“Quality-preserving image downsizing” by Trentacoste, Mantiuk and Heidrich
Conference:
Type(s):
Entry Number: 74
Title:
- Quality-preserving image downsizing
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
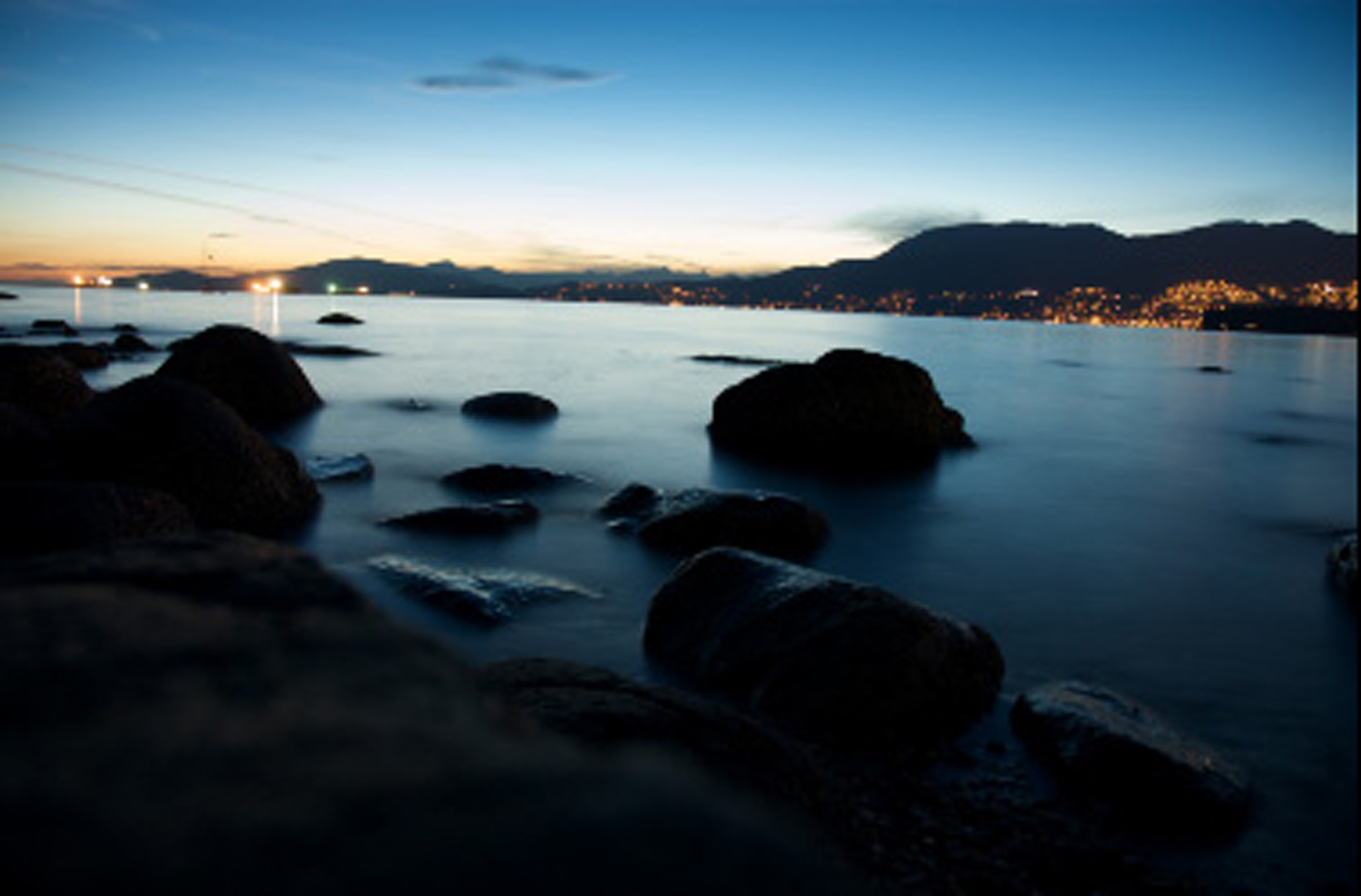
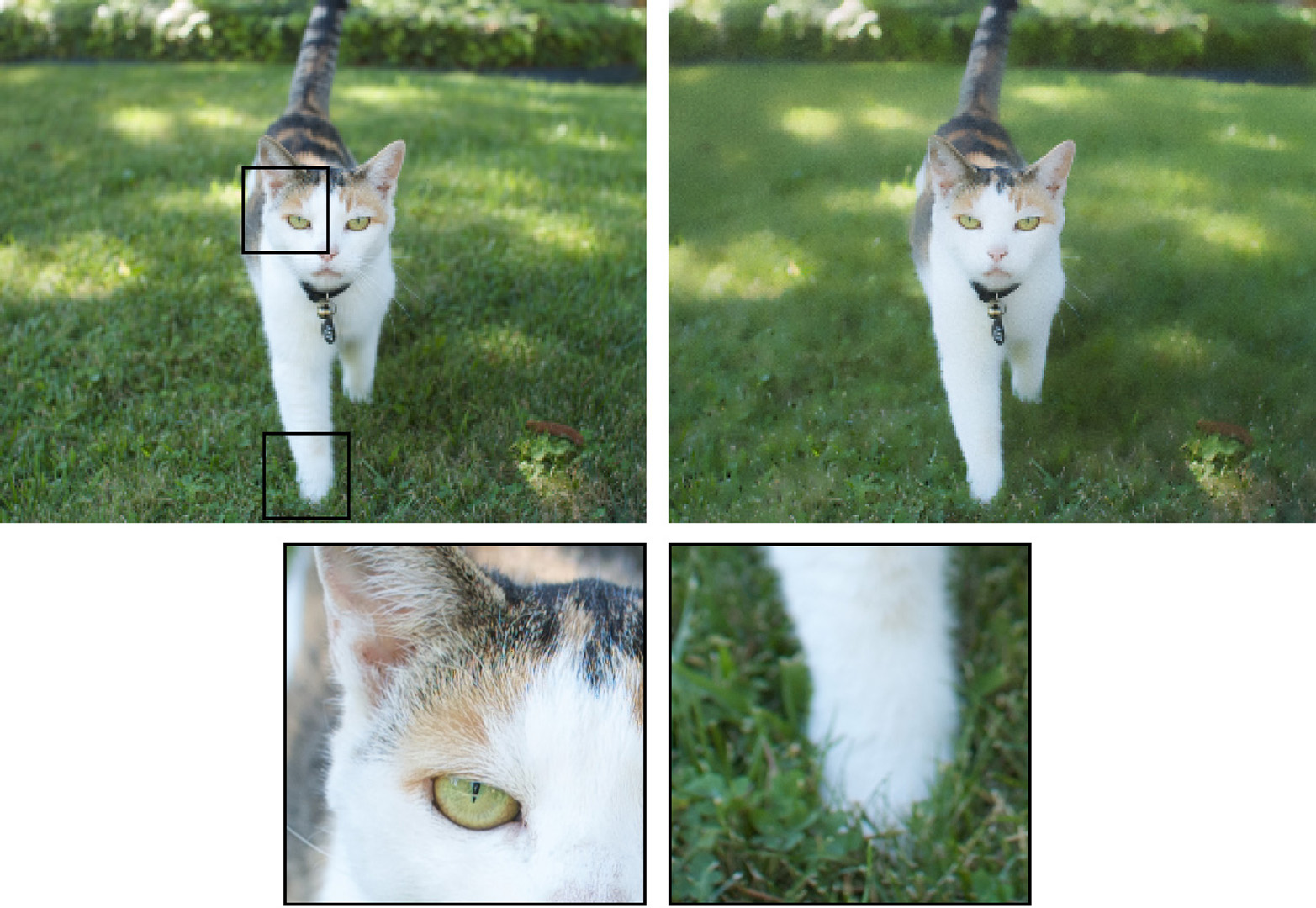
The image quality of a digital viewfinder is considerably lower than that of a through-the-lens optical system. While the sensor may be capable of capturing 10 or 20 megapixels, the screen of the viewfinder is typically constrained to resolutions under 1 megapixel. The limited resolution makes it impossible to discern all the small details of the captured image. Small blurs and noise that are present in the full-size image can render the image unusable for certain tasks, yet these artifacts may be too small to be discernible in the downsampled version shown on the camera viewfinder.
References:
Bae, S., and Durand, F. 2007. Defocus magnification. Computer Graphics Forum 26, 3, 571–579.Google Scholar
Samadani, R., Mauer, T. A., Berfanger, D. M., and Clark, J. H. 2010. Image thumbnails that represent blur and noise. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 19, 2, 363–373. Google ScholarDigital Library
Additional Images: