“MeisterGRIP: Cylindrical Interface for Intuitional Robot Manipulation” by Komeiji, Sato, Minamizawa, Nii, Kawakami, et al. …
Notice: Pod Template PHP code has been deprecated, please use WP Templates instead of embedding PHP. has been deprecated since Pods version 2.3 with no alternative available. in /data/siggraph/websites/history/wp-content/plugins/pods/includes/general.php on line 518
Conference:
- SIGGRAPH 2008
-
More from SIGGRAPH 2008:
Notice: Array to string conversion in /data/siggraph/websites/history/wp-content/plugins/siggraph-archive-plugin/src/next_previous/source.php on line 345

Notice: Array to string conversion in /data/siggraph/websites/history/wp-content/plugins/siggraph-archive-plugin/src/next_previous/source.php on line 345

Type(s):
Entry Number: 26
Title:
- MeisterGRIP: Cylindrical Interface for Intuitional Robot Manipulation
Presenter(s):
Description:
In recent times, robot manipulations have been used to perform operations in extreme environments, communicate with people in remote locations, and realize entertainment systems that control virtual robots. In all these activities, an interface for robotic hand and arm manipulations is important to interact with the external environment [Bar-Cohen, 2000]. Conventional interfaces consist of a few levers and switches; unfortunately, such interfaces are difficult to control, and the users must have prior experience as far as the operation of these interfaces is concerned. The other type of interfaces reflects the postures of the user’s hand and arm directly in the robotic hand and arm so that the robots are capable of intuitive manipulation. However, these devices have a trouble of wearing and restrict the hand size of the user.
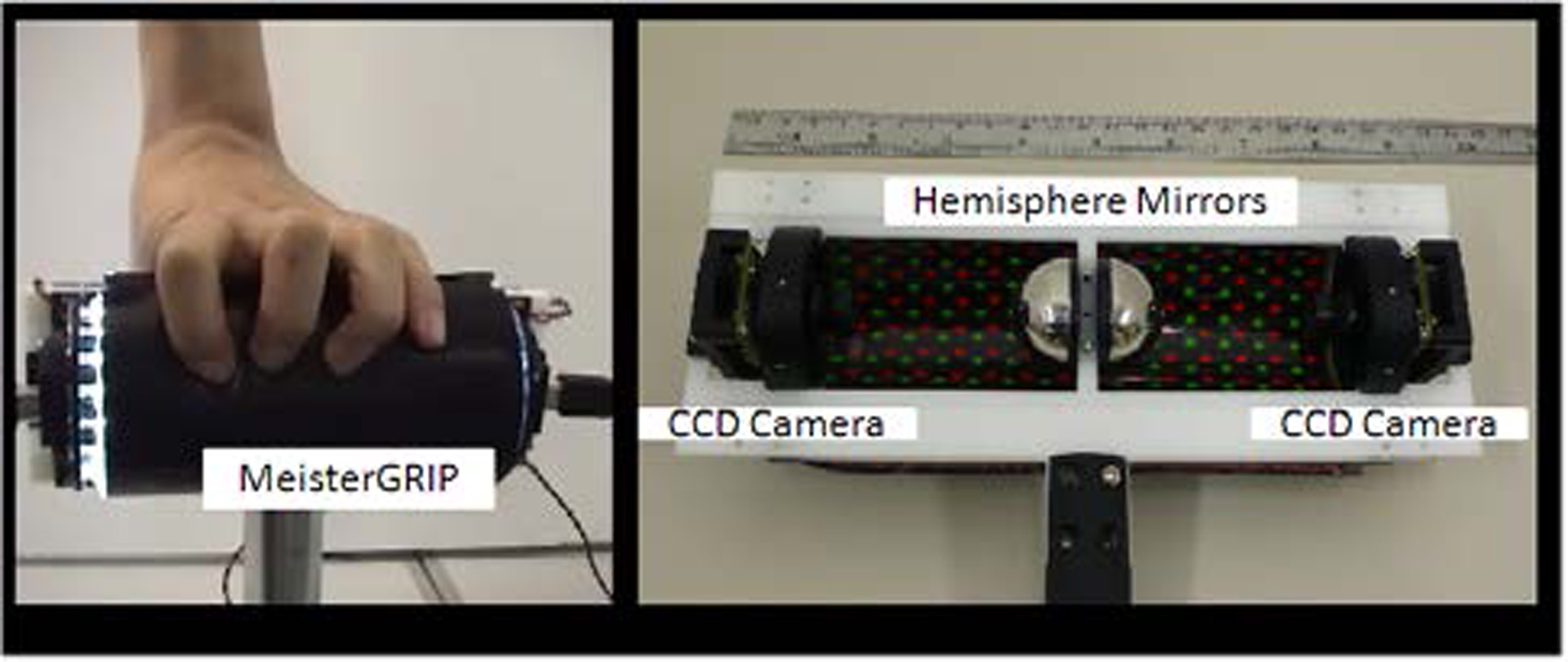
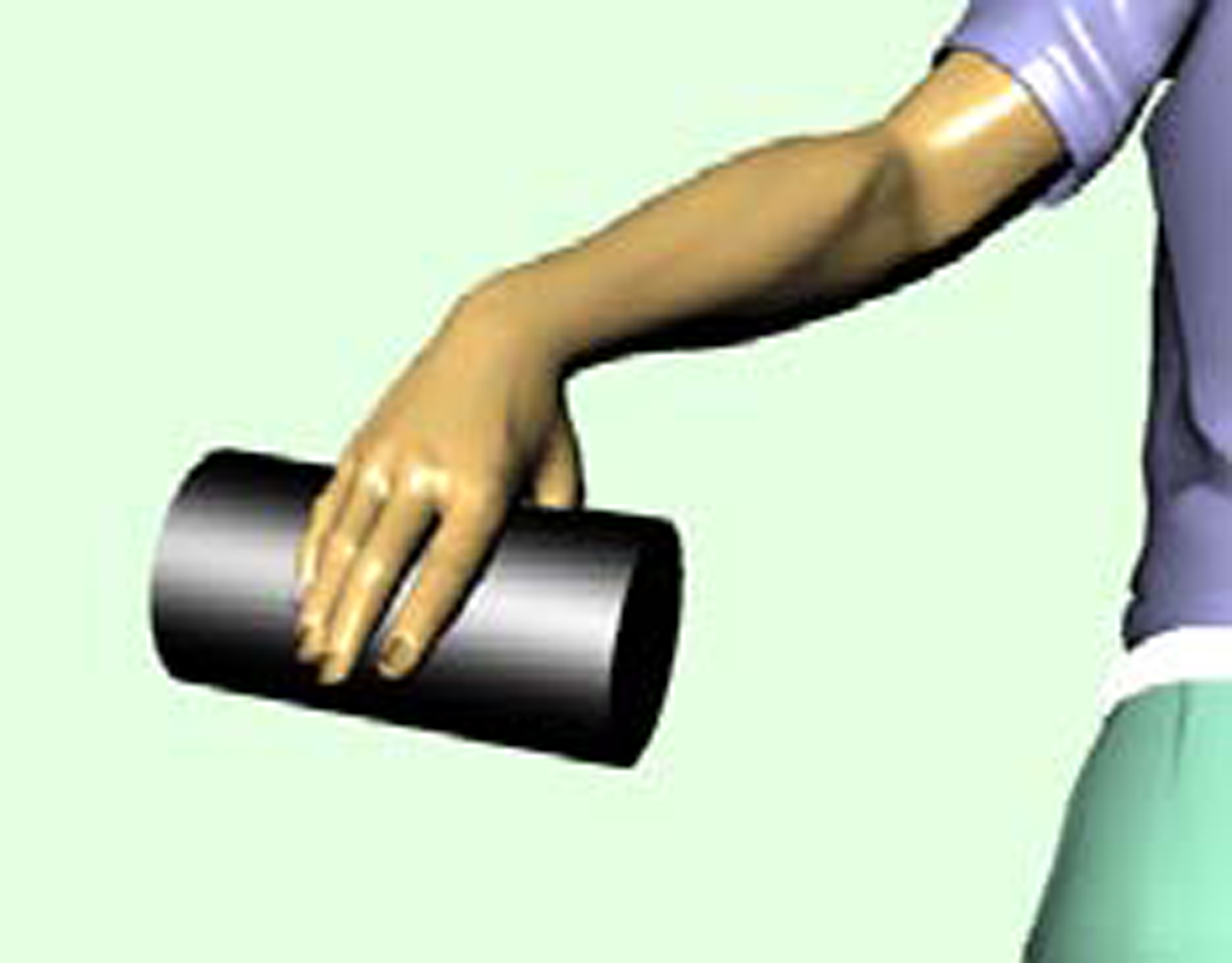
We believe that an interface for robotic hand manipulations should be developed in such a manner that anyone can use it intuitively and easily. Therefore, we developed a novel interface called “MeisterGRIP.” This device measures the user’s grasping conditions and reflects this information in the robotic hand and arm control. The user is simply required to grasp the device; therefore, the complexity of the setup is reduced and there are fewer restrictions on the user. Furthermore, by reflecting the grasping force of the user directly in the robotic hand and arm, intuitive manipulation is possible. MeisterGRIP allows robot manipulations to be easily conducted, and it can be widely used in general households. In the future, it will be possible to travel and interact with objects at remote locations by using our proposed device, even if the user is sitting on a sofa in his/her living room.
Other Information:
References
BAR-COHEN, Y. 1999. Haptic Interfaces, In Automation, Miniature Robotics and Sensors for Nondestructive Evaluation and Testing, Volume 4 of the Topics on NDE Series, ASNT, Columbus.
KAMIYAMA, K., KAJIMOTO, H., KAWAKAMI, N., AND TACHI, S. 2004. Evaluation of a Vision-based Tactile Sensor, In Proceedings of International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA2004).
Additional Images: