“Force reflecting porous media with dynamic elasticity change” by Kuroda, Ashida, Imura, Kagiyama and Oshiro
Conference:
Type(s):
Entry Number: 82
Title:
- Force reflecting porous media with dynamic elasticity change
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
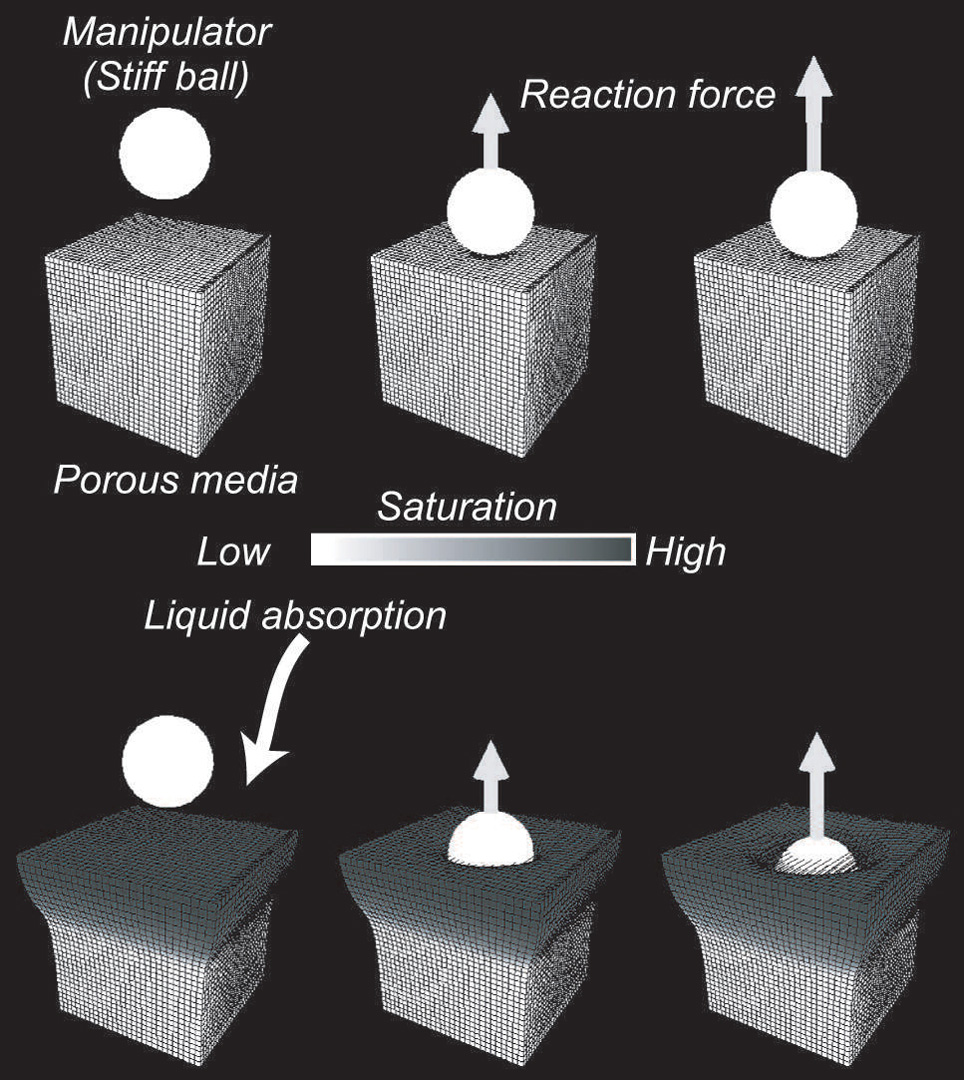
Liquid absorption affects the behavior of objects. Rain absorbed in the barrage can weaken its structure and cause the dam failure. A wet sponge ball bounces differently from a dry one. Porous media is a material that has internal pore space and is able to absorb liquid (e.g. a sponge or soil). Liquid absorption changes not only geometrical properties, e.g. volume, but also mechanical properties, e.g. elasticity. The aim of this study is to physically model the structural change of a porous media due to liquid absorption. Previous studies have focused on liquid flow inside the media[Lenaerts et al. 2008]. In contrast, this paper proposes a porous model that is able to simulate elastic change in a real sponge.
References:
Lenaerts, T., Adams, B., and Dutré, P. 2008. Porous flow in particle-based fluid simulations. ACM Transactions on Graphics 27, 491–498. Google ScholarDigital Library
Terzaghi, K. 1936. The shearing resistance of saturated soils and the angle between the planes of shear. First international conference on soil Mechanics, Vol.1, 54–59.Google Scholar