“Learning behavior styles with inverse reinforcement learning” by Lee and Popovic
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Learning behavior styles with inverse reinforcement learning
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
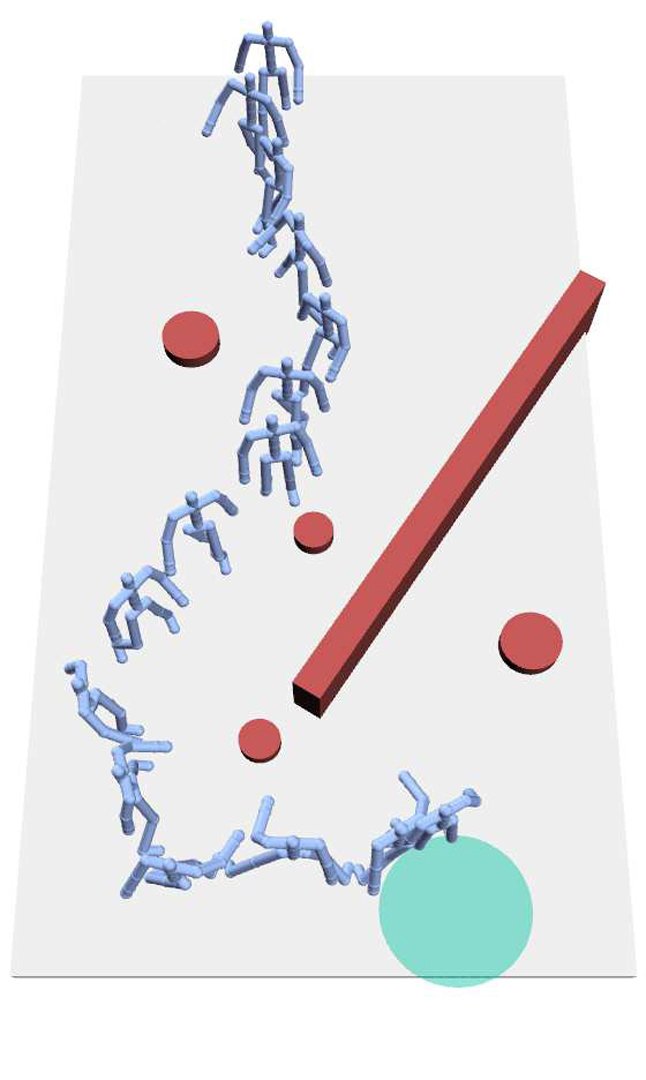
We present a method for inferring the behavior styles of character controllers from a small set of examples. We show that a rich set of behavior variations can be captured by determining the appropriate reward function in the reinforcement learning framework, and show that the discovered reward function can be applied to different environments and scenarios. We also introduce a new algorithm to recover the unknown reward function that improves over the original apprenticeship learning algorithm. We show that the reward function representing a behavior style can be applied to a variety of different tasks, while still preserving the key features of the style present in the given examples. We describe an adaptive process where an author can, with just a few additional examples, refine the behavior so that it has better generalization properties.
References:
1. Abbeel, P., and Ng, A. Y. 2004. Apprenticeship learning via inverse reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Machine Learning, ACM Press. Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Abbeel, P., Dolgov, D., Ng, A., and Thrun, S. 2008. Apprenticeship learning for motion planning, with application to parking lot navigation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IEEE.Google Scholar
3. Barber, C. B., Dobkin, D. P., and Huhdanpaa, H. 1995. The quickhull algorithm for convex hulls. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 22, 469–483. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Beaudoin, P., Coros, S., van de Panne, M., and Poulin, P. 2008. Motion-motif graphs. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGGRAPH / Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, 117–126. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Bellman, R. E. 1957. Dynamic Programming. Princeton University Press. Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Brand, M., and Hertzmann, A. 2000. Style machines. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 2000, ACM Press / ACM SIGGRAPH, Computer Graphics Proceedings, Annual Conference Series, ACM, 183–192. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Coates, A., Abbeel, P., and Ng, A. Y. 2009. Apprenticeship learning for helicopter control. Communications of the ACM 52, 7, 97–105. Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Funge, J., Tu, X., and Terzopoulos, D. 1999. Cognitive modeling: knowledge, reasoning and planning for intelligent characters. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 99, ACM Press / ACM SIGGRAPH, Computer Graphics Proceedings, Annual Conference Series, ACM, 29–38. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Grochow, K., Martin, S. L., Hertzmann, A., and Popović, Z. 2004. Style-based inverse kinematics. ACM Transactions on Graphics 23, 3, 522–531. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Heck, R., and Gleicher, M. 2007. Parametric motion graphs. In Proceedings of the 2007 symposium on Interactive 3D graphics and games, ACM, 129–136. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Hsu, E., Pulli, K., and Popović, J. 2005. Style translation for human motion. ACM Transactions on Graphics 24, 3, 1082–1089. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Kovar, L., Gleicher, M., and Pighin, F. 2002. Motion graphs. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 2002, ACM Press / ACM SIGGRAPH, Computer Graphics Proceedings, Annual Conference Series, ACM, 473–482. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Lau, M., and Kuffner, J. J. 2006. Precomputed search trees: Planning for interactive goal-driven animation. In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM SIGGRAPH / Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, Eurographics Association, 299–308. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Lee, J., and Lee, K. 2006. Precomputing avatar behavior from human motion data. Graphics Models 68, 2, 158–174. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Lee, K. H., Choi, M. G., Hong, Q., and Lee, J. 2007. Group behavior from video: a data-driven approach to crowd simulation. In Proceedings of the 2007 ACM SIGGRAPH / Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, Eurographics Association, 109–118. Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Lee, Y., Lee, S., and Popović, Z. 2009. Compact character controllers. ACM Transaction on Graphics 28, 5, 169:1–169:8. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Liu, K., Hertzmann, A., and Popović, Z. 2005. Learning physics-based motion style with nonlinear inverse optimization. ACM Transactions on Graphics 24, 3 (Aug.), 1071–1081. Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Lo, W., and Zwicker, M. 2008. Real-time planning for parameterized human motion. In Proceedings of the 2008 Eurographics / ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Computer Animation, Eurographics Association, 29–38. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. McCann, J., and Pollard, N. 2007. Responsive characters from motion fragments. ACM Transactions on Graphics 26, 3 (July), 6:1–6:7. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Ng, A. Y., and Russell, S. 2000. Algorithms for inverse reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Machine Learning, Morgan Kaufmann, 663–670. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Reitsma, P. S. A., and Pollard, N. S. 2004. Evaluating motion graphs for character navigation. In Proceedings of the 2004 ACM SIGGRAPH / Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, Eurographics Association, 89–98. Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Russell, S. 1998. Learning agents for uncertain environments (extended abstract). In Proceedings of the Eleventh Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory, ACM Press, 101–103. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Shin, H. J., and Oh, H. S. 2006. Fat graphs: constructing an interactive character with continuous controls. In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM SIGGRAPH / Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, Eurographics Association, 291–298. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Sung, M., Gleicher, M., and Chenney, S. 2004. Scalable behaviors for crowd simulation. Computer Graphics Forum 23, 3, 519–528.Google ScholarCross Ref
25. Syed, U., Bowling, M., and Schapire, R. E. 2008. Apprenticeship learning using linear programming. In Proceedings of the 25th international conference on Machine learning, ACM, 1032–1039. Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Treuille, A., Lee, Y., and Popović, Z. 2007. Near-optimal character animation with continuous control. ACM Transactions on Graphics 26, 3 (July), 7:1–7:7. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Ziebart, B. D., Maas, A., Bagnell, J. A., and Dey, A. K. 2008. Maximum entropy inverse reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 23rd national conference on Artificial intelligence, AAAI Press, 1433–1438. Google ScholarDigital Library