“Wavelet turbulence for fluid simulation” by Kim, Thürey, James and Gross
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Wavelet turbulence for fluid simulation
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
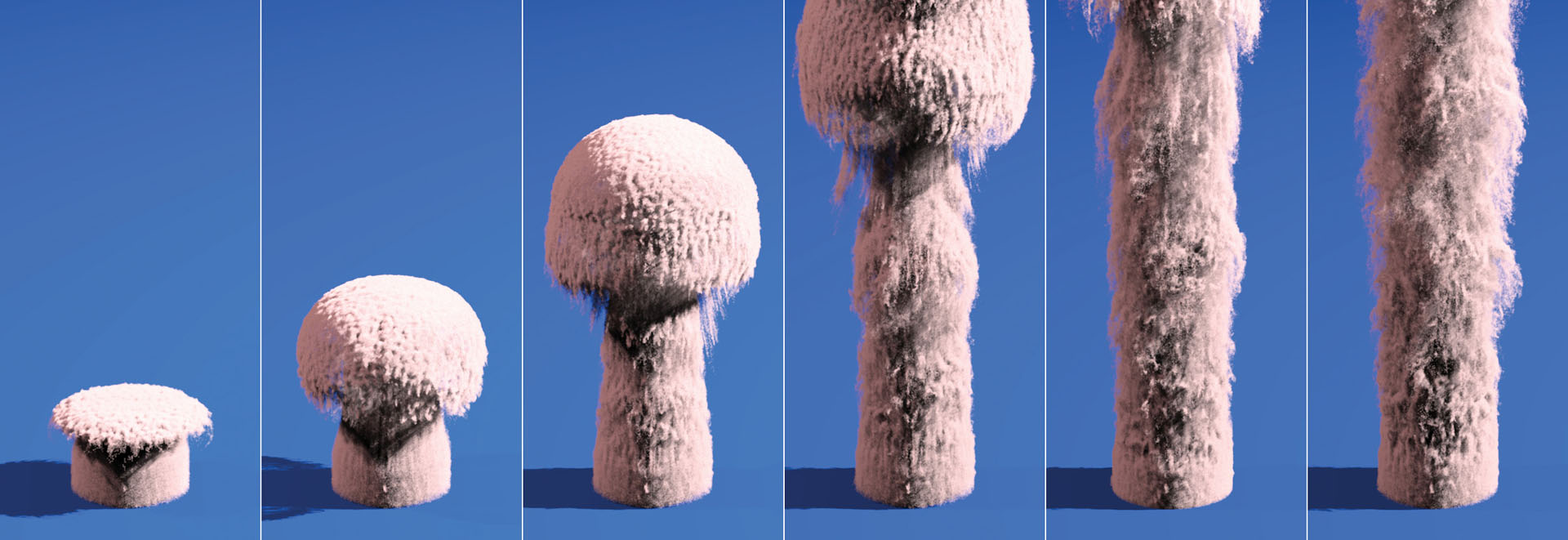
We present a novel wavelet method for the simulation of fluids at high spatial resolution. The algorithm enables large- and small-scale detail to be edited separately, allowing high-resolution detail to be added as a post-processing step. Instead of solving the Navier-Stokes equations over a highly refined mesh, we use the wavelet decomposition of a low-resolution simulation to determine the location and energy characteristics of missing high-frequency components. We then synthesize these missing components using a novel incompressible turbulence function, and provide a method to maintain the temporal coherence of the resulting structures. There is no linear system to solve, so the method parallelizes trivially and requires only a few auxiliary arrays. The method guarantees that the new frequencies will not interfere with existing frequencies, allowing animators to set up a low resolution simulation quickly and later add details without changing the overall fluid motion.
References:
1. Angelidis, A., Neyret, F., Singh, K., and Nowrouzezahrai, D. 2006. A controllable, fast and stable basis for vortex based smoke simulation. In ACM SIGGRAPH/EG Symposium on Computer Animation (SCA). Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Basu, S., Foufoula-Georgiou, E., and Porte-Agel, F. 2004. Synthetic turbulence, fractal interpolation, and large-eddy simulation. Physical Review E, 026310.Google Scholar
3. Batty, C., Bertails, F., and Bridson, R. 2007. A fast variational framework for accurate solid-fluid coupling. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Bridson, R., Hourihan, J., and Nordenstam, M. 2007. Curl-noise for procedural fluid flow. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Cook, R., and DeRose, T. 2005. Wavelet noise. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Elcott, S., Tong, Y., Kanso, E., Schröder, P., and Desbrun, M. 2007. Stable, circulation-preserving, simplicial fluids. ACM Transactions on Graphics. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Farge, M., Kevlahan, N., Perrier, V., and Goirand, E. 1996. Wavelets and turbulence. Proceedings of the IEEE 84, 4, 639–669.Google ScholarCross Ref
8. Fattal, R., and Lischinski, D. 2004. Target-driven smoke animation. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Fedkiw, R., Stam, J., and Jensen, H. W. 2001. Visual simulation of smoke. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH, 15–22. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Frisch, U. 1995. Turbulence: The Legacy of A. N. Kolmogorov. Cambridge University Press.Google ScholarCross Ref
11. Kim, B., Liu, Y., Llamas, I., and Rossignac, J. 2005. Flow-fixer: Using BFECC for fluid simulation. In Proceedings of Eurographics Workshop on Natural Phenomena. Google ScholarCross Ref
12. Klingner, B. M., Feldman, B. E., Chentanez, N., and O’Brien, J. F. 2006. Fluid animation with dynamic meshes. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Lamorlette, A., and Foster, N. 2002. Structural modeling of flames for a production environment. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Losasso, F., Gibou, F., and Fedkiw, R. 2004. Simulating water and smoke with an octree data structure. Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH, 457–462. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. McNamara, A., Treuille, A., Popovic, Z., and Stam, J. 2004. Fluid control using the adjoint method. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Neyret, F. 2003. Advected textures. In ACM SIGGRAPH/EG Symposium on Computer Animation (SCA). Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Perlin, K. 1985. An image synthesizer. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH, 287–296. Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Perrier, V., Philipovitch, T., and Basdevant, C. 1995. Wavelet spectra compared to fourier spectra. Journal of Mathematical Physics 36.Google ScholarCross Ref
19. Rasmussen, N., Nguyen, D. Q., Geiger, W., and Fedkiw, R. 2003. Smoke simulation for large scale phenomena. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Scotti, A., and Meneveau, C. 1999. A fractal model for large eddy simulation of turbulent flows. Physica D, 198–232. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Selle, A., Rasmussen, N., and Fedkiw, R. 2005. A vortex particle method for smoke, water and explosions. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Selle, A., Fedkiw, R., Kim, B., Liu, Y., and Rossignac, J. 2008. An unconditionally stable MacCormack method. Journal of Scientific Computing (in press). Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Shraiman, B., and Siggia, E. 2000. Scalar turbulence. Nature, 405, 639–646.Google ScholarCross Ref
24. Stam, J., and Fiume, E. 1993. Turbulent wind fields for gaseous phenomena. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Stam, J. 1999. Stable fluids. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library