“GVS RIDE: Providing a Novel Experience Using a Head Mounted Display and Four-pole Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation” by Aoyama, Higuchi, Sakurai, Maeda and Ando
Notice: Pod Template PHP code has been deprecated, please use WP Templates instead of embedding PHP. has been deprecated since Pods version 2.3 with no alternative available. in /data/siggraph/websites/history/wp-content/plugins/pods/includes/general.php on line 518
Conference:
- SIGGRAPH 2017
-
More from SIGGRAPH 2017:
Notice: Array to string conversion in /data/siggraph/websites/history/wp-content/plugins/siggraph-archive-plugin/src/next_previous/source.php on line 345

Notice: Array to string conversion in /data/siggraph/websites/history/wp-content/plugins/siggraph-archive-plugin/src/next_previous/source.php on line 345

Type(s):
Entry Number: 09
Title:
- GVS RIDE: Providing a Novel Experience Using a Head Mounted Display and Four-pole Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation
Presenter(s):
Description:
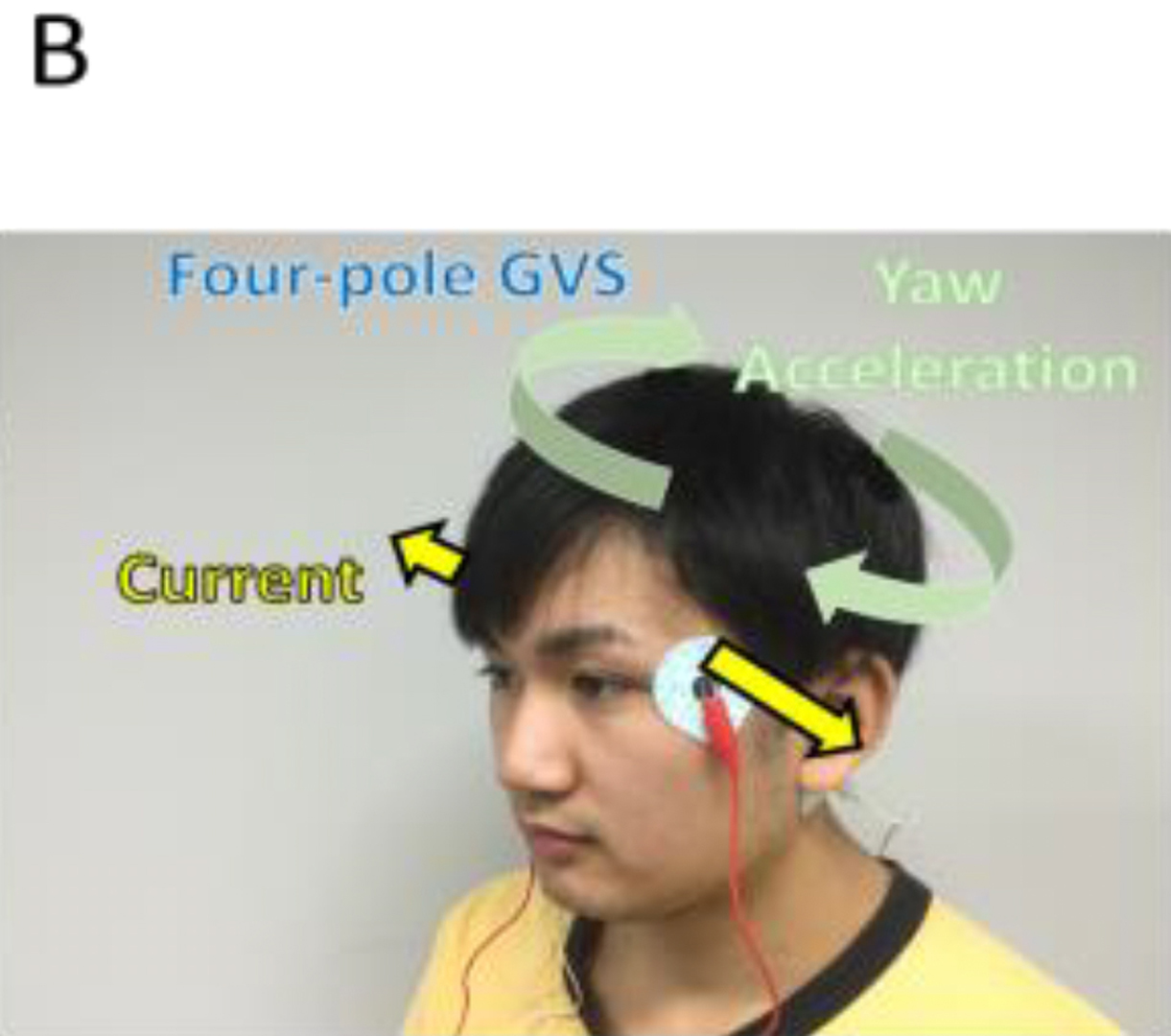
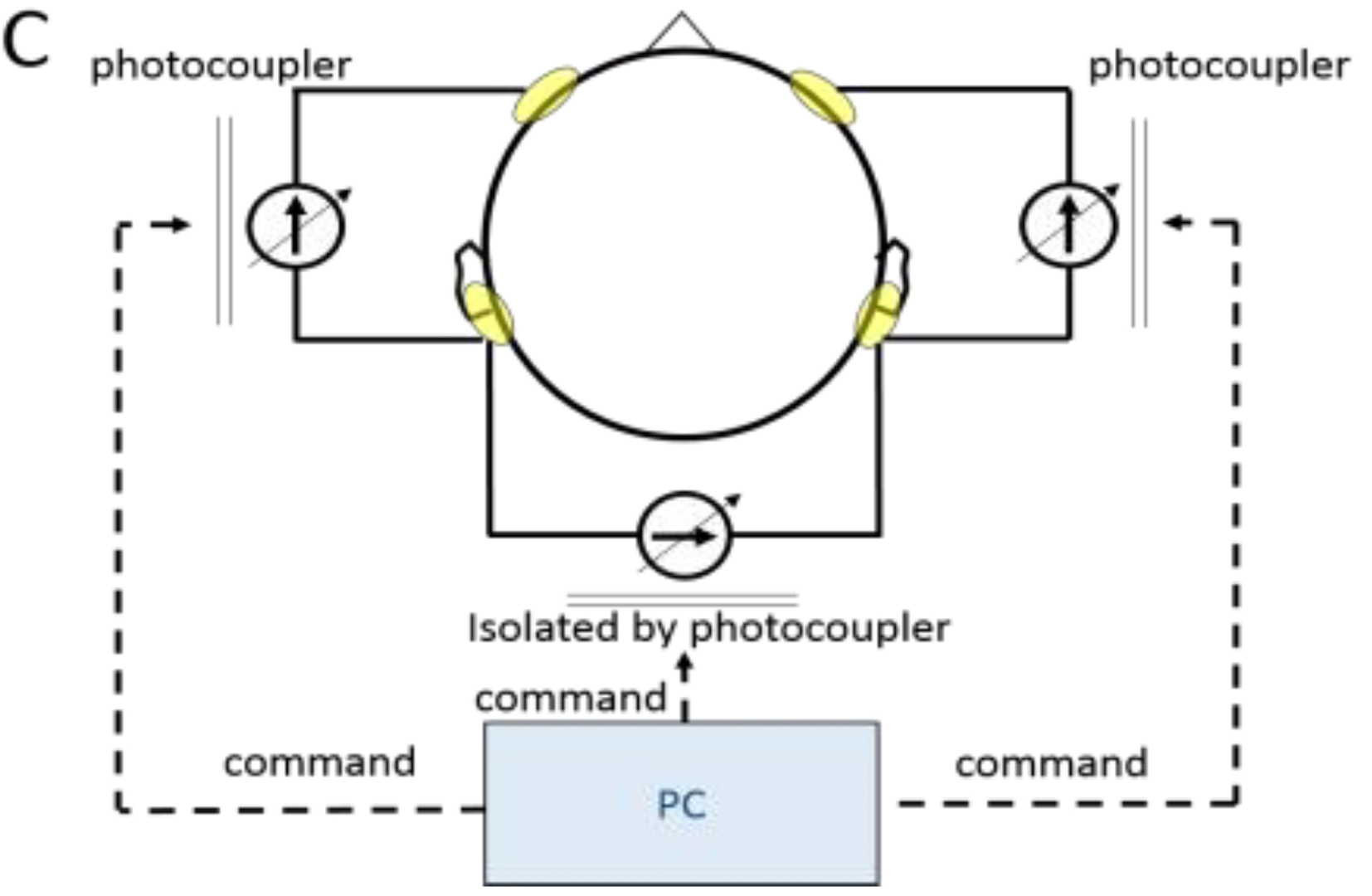
Galvanic 1Vestibular Stimulation (GVS) is a technique that induces virtual acceleration (or virtual head motion) by the application of current to electrodes placed on the bilateral mastoids. Since the vestibular sensation closely resembles real-life sensation, it is a promising technique for virtual reality (VR) systems for presenting a highly realistic experience. However, cannot induce lateral and anteroposterior directional acceleration. Thus, we invented methods to induce tri-directional acceleration (i.e., lateral, anteroposterior, and yaw rotation) to enhance virtual acceleration. The result is a new application named “GVS RIDE,” which gives a highly realistic experience using four-pole GVS and a Head Mounted Display (HMD) in synchronization. This paper and our demo introduce our novel GVS method and an application using GVS with HMD.
References:
REBECCCA J ST GEORGE., BRIAN L DAY. AND RICHARD C FITZPATRICK. 2011. Adaptation of vestibular signals for self-motion perception J. Physiol. 589, 4, 843-853.
SÉVERAC CAUQUIL A., MARTINEZ P., OUAKNINE, M., AND TARDY-GERVET, M, F., 2000, Orientation of the body response to galvanic stimulation as a function of the inter-vestibular imbalance, Exp. Brain Res., 133, 501-505.
KAZUMA AOYAMA., HIROYUKI IIZUKA., HIDEYUKI ANDO AND TARO MAEDA, 2015. Four-pole Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation Causes Body Sway about Three Axes. Sci. Rep. 5, 10168; doi:10.1038/grep10168.
Keyword(s):
- galvanic vestibular stimulation
- virtual head motion
- multi direction
- GVS RIDE
Additional Images:

Acknowledgements:
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (A) Grant Number 17H04690.