“Video super-resolution using texton substitution” by Kamimura, Tsumura, Nakaguchi, Miyake and Motomura
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Video super-resolution using texton substitution
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
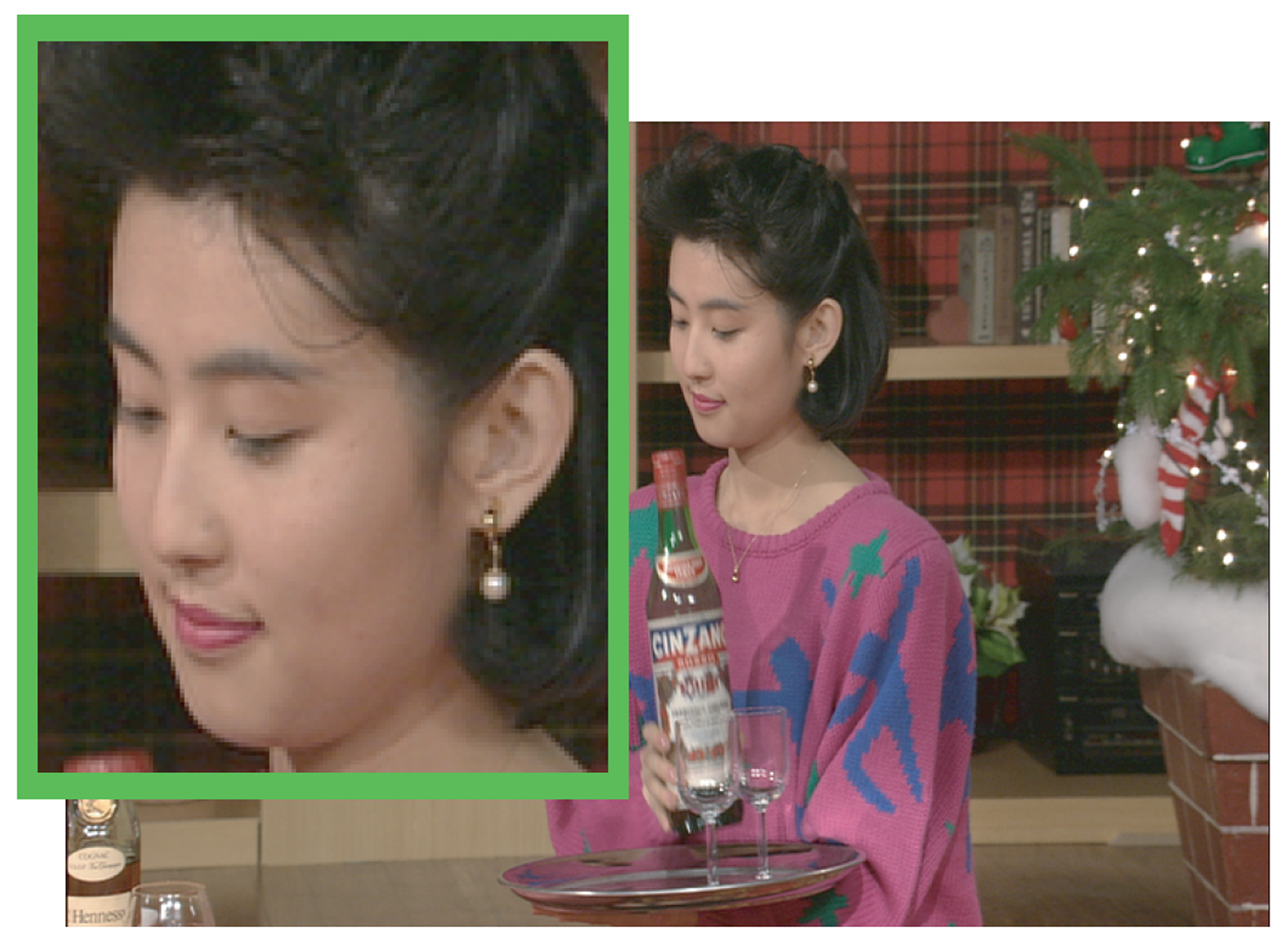
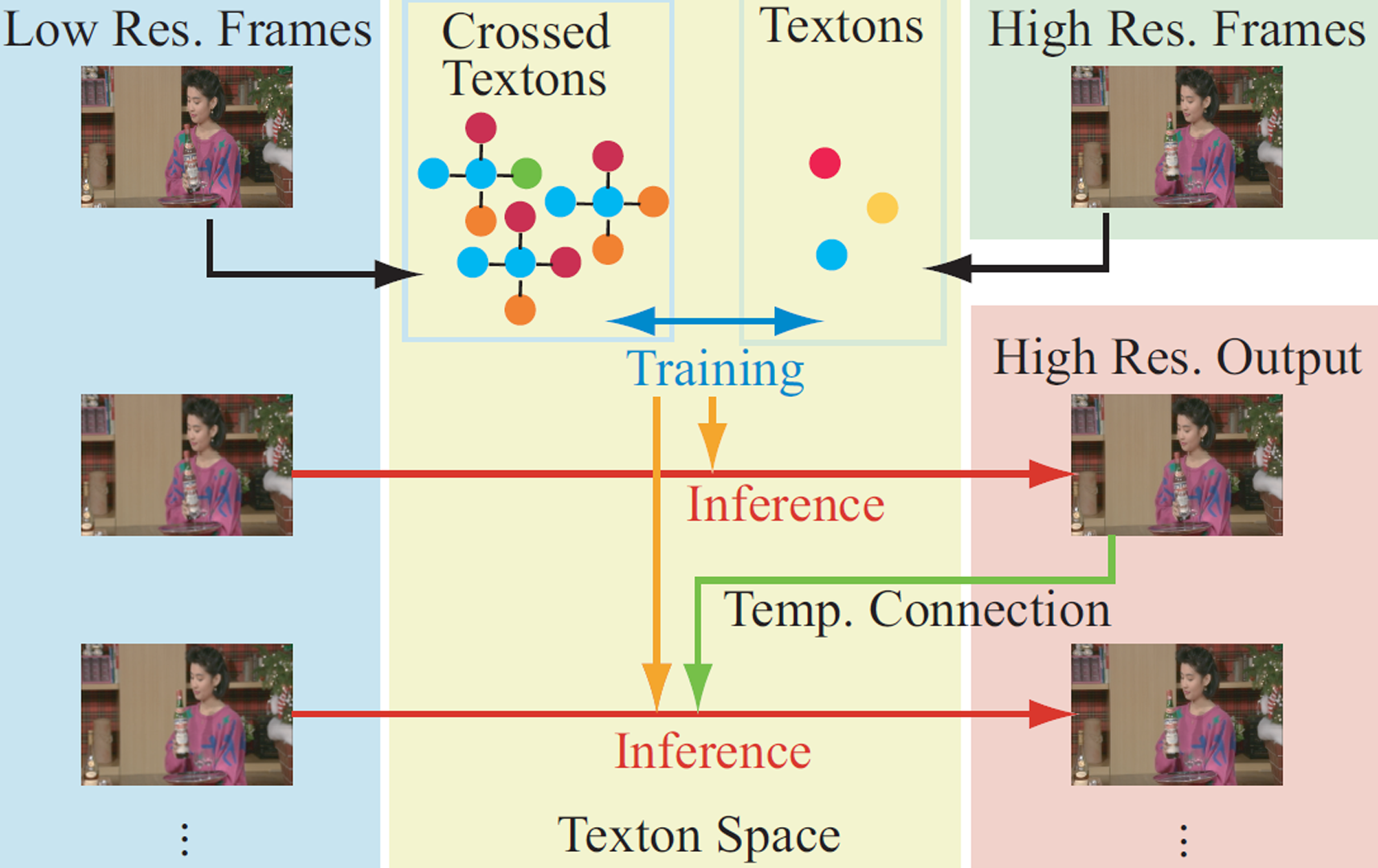
A video camera produces an image sequence with a specific frame rate (e.g. 30 frames per second). This imposes limits on the spatial resolution due to limited bandwidth. Image interpolation, such as bi-cubic interpolation, can increase the resolution, but yields a blurring of edges and image details. To create plausible high-frequency details in the blurred image, super-resolution technique has been a long studied area[Baker and Kanade 2002; Capel and Zisserman 2003]. However, it is difficult to apply these methods to a video sequence, since [Capel and Zisserman 2003] requires multiple images, and [Baker and Kanade 2002] requires a high computational cost. In order to resolve these problems, we proposed a method called “texton substitution”[Kamimura et al. 2006]. In this paper, we improve the method of texton substitution by using temporal connection.
References:
1. Baker, S., and Kanade, T. 2002. Limits on super-resolution and how to break them. IEEE Tran. on PAMI 24, 9, 1167–1183.
2. Capel, D., and Zisserman, A. 2003. Computer vision applied to super resolution. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 75–86.
3. Kamimura, K., Tsumura, N., Nakaguchi, T., Miyake, Y., Motomura, H., and Kanamori, K. 2006. Substituting crossed textons for super resolution of video. SIGGRAPH poster.