“Estimating Lighting Environments Based on Shadow Area in an Omni-Directional Image” by Baba, Haruta and Hiura
Conference:
Type(s):
Entry Number: 64
Title:
- Estimating Lighting Environments Based on Shadow Area in an Omni-Directional Image
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
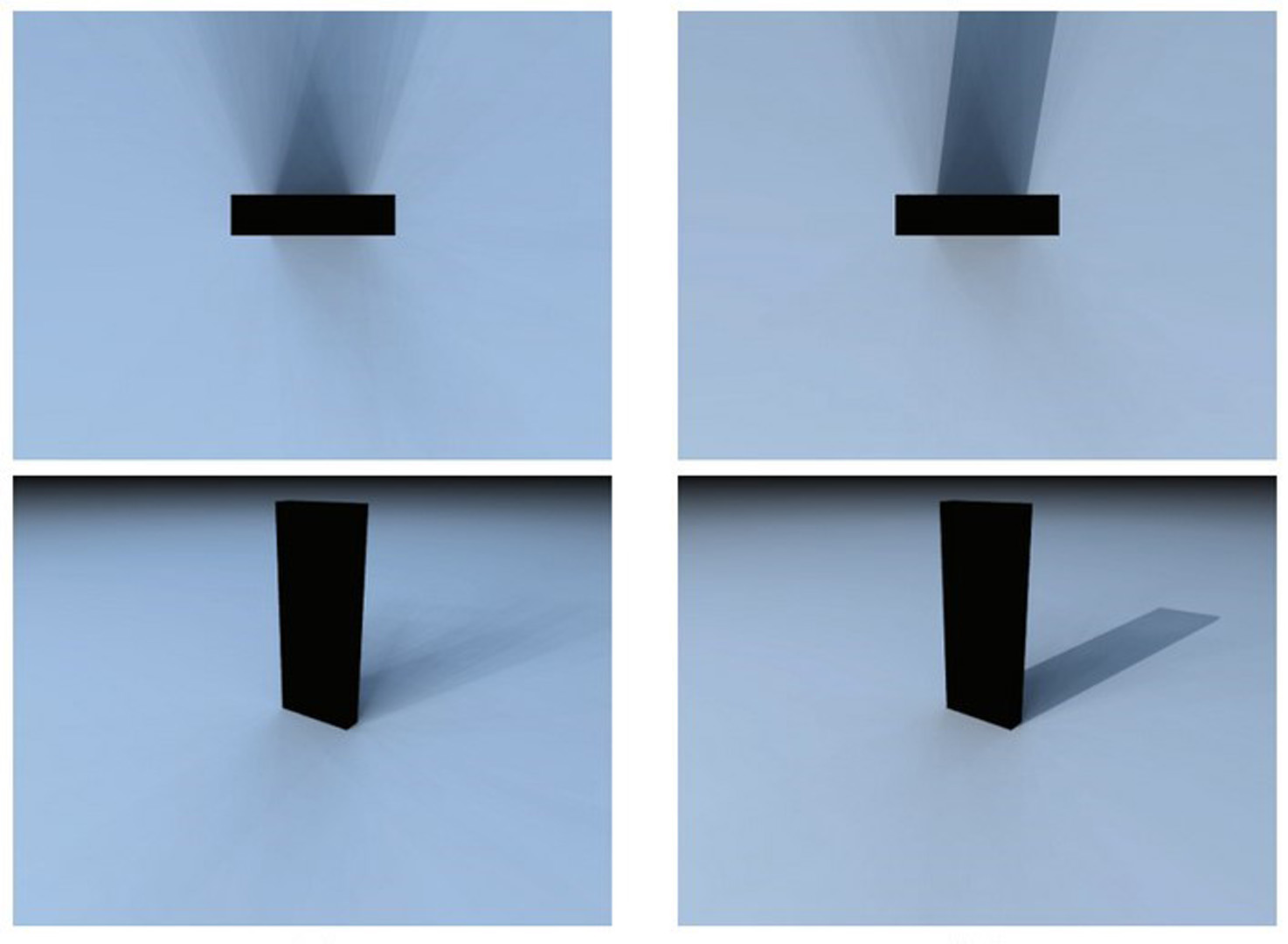
Abstract:
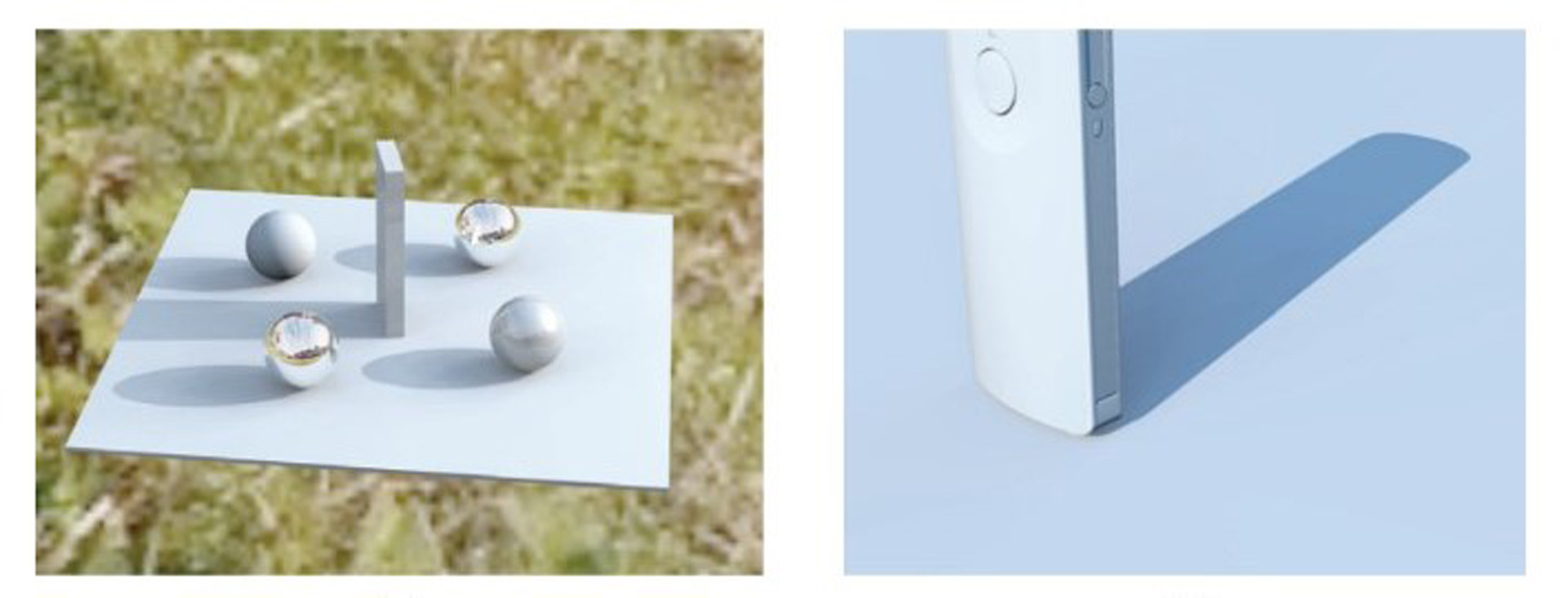
To create realistic CG images, the information about the lighting is very important. There are two ways to estimate the information of the light source. One is a direct measurement method using images captured with a fish-eye lens or a spherical mirror[Debevec 1998], and the other is an indirect measurement method to estimate positions and intensities of the light sources from the shadow information of objects[Sato et al. 2003]. In the direct measurement method, by concerning pixels of the captured image as light sources having corresponding intensities, it is possible to estimate the lighting environment densely. However, for a high-intensity light source like the sun, the dynamic range of the camera is insufficient, and the radiant intensity of the light source cannot be accurately estimated. So, we propose a method that combines a direct measurement technique and an indirect measurement method. In our proposed method, the light source information of the high-intensity area in the captured image is estimated by indirect measurement method. In the experiments using real images, even for outdoor scenes that contain the high-intensity light source like the sun, the measurement of the light source environment could be performed by the proposed method. Also, it was confirmed that images including realistic shadows equivalent to real images could be created.