“Construction and optimal search of interpolated motion graphs” by Safonova and Hodgins
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Construction and optimal search of interpolated motion graphs
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
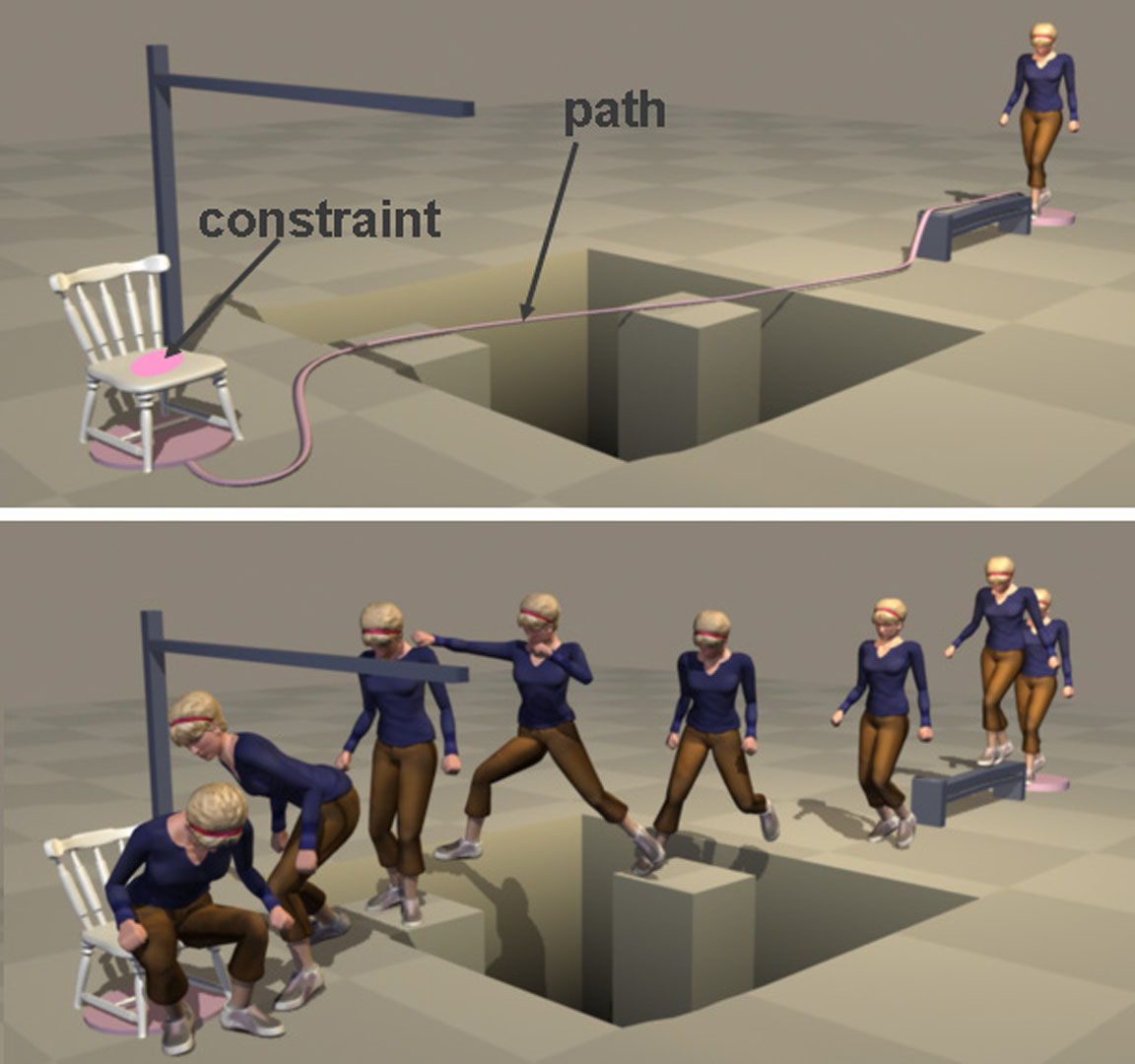
Many compelling applications would become feasible if novice users had the ability to synthesize high quality human motion based only on a simple sketch and a few easily specified constraints. We approach this problem by representing the desired motion as an interpolation of two time-scaled paths through a motion graph. The graph is constructed to support interpolation and pruned for efficient search. We use an anytime version of A* search to find a globally optimal solution in this graph that satisfies the user’s specification. Our approach retains the natural transitions of motion graphs and the ability to synthesize physically realistic variations provided by interpolation. We demonstrate the power of this approach by synthesizing optimal or near optimal motions that include a variety of behaviors in a single motion.
References:
1. Abe, Y., Liu, C. K., and Popović, Z. 2004. Momentum-based parameterization of dynamic character motion. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Animation, 173–182. Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Arikan, O., and Forsyth, D. A. 2002. Interactive motion generation from examples. ACM Trans. on Graphics 21, 3, 483–490. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Arikan, O., Forsyth, D. A., and O’Brien, J. F. 2003. Motion synthesis from annotations. ACM Trans. on Graphics 22, 3. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Callennec, B. L., and Boulic, R. 2006. Robust kinematic constraint detection for motion data. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Animation, 281–290. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Choi, M. G., Lee, J., and Shin, S. Y. 2003. Planning biped locomotion using motion capture data and probabilistic roadmaps. ACM Trans. on Graphics 22, 2, 182–203. Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Fang, A. C., and Pollard, N. S. 2003. Efficient synthesis of physically valid human motion. ACM Trans. on Graphics 22, 3, 417–426. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Gleicher, M., Shin, H., Kovar, L., and Jepsen, A. 2003. Snap-together motion: Assembling run-time animation. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Animation, 181–188. Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Guo, S., and Roberge, J. 1996. A high-level control mechanism for human locomotion based on parametric frame space interpolation. In EGCAS ’96: Seventh International Workshop on Computer Animation and Simulation, 95–107. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Heck, R., and Gleicher, M. 2007. Parametric motion graphs. In ACM Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics, 129–136. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Ikemoto, L., Arikan, O., and Forsyth, D. 2006. Knowing when to put your foot down. In ACM Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics, 49–53. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Ikemoto, L., Arikan, O., and Forsyth, D. 2007. Quick transitions with cached multi-way blends. In ACM Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics, 145–151. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Kovar, L., and Gleicher, M. 2003. Flexible automatic motion blending with registration curves. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Animation, 214–224. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Kovar, L., and Gleicher, M. 2004. Automated extraction and parameterization of motions in large data sets. ACM Trans. on Graphics 23, 3, 559–568. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Kovar, L., Gleicher, M., and Pighin, F. 2002. Motion graphs. ACM Trans. on Graphics 21, 3, 473–482. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Kwon, T., and Shin, S. Y. 2005. Motion modeling for on-line locomotion synthesis. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Animation, 29–38. Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Lau, M., and Kuffner, J. J. 2005. Behavior planning for character animation. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Animation, 271–280. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Lau, M., and Kuffner, J. 2006. Precomputed search trees: Planning for interactive goal-driven animation. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Animation, 299–308. Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Lee, J., and Lee, K. H. 2004. Precomputing avatar behavior from human motion data. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Animation, 79–87. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Lee, J., Chai, J., Reitsma, P. S. A., Hodgins, J. K., and Pollard, N. S. 2002. Interactive control of avatars animated with human motion data. ACM Trans. on Graphics 21, 3, 491–500. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Li, Y., Wang, T., and Shum, H.-Y. 2002. Motion texture: a two-level statistical model for character motion synthesis. ACM Trans. on Graphics 21, 3, 465–472. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Likhachev, M., Gordon, G., and Thrun, S. 2003. ARA*: Anytime A* with provable bounds on sub-optimality. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS) 16, Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Park, S. I., Shin, H. J., and Shin, S. Y. 2002. On-line locomotion generation based on motion blending. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Animation, 105–112. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Park, S. I., Shin, H. J., Kim, T. H., and Shin, S. Y. 2004. On-line motion blending for real-time locomotion generation. Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds 15, 3–4, 125–138. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Pearl, J. 1984. Heuristics: Intelligent Search Strategies for Computer Problem Solving. Addison-Wesley. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Perlin, K. 1995. Real time responsive animation with personality. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 1, 1, 5–15. Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Pullen, K., and Bregler, C. 2002. Motion capture assisted animation: texturing and synthesis. ACM Trans. on Graphics 22, 2, 501–508. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Reitsma, P. S. A., and Pollard, N. S. 2004. Evaluating motion graphs for character navigation. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Animation, 89–98. Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Rose, C., Cohen, M. F., and Bodenheimer, B. 1998. Verbs and adverbs: Multidimensional motion interpolation. IEEE Computer Graphics & Applications 18, 5, 32–40. Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Russell, S., and Norvig, P. 2003. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Safonova, A., and Hodgins, J. K. 2005. Analyzing the physical correctness of interpolated human motion. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Animation, 171–180. Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Safonova, A., Hodgins, J. K., and Pollard, N. S. 2004. Synthesizing physically realistic human motion in low-dimensional, behavior-specific spaces. ACM Trans. on Graphics 23, 3, 514–521. Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Shin, H. J., and Oh, H. S. 2006. Fat graphs: Constructing an interactive character with continuous controls. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Animation, 291–298. Google ScholarDigital Library
33. Srinivasan, M., Metoyer, R. A., and Mortensen, E. N. 2005. Controllable real-time locomotion using mobility maps. In Proc. of Graphics Interface, 51–59. Google ScholarDigital Library
34. Sulejmanpašić, A., and Popović, J. 2005. Adaptation of performed ballistic motion. ACM Trans. on Graphics 24, 1, 165–179. Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Sung, M., Kovar, L., and Gleicher, M. 2005. Fast and accurate goal-directed motion synthesis for crowds. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Animation, 291–300. Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Wiley, D. J., and Hahn, J. K. 1997. Interpolation synthesis of articulated figure motion. IEEE Computer Graphics Applications 17, 6, 39–45. Google ScholarDigital Library
37. Witkin, A., and Kass, M. 1988. Spacetime constraints. Computer Graphics (Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 88) 22, 4, 159–168. Google ScholarDigital Library