“Circle Tracing for Subsurface Scattering”
Conference:
Type(s):
Entry Number: 50
Title:
- Circle Tracing for Subsurface Scattering
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
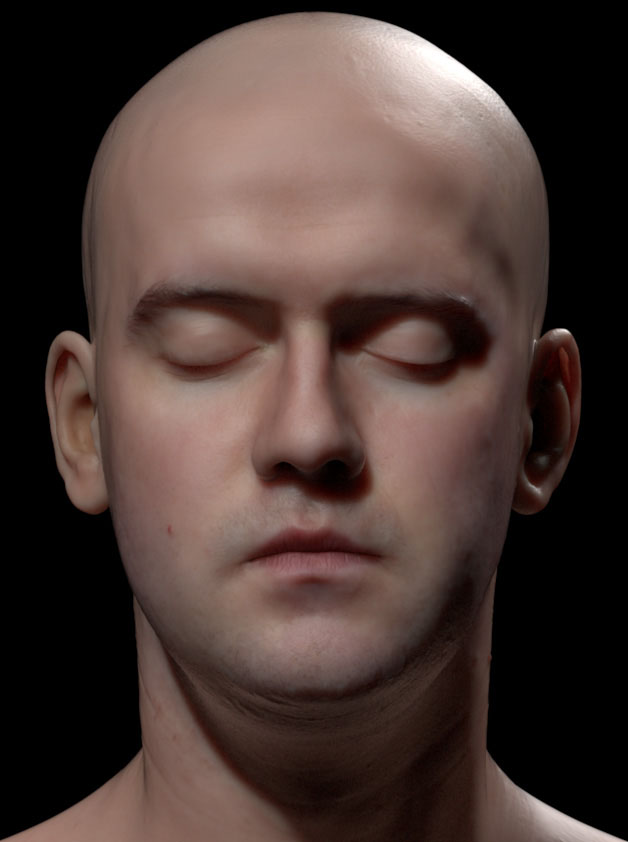
Rendering of translucent materials such as skin, marble or wax is a requirement for animation and visual effects production, either photo realistic or non photo realistic styles. Monte-Carlo integration of light transport by simulating scattering events of light within the translucent medium is prohibitive and difficult to parametrize for artistically driven applications.
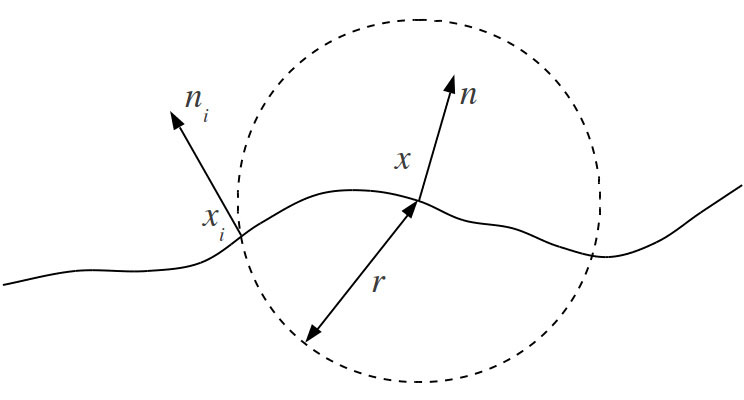
Light transport in a medium is modeled as a BSSRDF that characterizes the propagation of light from an entry point xi to an exit point x.
[EQUATION]
We assume f = fs(||x – xi||) * ft(n, ωo, ni, ωi) as the product of a scattering profile function and a transmission function.
[King et al. 2013] proposed a disk based sampling technique to importance sample the fs term. We propose in this presentation a different strategy that samples points on the surface at an exact distance, even on non flat surfaces, and doesn’t require additional strategies that would potentially result in no sample at all.
References:
d’Eon, E., and Luebke, D., 2007. Advanced techniques for realistic real-time skin rendering. GPU Gems 3 Addison Wesley.Google Scholar
Jensen, H. W., Marschner, S. R., Levoy, M., and Hanrahan, P., 2001. A practical model for subsurface light transport. ACM SIGGRAPH 2001. Google ScholarDigital Library
King, A., Kulla, C., Conty, A., and Fajardo, M., 2013. Bssrdf importance sampling. ACM SIGGRAPH 2013 Talk, July. Google ScholarDigital Library