“Pose-space subspace dynamics”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Pose-space subspace dynamics
Session/Category Title: RIGGING & SKINNING
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
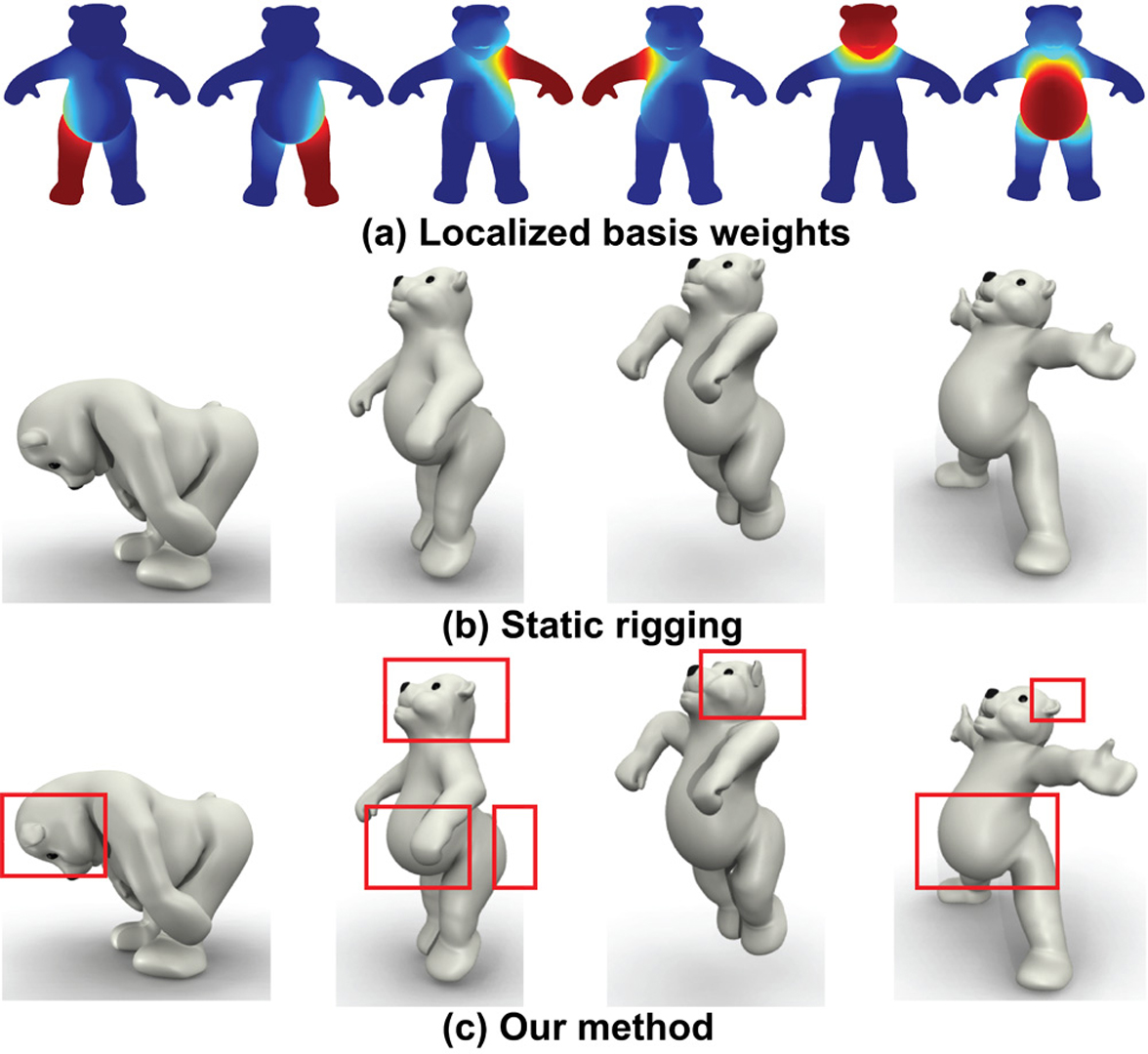
We enrich character animations with secondary soft-tissue Finite Element Method (FEM) dynamics computed under arbitrary rigged or skeletal motion. Our method optionally incorporates pose-space deformation (PSD). It runs at milliseconds per frame for complex characters, and fits directly into standard character animation pipelines. Our simulation method does not require any skin data capture; hence, it can be applied to humans, animals, and arbitrary (real-world or fictional) characters. In standard model reduction of three-dimensional nonlinear solid elastic models, one builds a reduced model around a single pose, typically the rest configuration. We demonstrate how to perform multi-model reduction of Finite Element Method (FEM) nonlinear elasticity, where separate reduced models are precomputed around a representative set of object poses, and then combined at runtime into a single fast dynamic system, using subspace interpolation. While time-varying reduction has been demonstrated before for offline applications, our method is fast and suitable for hard real-time applications in games and virtual reality. Our method supports self-contact, which we achieve by computing linear modes and derivatives under contact constraints.
References:
1. Amsallem, D., and Farhat, C. 2008. Interpolation method for adapting reduced-order models and application to aeroelasticity. AIAA J. 46, 7, 1803–1813.Google ScholarCross Ref
2. Amsallem, D., and Farhat, C. 2011. An online method for interpolating linear parametric reduced-order models. SIAM J. on Scientific Computing 33, 5, 2169–2198. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. An, S. S., Kim, T., and James, D. L. 2008. Optimizing cubature for efficient integration of subspace deformations. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH Asia 2008) 27, 5, 165:1–165:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Anjyo, K., Lewis, J. P., and Pighin, F. 2014. Scattered data interpolation for computer graphics. In SIGGRAPH Courses, 27. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Barbič, J., and James, D. L. 2005. Real-time subspace integration for St. Venant-Kirchhoff deformable models. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2005) 24, 3, 982–990. Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Barbič, J., and Zhao, Y. 2011. Real-time large-deformation substructuring. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2011) 30, 4, 91:1–91:7. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Barbič, J., da Silva, M., and Popović, J. 2009. Deformable object animation using reduced optimal control. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2009) 28, 3. Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Barnhill, R., Dube, R., and Little, F. 1983. Properties of Shepards Surfaces. Rocky Mountain J. Math. 13, 365–382.Google ScholarCross Ref
9. Capell, S., Green, S., Curless, B., Duchamp, T., and Popović, Z. 2002. Interactive skeleton-driven dynamic deformations. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2002) 21, 3, 586–593. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Capell, S., Burkhart, M., Curless, B., Duchamp, T., and Popović, Z. 2005. Physically based rigging for deformable characters. In Symp. on Computer Animation (SCA), 301–310. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Carr, J. C., Beatson, R. K., Cherrie, J. B., Mitchell, T. J., Fright, W. R., McCallum, B. C., and Evans, T. R. 2001. Reconstruction and representation of 3d objects with radial basis functions. In Proc. of ACM SIGGRAPH 2001, 67–76. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Chen, D., and Plemmons, R. J. 2006. Nonnegativity constraints in numerical analysis. In Symp. on the Birth of Numerical Analysis.Google Scholar
13. Degroote, J., Vierendeels, J., and Willcox, K. 2010. Interpolation among reduced-order matrices to obtain parameterized models for design, optimization and probabilistic analysis. Int. J. for Numerical Methods in Fluids 63, 2, 207–230.Google Scholar
14. Feng, A., Casas, D., and Shapiro, A. 2015. Avatar reshaping and automatic rigging using a deformable model. In Proc. of the Motion in Games (MIG) Conf., 57–64. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Galoppo, N., Otaduy, M. A., Tekin, S., Gross, M., and Lin, M. C. 2007. Soft articulated characters with fast contact handling. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 26, 243–253.Google ScholarCross Ref
16. Galoppo, N., Otaduy, M. A., Moss, W., Sewall, J., Curtis, S., and Lin, M. C. 2009. Controlling deformable material with dynamic morph targets. In Proc. of the Symp. on Interactive 3D graphics and games (I3D), ACM, 39–47. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Gower, J. C., and Dijksterhuis, G. B. 2004. Procrustes problems, vol. 3. Oxford University Press Oxford.Google Scholar
18. Hahn, F., Martin, S., Thomaszewski, B., Sumner, R., Coros, S., and Gross, M. 2012. Rig-space physics. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2012) 31, 4, 72:1–72:8. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Hahn, F., Thomaszewski, B., Coros, S., Sumner, R., and Gross, M. 2013. Efficient simulation of secondary motion in rig-space. In Symp. on Computer Animation (SCA), 165–171. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Hahn, F., Thomaszewski, B., Coros, S., Sumner, R. W., Cole, F., Meyer, M., DeRose, T., and Gross, M. 2014. Subspace clothing simulation using adaptive bases. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2014) 33, 4, 105:1–105:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Harmon, D., and Zorin, D. 2013. Subspace integration with local deformations. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2013) 32, 4, 107:1–107:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Hauser, K. K., Shen, C., and O’Brien, J. F. 2003. Interactive deformation using modal analysis with constraints. In Proc. of Graphics Interface, 247–256.Google Scholar
23. Hildebrandt, K., Schulz, C., von Tycowicz, C., and Polthier, K. 2012. Interactive spacetime control of deformable objects. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2012) 31, 4, 71:1–71:8. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Huang, H., Yin, K., Zhao, L., Qi, Y., Yu, Y., and Tong, X. 2012. Detail-preserving controllable deformation from sparse examples. IEEE Trans. on Visualization and Computer Graphics 18, 8, 1215–1227. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Jacobson, A., Baran, I., Popović, J., and Sorkine, O. 2011. Bounded biharmonic weights for real-time deformation. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2011) 30, 4, 78:1–78:8. Google ScholarDigital Library
26. James, D. L., and Pai, D. K. 2002. DyRT: Dynamic Response Textures for Real Time Deformation Simulation With Graphics Hardware. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2002) 21, 3, 582–585. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Kim, T., and James, D. 2009. Skipping steps in deformable simulation with online model reduction. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH Asia 2009) 28, 5, 123:1–123:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Kim, T., and James, D. L. 2012. Physics-based character skinning using multidomain subspace deformations. IEEE Trans. on Visualization and Computer Graphics 18, 8, 1228–1240. Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Kim, J., and Pollard, N. S. 2011. Fast simulation of skeleton-driven deformable body characters. ACM Trans. on Graphics (TOG) 30, 5, 121. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Kry, P. G., James, D. L., and Pai, D. K. 2002. EigenSkin: Real Time Large Deformation Character Skinning in Hardware. In Symp. on Computer Animation (SCA), 153–160. Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Kurihara, T., and Miyata, N. 2004. Modeling deformable human hands from medical images. In Symp. on Computer Animation (SCA), 355–363. Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Lehoucq, R., Sorensen, D., and Yang, C. 1997. ARPACK Users’ Guide: Solution of large scale eigenvalue problems with implicitly restarted Arnoldi methods. Tech. rep., Comp. and Applied Mathematics, Rice Univ.Google Scholar
33. Lewis, J. P., Cordner, M., and Fong, N. 2000. Pose Space Deformations: A Unified Approach to Shape Interpolation and Skeleton-Driven Deformation. In Proc. of ACM SIGGRAPH 2000, 165–172. Google ScholarDigital Library
34. Liu, L., Yin, K., Wang, B., and Guo, B. 2013. Simulation and control of skeleton-driven soft body characters. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH Asia 2013) 32, 6, 215. Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Magnenat-Thalmann, N., Laperrire, R., and Thalmann, D. 1988. Joint-dependent local deformations for hand animation and object grasping. In Proc. of Graphics Interface. Google ScholarDigital Library
36. McAdams, A., Zhu, Y., Selle, A., Empey, M., Tamstorf, R., Teran, J., and Sifakis, E. 2011. Efficient elasticity for character skinning with contact and collisions. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2011) 30, 4, 37:1–37:11. Google ScholarDigital Library
37. Neumann, T., Varanasi, K., Wenger, S., Wacker, M., Magnor, M., and Theobalt, C. 2013. Sparse localized deformation components. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH Asia 2013) 32, 6, 179:1–179:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Pardiso, 2015. Parallel Direct Sparse Solver Interface, Pardiso project, http://www.pardiso-project.org and Intel MKL, http://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/intel-mkl.Google Scholar
39. Pons-Moll, G., Romero, J., Mahmood, N., and Black, M. J. 2015. Dyna: A model of dynamic human shape in motion. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2015) 34, 4, 120:1–120:14. Google ScholarDigital Library
40. Teng, Y., Otaduy, M. A., and Kim, T. 2014. Simulating articulated subspace self-contact. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2014) 33, 4, 106:1–106:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
41. Teng, Y., Meyer, M., DeRose, T., and Kim, T. 2015. Subspace condensation: Full space adaptivity for subspace deformations. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2015) 34, 4, 76:1–76:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
42. von Tycowicz, C., Schulz, C., Seidel, H.-P., and Hildebrandt, K. 2013. An efficient construction of reduced deformable objects. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH Asia 2013) 32, 6, 213. Google ScholarDigital Library
43. Wang, Y., Jacobson, A., Barbič, J., and Kavan, L. 2015. Linear subspace design for real-time shape deformation. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2015) 34, 4, 57:1–57:11. Google ScholarDigital Library
44. Xu, H., and Barbič, J. 2014. Signed distance fields for polygon soup meshes. In Proc. of Graphics Interface, 35–41. Google ScholarDigital Library
45. Xu, H., Li, Y., Chen, Y., and Barbič, J. 2015. Interactive material design using model reduction. ACM Trans. on Graphics (TOG) 34, 2, 18. Google ScholarDigital Library
46. Xu, H., Sin, F., Zhu, Y., and Barbič, J. 2015. Nonlinear material design using principal stretches. ACM Trans. on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2015) 34, 4, 75:1–75:11. Google ScholarDigital Library
47. Yang, Y., Xu, W., Guo, X., Zhou, K., and Guo, B. 2013. Boundary-aware multidomain subspace deformation. IEEE Trans. on Visualization and Computer Graphics 19, 10, 1633–1645.Google ScholarCross Ref