“HangerON : A Belt-Type Human Walking Controller Using the Hanger Reflex Haptic Illusion” by Kon, Nakamura and Kajimoto
Conference:
- SIGGRAPH 2017
-
More from SIGGRAPH 2017:


Type(s):
Entry Number: 10
Title:
- HangerON : A Belt-Type Human Walking Controller Using the Hanger Reflex Haptic Illusion
Presenter(s):
Description:
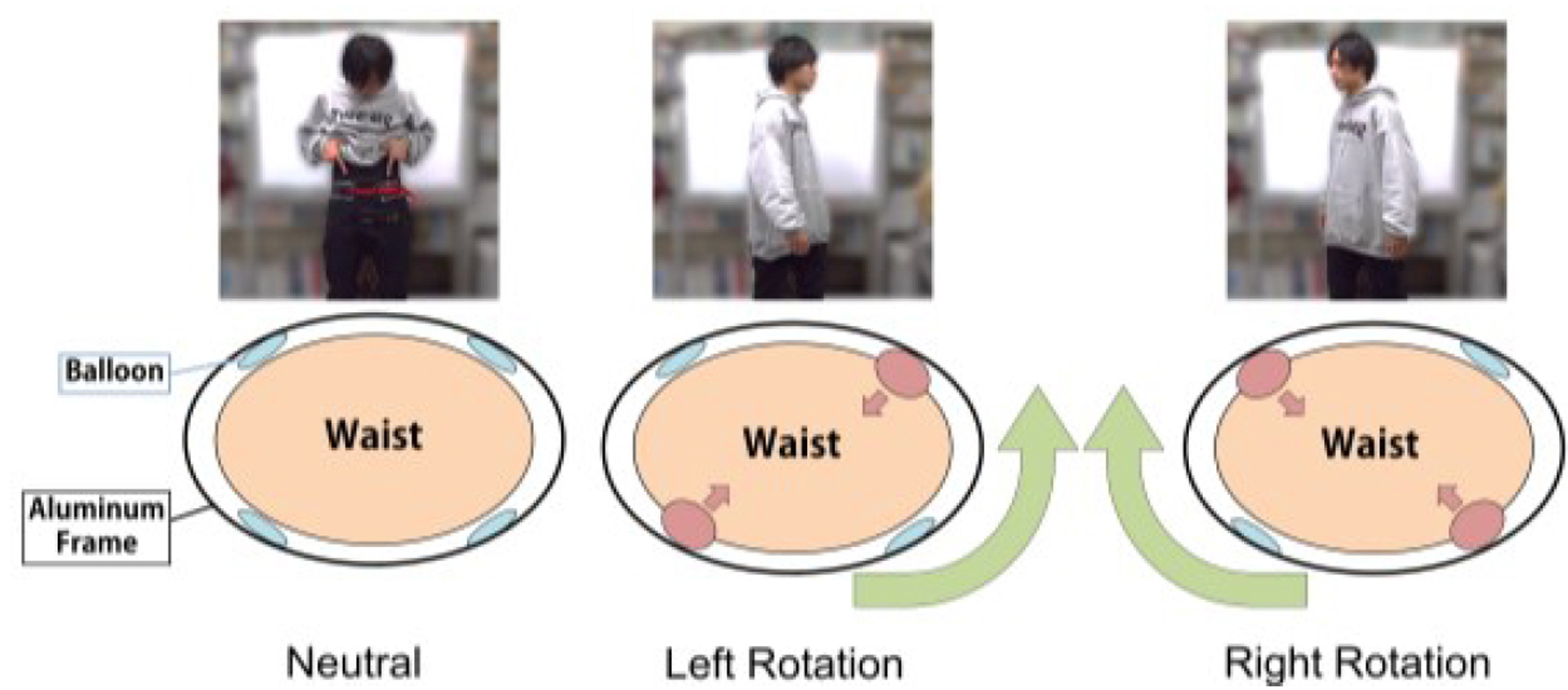
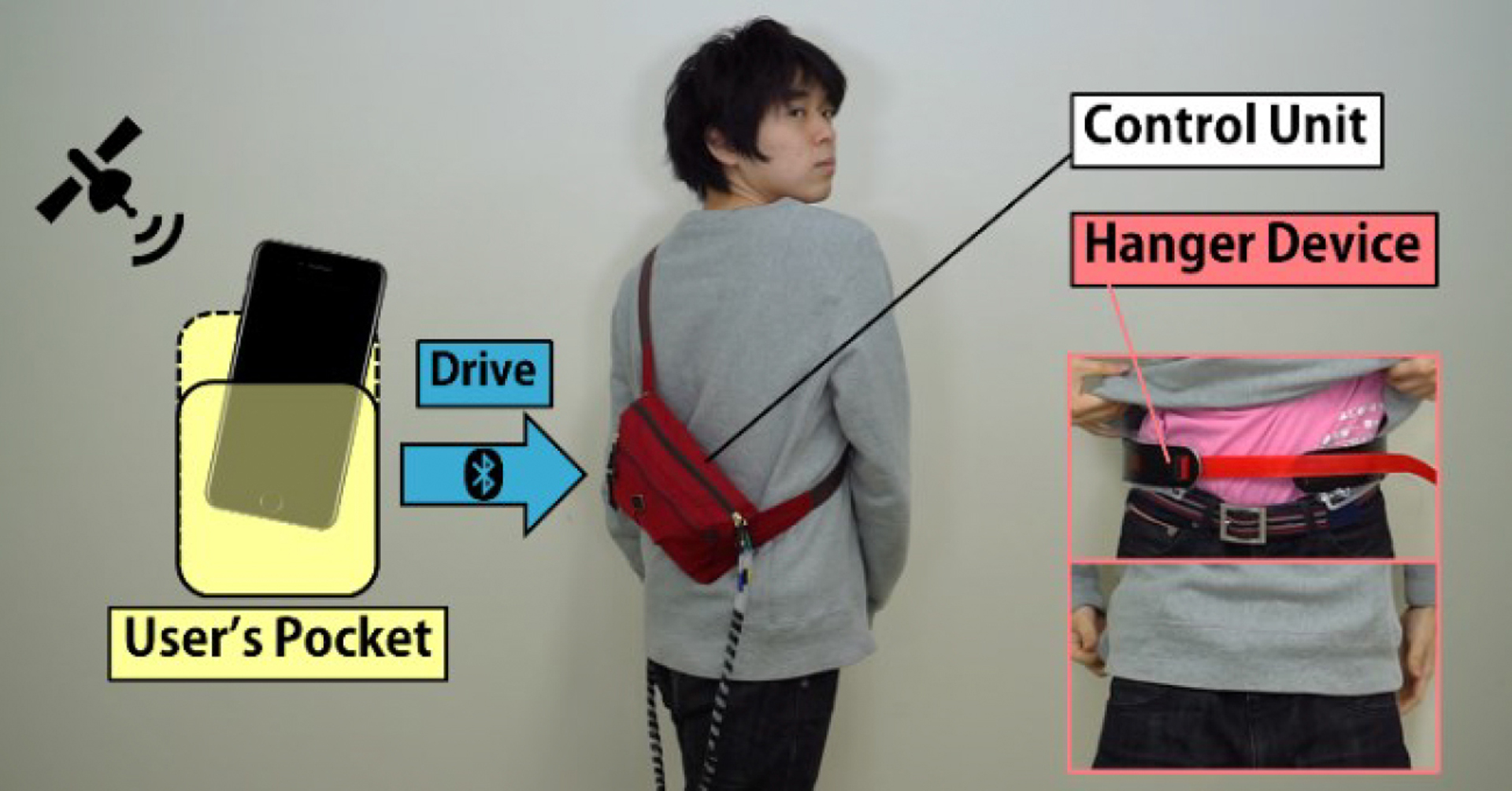
While walking with a navigation device, visual and auditory navigation information can require interpretation, and may distract the user from potential hazards. As a novel way to provide navigation information without distraction, we propose a method whereby the Hanger Reflex, which is an illusory phenomenon caused by haptic stimulus, influences walking. We have developed a way to stimulate the Hanger Reflex at the user’s waist, thus eliciting rotation towards the left or right. In this paper, we describe three different uses of our system: 1) Normal walking navigation, in which the device automatically navigates the user to the destination; 2) remote control of one user by another user; and 3) self-control of walking.
References:
R.C.FIZPATRICK, D.L.WARDMAN, J.L.TAYLOR. 1999. Effects of galvanic vestibular stimulation during human walking, J. Physiol., 517(3), pp. 931-939.
H.Wiliam, Jr.Warren, B. A.Kay, W. D.Zosh, A.P.Duchon, S.Sahuc. 2001. Optic flow is used to control human walking, Nature Neuroscience4, pp.213-216.
M.FREY.2005.CabBoots, ArsElectronica, http://www.freymartin.de/en/projects/cabboots
M.PFEIFFER,T.DUENTE,S.SCHNEEGASS,F.ALT,M.ROHS.2015.Cruise Control for Pedestrians: Controlling Walking Direction using Electrical Muscle Stimulation, CHI, pp.2505–2514.
A.Ishii, I.Suzuki, S.Sakamoto, K.Kanai, K.Takazawa, H.Doi, Y.Ochiai. 2016. Optical Marionette: Graphical Manipulation of Human’s Walking Direction, UIST, pp.705–716.
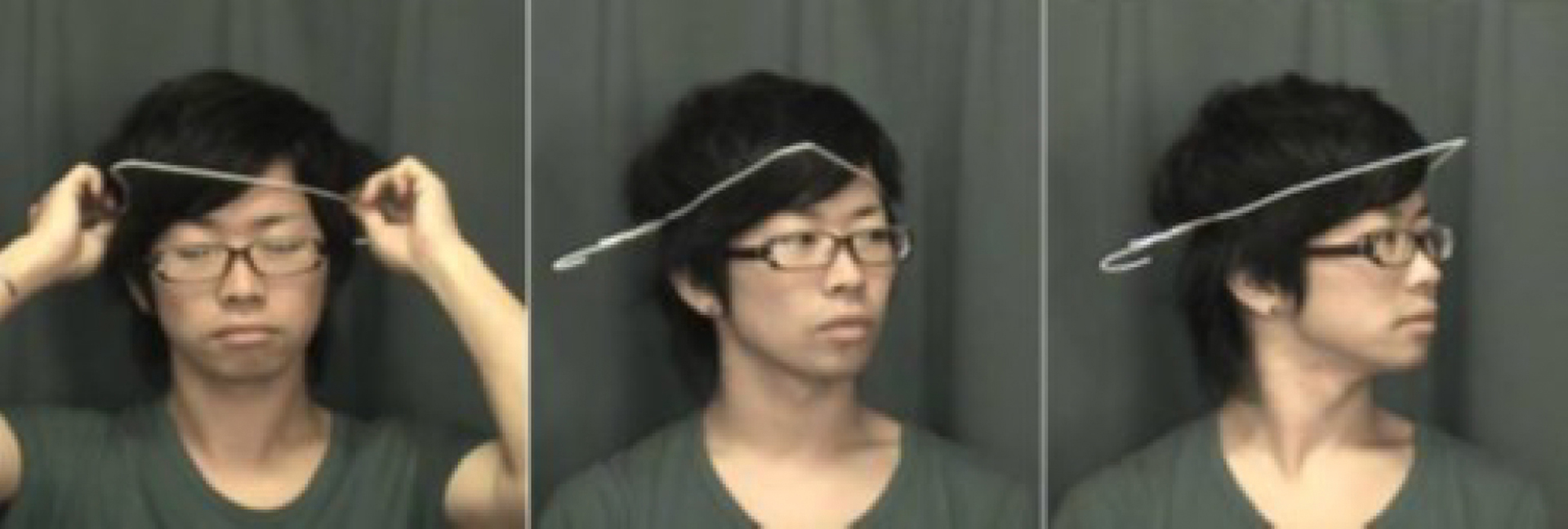
M.SATO,R.MATSUE,Y.HASHIMOTO,H.KAJIMOTO.2009.Development of a Head Rotation Interface by Using Hanger Reflex, IEEE RO-MAN, pp.534–538.
Y.KON,T.NAKAMURA,H.KAJIMOTO.2016.Effect of Hanger Reflex on Walking, IEEE HapticsSymposium, pp.313–318.
Y.KON,T.NAKAMURA,H.KAJIMOTO.2017.Interpretation of Navigation Information Modulates the Effect of the Waist-type Hanger Reflex on Walking, IEEE 3DUI, pp.107–115.
Keyword(s):
- Hanger Reflex
- Walking Navigation
- Pseudo-Force
Additional Images:
Acknowledgements:
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP15K12079.





