“Rainbow particle imaging velocimetry for dense 3D fluid velocity imaging” by Xiong, Idoughi, Aguirre-Pablo, Aljedaani, Dun, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Rainbow particle imaging velocimetry for dense 3D fluid velocity imaging
Session/Category Title: Imaginative Imaging
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
- Jinhui Xiong
- Ramzi Idoughi
- Andres Aguirre-Pablo
- Abdulrahman Aljedaani
- Xiong Dun
- Qiang Fu
- Sigurdur Thoroddsen
- Wolfgang Heidrich
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
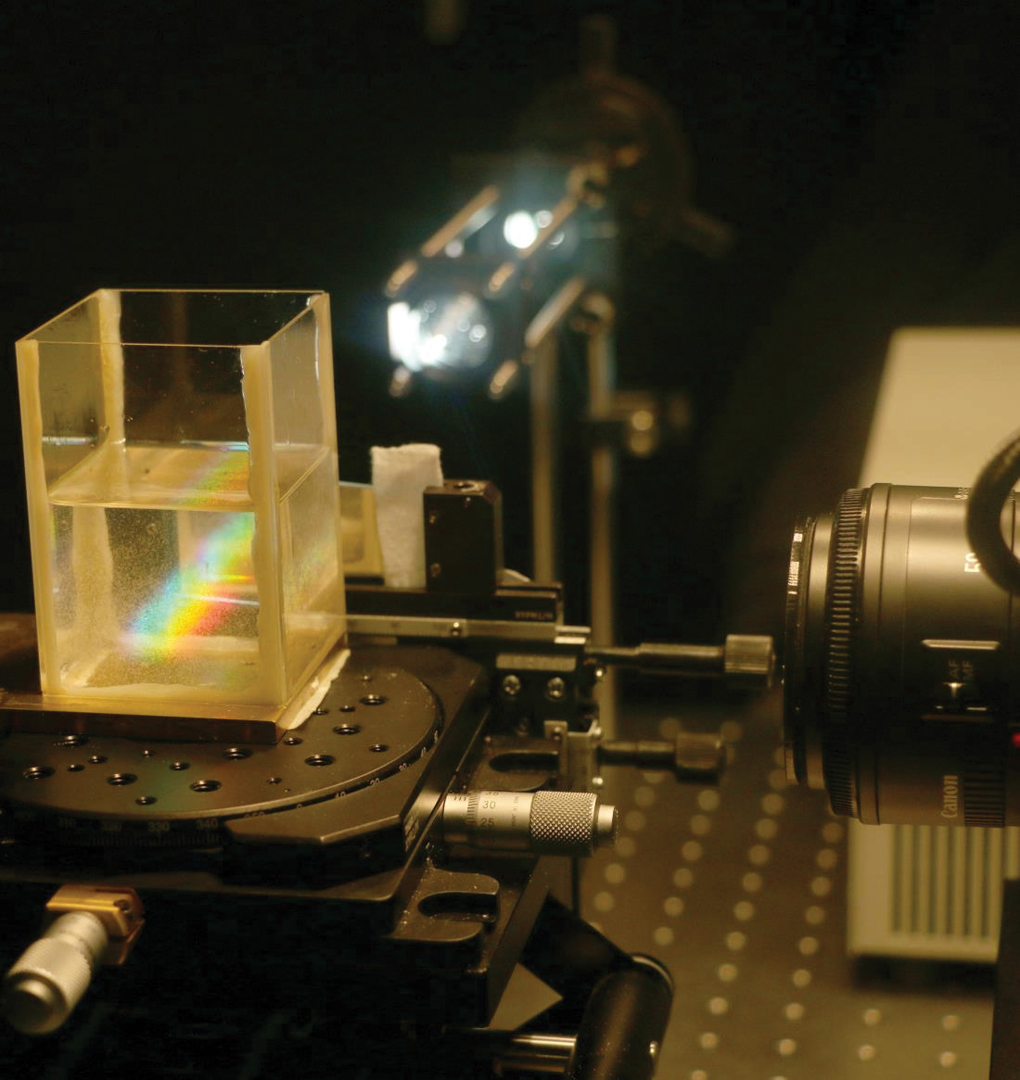
Despite significant recent progress, dense, time-resolved imaging of complex, non-stationary 3D flow velocities remains an elusive goal. In this work we tackle this problem by extending an established 2D method, Particle Imaging Velocimetry, to three dimensions by encoding depth into color. The encoding is achieved by illuminating the flow volume with a continuum of light planes (a “rainbow”), such that each depth corresponds to a specific wavelength of light. A diffractive component in the camera optics ensures that all planes are in focus simultaneously. With this setup, a single color camera is sufficient for tracking 3D trajectories of particles by combining 2D spatial and 1D color information.For reconstruction, we derive an image formation model for recovering stationary 3D particle positions. 3D velocity estimation is achieved with a variant of 3D optical flow that accounts for both physical constraints as well as the rainbow image formation model. We evaluate our method with both simulations and an experimental prototype setup.
References:
1. R.J. Adrian and J. Westerweel. 2011. Particle image velocimetry. Cambridge University Press.Google Scholar
2. B. Atcheson, I. Ihrke, W. Heidrich, A. Tevs, D. Bradley, M. Magnor, and H-P. Seidel. 2008. Time-resolved 3D Capture of Non-stationary Gas Flows. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 5 (2008), 132. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. I. Barbu, C. Herzet, and E. Mémin. 2013. Joint estimation of volume and velocity in TomoPIV. In 10TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON PARTICLE IMAGE VELOCIMETRY-PIV13. 45.Google Scholar
4. S. Boyd, N. Parikh, E. Chu, B. Peleato, and J. Eckstein. 2011. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning 3, 1 (2011), 1–122. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. E.J. Candes, M.B. Wakin, and S.P. Boyd. 2008. Enhancing sparsity by reweighted âĎŞ 1 minimization. J. Fourier analysis and applications 14, 5–6 (2008), 877–905.Google Scholar
6. T.A. Casey, J. Sakakibara, and S.T. Thoroddsen. 2013. Scanning Tomographic Particle Image Velocimetry Applied to a Turbulent Jet. Phys. Fluids 25 (2013), 025102. Google ScholarCross Ref
7. G.E. Elsinga, F. Scarano, B. Wieneke, and B.W. van Oudheusden. 2006. Tomographic particle image velocimetry. Experiments in Fluids 41, 6 (2006), 933–947. Google ScholarCross Ref
8. R. Fedkiw, J. Stam, and H.W. Jensen. 2001. Visual simulation of smoke. In Proc. ACM Siggraph. 15–22. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. N. Foster and D. Metaxas. 1997. Modeling the motion of a hot, turbulent gas. In Proc. ACM Siggraph. 181–188. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. J. Gregson, I. Ihrke, N. Thuerey, and W. Heidrich. 2014. From capture to simulation: connecting forward and inverse problems in fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (2014), 139. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. J. Gregson, M. Krimerman, M.B. Hullin, and W. Heidrich. 2012. Stochastic tomography and its applications in 3D imaging of mixing fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4 (2012), 52–1. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. J. Gu, S.K. Nayar, E. Grinspun, P.N. Belhumeur, and R. Ramamoorthi. 2013. Compressive Structured Light for Recovering Inhomogeneous Participating Media. IEEE PAMI 35, 3 (2013), 555–567.Google Scholar
13. S.W. Hasinoff and K.N. Kutulakos. 2007. Photo-consistent Reconstruction of Semitransparent Scenes by Density-sheet Decomposition. IEEE PAMI 29, 5 (2007), 870–885. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. T. Hawkins, P. Einarsson, and P. Debevec. 2005. Acquisition of Time-Varying Participating Media. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3 (2005), 812–815. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. F. Heide, Q. Fu, Y. Peng, and W. Heidrich. 2016. Encoded diffractive optics for full-spectrum computational imaging. Scientific Reports 6, 33543 (Sept. 2016), 10.Google ScholarCross Ref
16. D. Heitz, P. Héas, E. Mémin, and J. Carlier. 2008. Dynamic consistent correlation-variational approach for robust optical flow estimation. Experiments in fluids 45, 4 (2008), 595–608. Google ScholarCross Ref
17. D. Heitz, E. Mémin, and C. Schnörr. 2010. Variational fluid flow measurements from image sequences: synopsis and perspectives. Experiments in Fluids 48, 3 (2010), 369–393. Google ScholarCross Ref
18. I. Herlin, D. Béréziat, N. Mercier, and S. Zhuk. 2012. Divergence-free motion estimation. In Proc. ECCV. 15–27. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. K.D. Hinsch. 2002. Holographic particle image velocimetry. Measurement Science and Technology 13, 7 (2002), R61.Google ScholarCross Ref
20. B.K.P. Horn and B.G. Schunck. 1981. Determining optical flow. Artificial Intelligence 17, 1–3 (1981), 185–203.Google ScholarDigital Library
21. I. Ihrke and M. Magnor. 2004. Image-Based Tomographic Reconstruction of Flames. In Proc. SCA. 367–375.Google Scholar
22. I. Kimura, Y. Kohno, T. Ogasawara, and T. Takamori. 1991. Measurement of three dimensional velocity vectors in a flow field using a color spectrum. Transactions of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers 27, 7 (1991), 755–761. Google ScholarCross Ref
23. M. Levoy, R. Ng, A. Adams, M. Footer, and M. Horowitz. 2006. Light field microscopy. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 3 (2006), 924–934. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. T. Liu, A. Merat, M.H.M. Makhmalbaf, C. Fajardo, and P. Merati. 2015. Comparison between optical flow and cross-correlation methods for extraction of velocity fields from particle images. Experiments in Fluids 56, 8 (2015), 1–23. Google ScholarCross Ref
25. T. Liu and L. Shen. 2008. Fluid flow and optical flow. J. Fluid Mechanics 614 (2008), 253–291. Google ScholarCross Ref
26. L.M. Lourenco, A. Krothapalli, and C.A. Smith. 1989. Particle image velocimetry. In Advances in Fluid Mechanics Measurements. Springer, 127–199. Google ScholarCross Ref
27. K.P. Lynch, T. Fahringer, and B. Thurow. 2012. Three-dimensional particle image velocimetry using a plenoptic camera. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA).Google Scholar
28. T.J. McGregor, D.J. Spence, and D.W. Coutts. 2007. Laser-based volumetric colour-coded three-dimensional particle velocimetry. Optics and Lasers in Engineering 45, 8 (2007), 882–889. Google ScholarCross Ref
29. E. Meinhardt-Llopis, J.S. Pérez, and D. Kondermann. 2013. Horn-schunck optical flow with a multi-scale strategy. Image Processing on line 2013 (2013), 151–172.Google Scholar
30. R. Ng, M. Levoy, M. Brédif, G. Duval, M. Horowitz, and P. Hanrahan. 2005. Light field photography with a hand-held plenoptic camera. Computer Science Technical Report CSTR 2, 11 (2005), 1–11.Google Scholar
31. K. Okamoto, S. Nishio, T. Saga, and T. Kobayashi. 2000. Standard images for particle-image velocimetry. Measurement Science and Technology 11, 6 (2000), 685.Google ScholarCross Ref
32. N. Parikh, S.P. Boyd, and others. 2014. Proximal Algorithms. Foundations and Trends in Optimization 1, 3 (2014), 127–239. Google ScholarDigital Library
33. Y. Peng, Q. Fu, H. Amata, S. Su, F. Heide, and W. Heidrich. 2015. Computational imaging using lightweight diffractive-refractive optics. Optics Express 23, 24 (2015), 31393–31407. Google ScholarCross Ref
34. S. Pick and F-O. Lehmann. 2009. Stereoscopic PIV on multiple color-coded light sheets and its application to axial flow in flapping robotic insect wings. Experiments in Fluids 47, 6 (2009), 1009–1023. Google ScholarCross Ref
35. A.K. Prasad. 2000. Particle image velocimetry. CURRENT SCIENCE-BANGALORE- 79, 1 (2000), 51–60.Google Scholar
36. P. Ruhnau, A. Stahl, and C. Schnörr. 2007. Variational estimation of experimental fluid flows with physics-based spatio-temporal regularization. Measurement Science and Technology 18, 3 (2007), 755.Google ScholarCross Ref
37. D. Schanz, S. Gesemann, and A. Schröder. 2016. Shake-The-Box: Lagrangian particle tracking at high particle image densities. Experiments in fluids 57, 5 (2016), 1–27. Google ScholarCross Ref
38. J. Stam. 1999. Stable fluids. In Proc. ACM Siggraph. 121–128. Google ScholarDigital Library
39. M. Stanislas, K. Okamoto, C.J. Kähler, J. Westerweel, and F. Scarano. 2008. Main results of the third international PIV challenge. Experiments in Fluids 45, 1 (2008), 27–71. Google ScholarCross Ref
40. H. Wang, M. Liao, Q. Zhang, R. Yang, and G. Turk. 2009. Physically guided liquid surface modeling from videos. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3 (2009), 90. Google ScholarDigital Library
41. T. Watamura, Y. Tasaka, and Y. Murai. 2013. LCD-projector-based 3D color PTV. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science 47 (2013), 68–80. Google ScholarCross Ref
42. C.E. Willert and M. Gharib. 1992. Three-dimensional particle imaging with a single camera. Experiments in Fluids 12, 6 (1992), 353–358. Google ScholarCross Ref
43. J. Yuan, C. Schörr, and G. Steidl. 2007. Simultaneous higher-order optical flow estimation and decomposition. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 29, 6 (2007), 2283–2304. Google ScholarDigital Library