“Blue-noise Dithered Sampling” by Georgiev and Fajardo
Conference:
Type(s):
Entry Number: 35
Title:
- Blue-noise Dithered Sampling
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
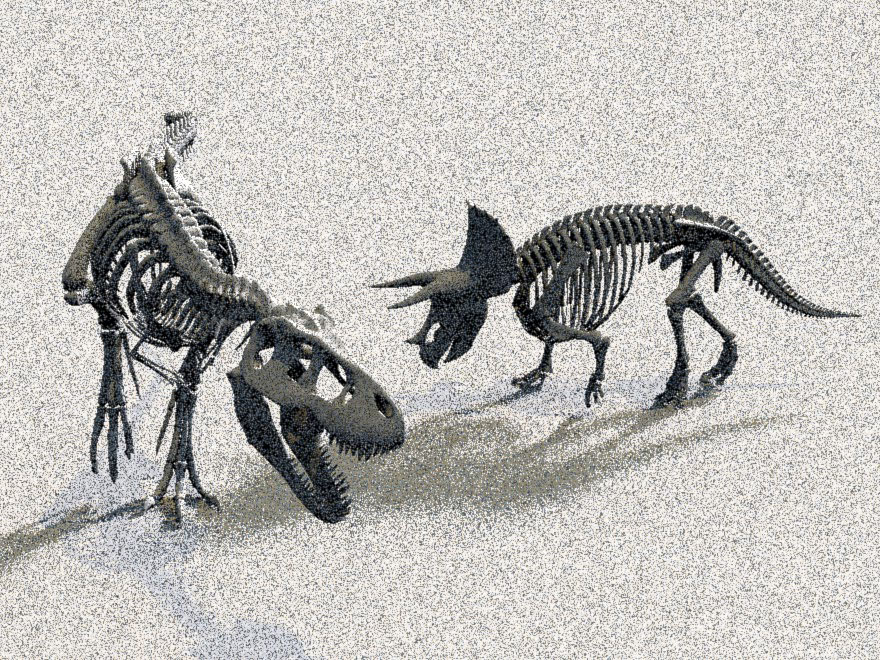
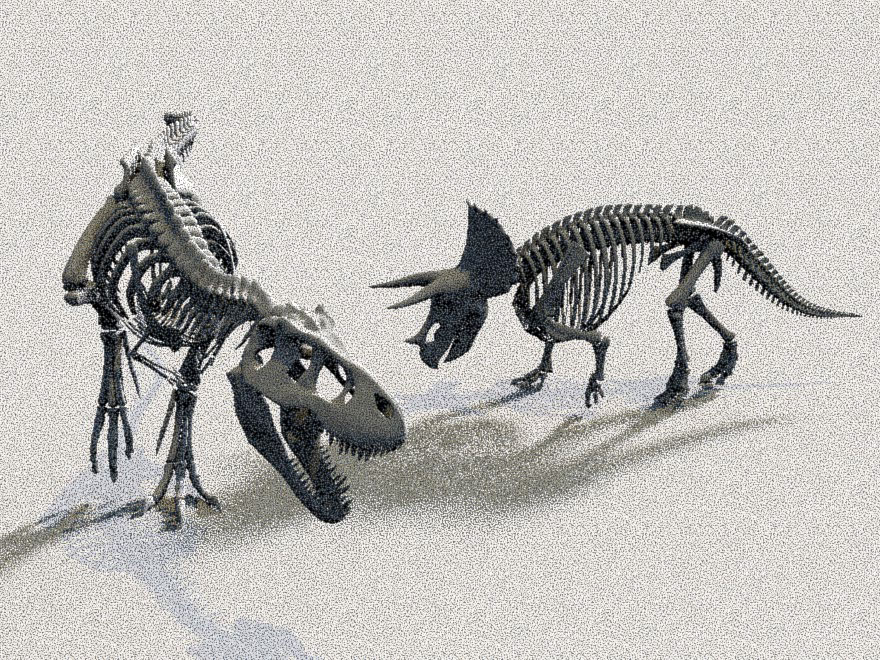
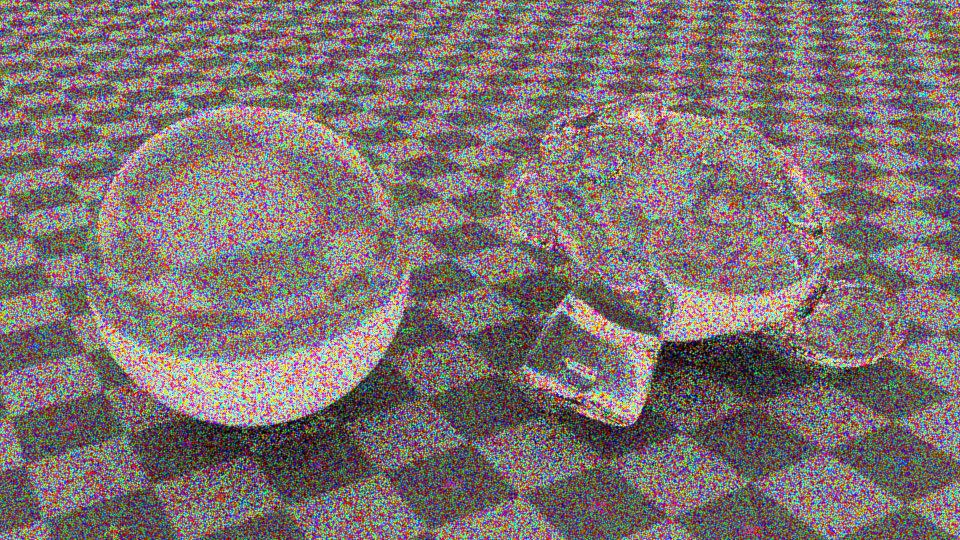
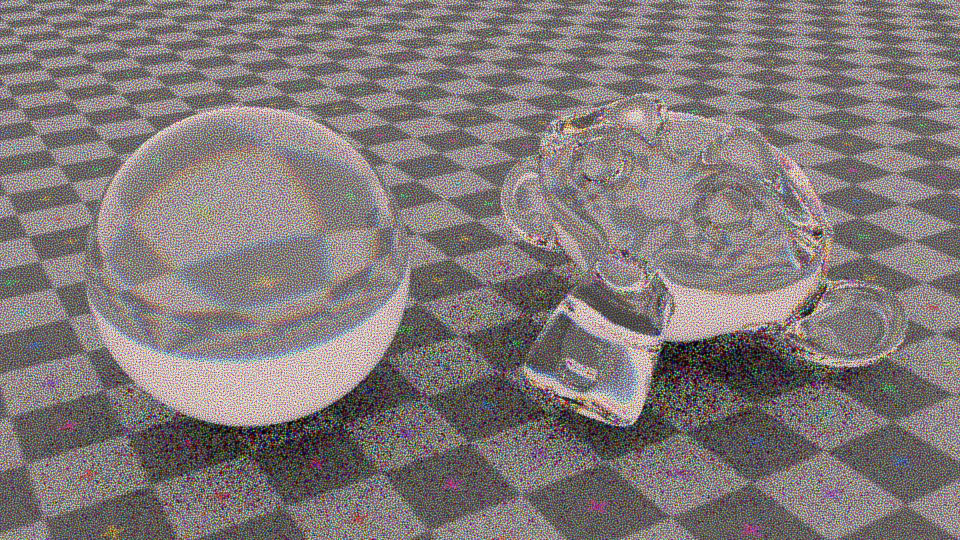
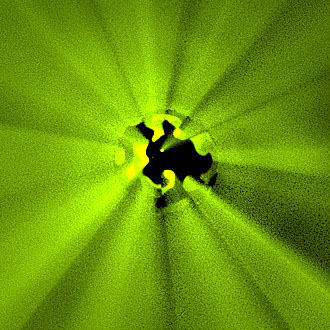
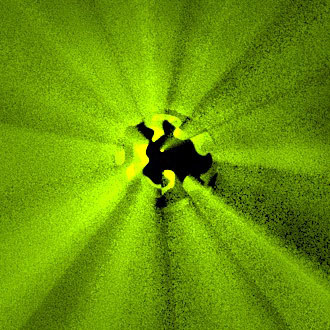
The visual fidelity of a Monte Carlo rendered image depends not only on the magnitude of the pixel estimation error but also on its distribution over the image. To this end, state-of-the-art methods use high-quality stratified sampling patterns, which are randomly scrambled or shifted to decorrelate the individual pixel estimates. While random pixel decorrelation yields an eye-pleasing whitenoise image error distribution, it is far from perceptually optimal. We show that visual fidelity can be substantially improved by instead correlating the samples among pixels in a way that minimizes the low-frequency content in the output noise. Inspired by digital halftoning, our blue-noise dithered sampling method can produce significantly more faithful images, especially at low sampling rates.
References:
Lau, D., and Arce, G. 2008. Modern Digital Halftoning, Second Edition. CRC Press. Google ScholarDigital Library
Mitchell, D. P. 1991. Spectrally optimal sampling for distribution ray tracing. ACM SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 25, 4. Google ScholarDigital Library
Ulichney, R. A. 1993. The void-and-cluster method for dither array generation. Proc. SPIE 1913, 332–343.