan, L., and Pauly, M. 2014. Projective dynamics: Fusing constraint projections for fast simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (July), 154:1–154:11. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Budsberg, J., Zafar, N. B., and Aldén, M. 2014. Elastic and plastic deformations with rigid body dynamics. In ACM SIGGRAPH Talks, 52:1–52:1. Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Clausen, P., Wicke, M., Shewchuk, J. R., and O’Brien, J. F. 2013. Simulating liquids and solid-liquid interactions with lagrangian meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 2 (Apr.), 17:1–15. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Clavet, S., Beaudoin, P., and Poulin, P. 2005. Particle-based viscoelastic fluid simulation. In Proccedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, 219–228. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Coumans, E., 2014. Bullet physics library. http://bulletphysics.org/.Google Scholar
11. Criswell, B., Lentine, M., and Sauers, S. 2010. Avatar: Bending rigid bodies. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2010 Talks.Google Scholar
12. Criswell, B., Smith, J., and Deuber, D. 2010. Transformers 2: Breaking buildings. In ACM SIGGRAPH Talks.Google Scholar
13. de Aguiar, E., Sigal, L., Treuille, A., and Hodgins, J. K. 2010. Stable spaces for real-time clothing. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 4, 106:1–106:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Fan, Y., Litven, J., Levin, D. I. W., and Pai, D. K. 2013. Eulerian-on-lagrangian simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 3, 22:1–22:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Faure, F., Gilles, B., Bousquet, G., and Pai, D. K. 2011. Sparse meshless models of complex deformable solids. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4, 73:1–73:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Feng, W.-W., Yu, Y., and Kim, B.-U. 2010. A deformation transformer for real-time cloth animation. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 4, 108:1–108:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Gilles, B., Bousquet, G., Faure, F., and Pai, D. K. 2011. Frame-based elastic models. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 2, 15:1–15:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Hahn, F., Thomaszewski, B., Coros, S., Sumner, R. W., Cole, F., Meyer, M., DeRose, T., and Gross, M. 2014. Subspace clothing simulation using adaptive bases. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4, 105:1–105:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Harmon, D., and Zorin, D. 2013. Subspace integration with local deformations. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4 (July), 107:1–107:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Hirota, K., Tanoue, Y., and Kaneko, T. 1998. Generation of crack patterns with a physical model. The Visual Computer 14, 3, 126–137.Google ScholarCross Ref
21. Hirota, K., Tanoue, Y., and Kaneko, T. 2000. Simulation of three-dimensional cracks. The Visual Computer 16, 7, 371–378.Google ScholarCross Ref
22. Irving, G., Teran, J., and Fedkiw, R. 2004. Invertible finite elements for robust simulation of large deformation. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, 131–140. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Jacobson, A., Baran, I., Popović, J., and Sorkine, O. 2011. Bounded biharmonic weights for real-time deformation. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4, 78:1–78:8. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Jacobson, A., Baran, I., Kavan, L., Popović, J., and Sorkine, O. 2012. Fast automatic skinning transformations. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4, 77:1–77:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Jones, B., Popović, J., McCann, J., Li, W., and Bargteil, A. 2013. Dynamic sprites. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH Conference on Motion in Games. Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Jones, B., Ward, S., Jallepalli, A., Perenia, J., and Bargteil, A. W. 2014. Deformation embedding for point-based elastoplastic simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 2, 21:1–21:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Kavan, L., and Zara, J. 2005. Spherical blend skinning: A real-time deformation of articulated models. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games, ACM Press, 9–16. Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Kavan, L., Sloan, P.-P., and O’Sullivan, C. 2010. Fast and efficient skinning of animated meshes. Comput. Graph. Forum 29, 2, 327–336.Google ScholarCross Ref
29. Kavan, L., Gerszewski, D., Bargteil, A., and Sloan, P. P. 2011. Physics-inspired upsampling for cloth simulation in games. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4, 93:1–93:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Kim, T.-Y., and Vendrovsky, E. 2008. Drivenshape: a data-driven approach for shape deformation. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, Eurographics Association, 49–55. Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Koyama, Y., Takayama, K., Umetani, N., and Igarashi, T. 2012. Real-time example-based elastic deformation. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, 19–24. Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Levine, J. A., Bargteil, A. W., Corsi, C., Tessendorf, J., and Geist, R. 2014. A peridynamic perspective on spring-mass fracture. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. Google ScholarDigital Library
33. Liu, T., Bargteil, A. W., O’Brien, J. F., and Kavan, L. 2013. Fast simulation of mass-spring systems. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 6, 214:1–214:7. Google ScholarDigital Library
34. Martin, S., Kaufmann, P., Botsch, M., Grinspun, E., and Gross, M. 2010. Unified simulation of elastic rods, shells, and solids. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 39:1–39:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Martin, S., Thomaszewski, B., Grinspun, E., and Gross, M. 2011. Example-based elastic materials. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4, 72:1–72:8. Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Molino, N., Bao, Z., and Fedkiw, R. 2004. A virtual node algorithm for changing mesh topology during simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3, 385–392. Google ScholarDigital Library
37. Müller, M., and Chentanez, N. 2010. Wrinkle meshes. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, 85–92. Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Müller, M., and Chentanez, N. 2011. Solid simulation with oriented particles. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4 (July), 92:1–92:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
39. Müller, M., McMillan, L., Dorsey, J., and Jagnow, R. 2001. Real-time simulation of deformation and fracture of stiff materials. In Proceedings of the Eurographics Workshop on Computer Animation and Simulation, 113–124. Google ScholarDigital Library
40. Müller, M., Keiser, R., Nealen, A., Pauly, M., Gross, M., and Alexa, M. 2004. Point based animation of elastic, plastic and melting objects. In The Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, 141–151. Google ScholarDigital Library
41. Müller, M., Heidelberger, B., Teschner, M., and Gross, M. 2005. Meshless deformations based on shape matching. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3, 471–478. Google ScholarDigital Library
42. Müller, M., Heidelberger, B., Hennix, M., and Ratcliff, J. 2007. Position based dynamics. J. Vis. Comun. Image Represent. 18, 2, 109–118. Google ScholarDigital Library
43. Norton, A., Turk, G., Bacon, R., Gerth, J., and Sweeney, P. 1991. Animation of fracture by physical modeling. The Visual Computer 7, 4, 210–219. Google ScholarDigital Library
44. O’Brien, J. F., and Hodgins, J. K. 1999. Graphical modeling and animation of brittle fracture. In The Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH, 137–146. Google ScholarDigital Library
45. O’Brien, J. F., Bargteil, A. W., and Hodgins, J. K. 2002. Graphical modeling and animation of ductile fracture. ACM Trans. Graph. 21, 3, 291–294. Google ScholarDigital Library
46. Parker, E. G., and O’Brien, J. F. 2009. Real-time deformation and fracture in a game environment. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, 156–166. Google ScholarDigital Library
47. Patkar, S., Aanjaneya, M., Bartle, A., Lee, M., and Fedkiw, R. 2014. Efficient Denting and Bending of Rigid Bodies. In Eurographics/ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Computer Animation. Google ScholarDigital Library
48. Pauly, M., Keiser, R., Adams, B., Dutré, P., Gross, M., and Guibas, L. J. 2005. Meshless animation of fracturing solids. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3, 957–964. Google ScholarDigital Library
49. Pratt, J., Chew, C.-M., Torres, A., Dilworth, P., and Pratt, G. 2001. Virtual model control: An intuitive approach for bipedal locomotion. The International Journal of Robotics Research 20, 2, 129–143.Google ScholarCross Ref
50. Schumacher, C., Thomaszewski, B., Coros, S., Martin, S., Sumner, R., and Gross, M. 2012. Efficient simulation of example-based materials. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, 1–8. Google ScholarDigital Library
51. Stauning, O., and Bendtsen, C., 2007. Fadbad++, flexible automatic differentiation using templates and operator overloading in c++. http://www.fadbad.com.Google Scholar
52. Stuart, A., Levine, J., Jones, B., and Bargteil, A. 2013. Automatic construction of coarse, high-quality tetrahedralizations that enclose and approximate surfaces for animation. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH Conference on Motion in Games. Google ScholarDigital Library
53. Su, J., Schroeder, C., and Fedkiw, R. 2009. Energy stability and fracture for frame rate rigid body simulations. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, 155–164. Google ScholarDigital Library
54. Terzopoulos, D., and Fleischer, K. 1988. Modeling inelastic deformation: Viscoelasticity, plasticity, fracture. In The Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH, 269–278. Google ScholarDigital Library
55. Terzopoulos, D., Platt, J., Barr, A., and Fleischer, K. 1987. Elastically deformable models. SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 21, 4, 205–214. Google ScholarDigital Library
56. Wang, H., Hecht, F., Ramamoorthi, R., and O’Brien, J. 2010. Example-based wrinkle synthesis for clothing animation. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 4, 107:1–107:8. Google ScholarDigital Library
57. Weinstein, R., Petterson, F., and Criswell, B. 2008. Destruction system. In ACM SIGGRAPH Talks, 71:1–71:1. Google ScholarDigital Library
58. Wicke, M., Ritchie, D., Klingner, B. M., Burke, S., Shewchuk, J. R., and O’Brien, J. F. 2010. Dynamic local remeshing for elastoplastic simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 49:1–49:11. Google ScholarDigital Library
59. Wojtan, C., and Turk, G. 2008. Fast viscoelastic behavior with thin features. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3, 1–8. Google ScholarDigital Library
60. Wojtan, C., Thürey, N., Gross, M., and Turk, G. 2009. Deforming meshes that split and merge. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3, 76:1–76:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
61. Xu, W., Umentani, N., Chao, Q., Mao, J., Jin, X., and Tong, X. 2014. Sensitivity-optimized rigging for example-based real-time clothing synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4, 107:1–107:11. Google ScholarDigital Library
62. Yang, Y., Li, D., Xu, W., Tian, Y., and Zheng, C. 2015. Expediting precomputation for reduced deformable simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6, 243:1–243:13. Google ScholarDigital Library
63. Zafar, N. B., Stephens, D., Larsson, M., Sakaguchi, R., Clive, M., Sampath, R., Museth, K., Blakey, D., Gazdik, B., and Thomas, R. 2010. Destroying LA for “2012”. In ACM SIGGRAPH Talks, 25:1–25:1. Google ScholarDigital Library