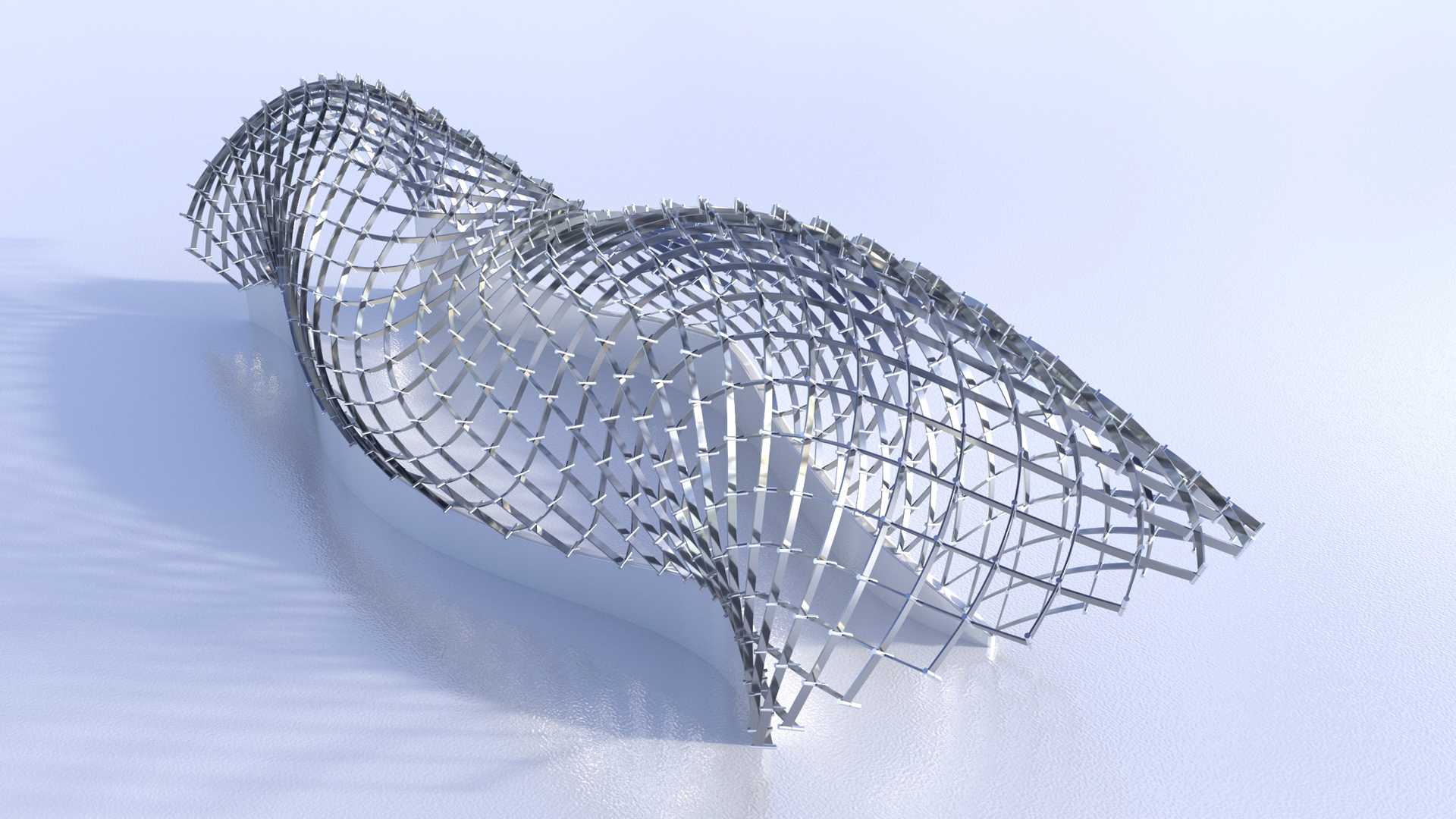
“Deployable strip structures” by Liu, Pellis, Chiang, Rist, Wallner, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Deployable strip structures
Session/Category Title:
- Surfaces, Strips, Lights
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
We introduce the new concept of C-mesh to capture kinetic structures that can be deployed from a collapsed state. Quadrilateral C-meshes enjoy rich geometry and surprising relations with differential geometry: A structure that collapses onto a flat and straight strip corresponds to a Chebyshev net of curves on a surface of constant Gaussian curvature, while structures collapsing onto a circular strip follow surfaces which enjoy the linear-Weingarten property. Interestingly, allowing more general collapses actually leads to a smaller class of shapes. Hexagonal C-meshes have more degrees of freedom, but a local analysis suggests that there is no such direct relation to smooth surfaces. Besides theory, this paper provides tools for exploring the shape space of C-meshes and for their design. We also present an application for freeform architectural skins, namely paneling with spherical panels of constant radius, which is an important fabrication-related constraint.
References:
1. Changyeob Baek, Andrew O. Sageman-Furnas, Mohammad K. Jawed, and Pedro M. Reis. 2018. Form finding in elastic gridshells. PNAS 115, 1 (2018), 75–80.
2. Miklós Bergou, Basile Audoly, Etienne Vouga, Max Wardetzky, and Eitan Grinspun. 2010. Discrete viscous threads. ACM Trans. Graphics 29, 4 (2010), 116:1–10.
3. Miklós Bergou, Max Wardetzky, Stephen Robinson, Basile Audoly, and Eitan Grinspun. 2008. Discrete elastic rods. ACM Trans. Graphics) 27, 3 (2008), 63:1–12.
4. Alexander Bobenko and Yuri Suris. 2008. Discrete differential geometry: Integrable Structure. American Math. Soc.
5. David Bommes, Henrik Zimmer, and Leif Kobbelt. 2009. Mixed-integer quadrangulation. ACM Trans. Graphics 28, 3 (2009), 77:1–10.
6. Raphaël Charrondière, Florence Bertails-Descoubes, Sébastien Neukirch, and Victor Romero. 2020. Numerical modeling of inextensible elastic ribbons with curvature-based elements. Computer Methods in Applied Mech. & Engrg. 364, Article 112922 (2020), 24 pages.
7. Tian Chen, Julian Panetta, Max Schnaubelt, and Mark Pauly. 2021. Bistable auxetic surface structures. ACM Trans. Graph 40, 4 (2021), 39:1–9.
8. Bernardino D’Amico, Abdy Kermani, Hexin Zhang, Alberto Pugnale, Sofia Colabella, and Sergio Pone. 2015. Timber gridshells: Numerical simulation, design and construction of a full scale structure. Structures 3 (2015), 227–235.
9. Crispin Deul, Tassilo Kugelstadt, Marcel Weiler, and Jan Bender. 2018. Direct position-based solver for stiff rods. Computer Graphics Forum 37, 6 (2018), 313–324.
10. Manfredo do Carmo. 1976. Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces. Prentice-Hall.
11. Olly Duncan, Todd Shepherd, Charlotte Moroney, Leon Foster, Praburaj Venkatraman, Keith Winwood, Tom Allen, and Andrew Alderson. 2018. Review of Auxetic Materials for Sports Applications: Expanding Options in Comfort and Protection. Applied Sciences 8, 6, Article 941 (2018), 33 pages.
12. Roger Fosdick and Eliot Fried (Eds.). 2016. The mechanics of ribbons and Möbius bands. Springer.
13. Akash Garg, Andrew O. Sageman-Furnas, Bailin Deng, Yonghao Yue, Eitan Grinspun, Mark Pauly, and Max Wardetzky. 2014. Wire mesh design. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (2014), 66:1–12.
14. Christian Hafner and Bernd Bickel. 2021. The design space of plane elastic curves. ACM Trans. Graph. 40, 4 (2021), 126:1–20.
15. Charles Hoberman. 1990. Reversibly expandable doubly-curved truss structure. U.S. Patent 4942400.
16. Yaoye Hong, Yinding Chi, Shuang Wu, Yanbin Li, Yong Zhu, and Jie Yin. 2022. Boundary curvature guided programmable shape-morphing kirigami sheets. Nature communications 13, 1 (2022), 530.
17. M. Khalid Jawed, Alyssa Novelia, and Oliver M O’Reilly. 2018. A Primer on the Kinematics of Discrete Elastic Rods. Springer.
18. Caigui Jiang, Chengcheng Tang, Amir Vaxman, Peter Wonka, and Helmut Pottmann. 2015. Polyhedral patterns. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6 (2015), 172:1–12.
19. Leif Kobbelt, Swen Campagna, Jens Vorsatz, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 1998. Interactive multi-resolution modeling on arbitrary meshes. In Proc. SIGGRAPH. 105–114.
20. Mina Konaković-Luković, Julian Panetta, Keenan Crane, and Mark Pauly. 2018. Rapid deployment of curved surfaces via programmable auxetics. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4 (2018), 106:1–13.
21. Luigi Malomo, Jesús Pérez, Emmanuel Iarussi, Nico Pietroni, Eder Miguel, Paolo Cignoni, and Bernd Bickel. 2018. FlexMaps: Computational design of flat flexible shells for shaping 3D objects. ACM Tran. Graph. 37, 6 (2018), 214:1–14.
22. Saurabh Mhatre, Elisa Boatti, David Melancon, Ahmad Zareei, Maxime Dupont, Martin Bechthold, and Katia Bertoldi. 2021. Deployable structures based on buckling of curved beams upon a rotational input. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, Article 2170261 (2021), 7 pages.
23. David Mount and Sunil Arya. 2010. ANN Library (Version 1.1.2). http://www.cs.umd.edu/~mount/ANN/
24. Jorge Nocedal and Stephen Wright. 2006. Numerical Optimization (2nd ed.). Springer.
25. Joseph Reuben Harry Otter, Alfred Carlo Cassell, and Roger Edwin Hobbs. 1966. Dynamic relaxation. Proc. Institution of Civil Engineers 35, 4 (1966), 633–656.
26. Eda Özdemir, Laura Kiesewetter, Karen Antorveza, Tiffany Cheng, Samuel Leder, Dylan Wood, and Achim Menges. 2022. Towards Self-shaping Metamaterial Shells:. In Proceedings of the 2021 DigitalFUTURES. Springer, 275–285.
27. Dinesh K Pai. 2002. Strands: interactive simulation of thin solids using Cosserat models. Computer Graphics Forum 21, 3 (2002), 347–352.
28. Julian Panetta, Florin Isvoranu, Tian Chen, Emmanuel Siéfert, Benoît Roman, and Mark Pauly. 2021. Computational inverse design of surface-based inflatables. ACM Trans. Graph. 40, 4 (2021), 40:1–14.
29. Julian Panetta, Mina Konaković-Luković, Florin Isvoranu, Etienne Bouleau, and Mark Pauly. 2019. X-Shells: A New Class of Deployable Beam Structures. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 4 (2019), 83:1–15.
30. Davide Pellis, Martin Kilian, Helmut Pottmann, and Mark Pauly. 2021. Computational design of Weingarten surfaces. ACM Trans. Graph. 40, 4 (2021), 114:1–11.
31. Davide Pellis, Hui Wang, Martin Kilian, Florian Rist, Helmut Pottmann, and Christian Müller. 2020. Principal symmetric meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 4 (2020), 127:1–17.
32. Jesús Pérez, Bernhard Thomaszewski, Stelian Coros, Bernd Bickel, José A. Canabal, Robert Sumner, and Miguel A. Otaduy. 2015. Design and fabrication of flexible rod meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4 (2015), 138:1–12.
33. Stefan Pillwein, Kurt Leimer, Michael Birsak, and Przemyslaw Musialski. 2020. On Elastic Geodesic Grids and Their Planar to Spatial Deployment. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 4 (2020), 125:1–12.
34. Stefan Pillwein and Przemyslaw Musialski. 2021. Generalized Deployable Elastic Geodesic Grids. ACM Trans. Graph. 40, 6 (2021), 271:1–15.
35. Kacper Pluta, Michal Edelstein, Amir Vaxman, and Mirela Ben-Chen. 2021. PH-CPF: Planar Hexagonal Meshing Using Coordinate Power Fields. ACM Trans. Graph. 40, 4 (2021), 156:1–19.
36. Yingying Ren, Uday Kusupati, Julian Panetta, Florin Isvoranu, Davide Pellis, Tian Chen, and Mark Pauly. 2022. Umbrella meshes: elastic mechanisms for freeform shape deployment. ACM Trans. Graph. 41, 4 (2022), 152:1–15.
37. Yingying Ren, Julian Panetta, Tian Chen, Florin Isvoranu, Samuel Poincloux, Christopher Brandt, Alison Martin, and Mark Pauly. 2021. 3D weaving with curved ribbons. ACM Trans. Graph. 40, 4 (2021), 127:1–15.
38. Andrew O. Sageman-Furnas, Albert Chern, Mirela Ben-Chen, and Amir Vaxman. 2019. Chebyshev nets from commuting PolyVector fields. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 6 (2019), 172:1–16.
39. Robert Sauer. 1970. Differenzengeometrie. Springer.
40. Jonas Schikore, Eike Schling, Thomas Oberbichler, and Anna Bauer. 2021. Kinetics and design of semi-compliant grid mechanisms. In Adv. in Architectural Geometry 2020. Presses des Ponts, 108–129.
41. Eike Schling. 2018. Repetitive Structures – Design and construction of curved support structures with repetitive parameters. Ph. D. Dissertation. TU Munich.
42. Eike Schling and Jonas Schikore. 2022. Morphology of kinetic asymptotic grids. In Towards Radical Regeneration. Springer, 374–393. Proc. Design Modelling Symposium.
43. Eike Schling, Hui Wang, Sebastian Hoyer, and Helmut Pottmann. 2022. Designing asymptotic geodesic hybrid gridshells. Computer-Aided Design 152, Article 103378 (2022), 17 pages.
44. Toby L Shearman and Shankar C Venkataramani. 2021. Distributed branch points and the shape of elastic surfaces with constant negative curvature. J. Nonlinear Science 31, 1, Article 13 (2021), 60 pages.
45. Carlota Soler, Tobias Martin, and Olga Sorkine-Hornung. 2018. Cosserat rods with projective dynamics. Computer Graphics Forum 37, 8 (2018), 137–147.
46. Chengcheng Tang, Xiang Sun, Alexandra Gomes, Johannes Wallner, and Helmut Pottmann. 2014. Form-finding with polyhedral meshes made simple. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (2014), 70:1–9.
47. Xavier Tellier. 2022. Bundling elastic gridshells with alignable nets. Part I: Analytical approach. Part II: Form-finding. Automation in Construction 141 (2022). Articles 104291, 104292, 19+13pp..
48. Xavier Tellier, Cyril Douthe, Laurent Hauswirth, and Olivier Baverel. 2020. Caravel meshes: A new geometrical strategy to rationalize curved envelopes. Structures 28 (2020), 1210–1228.
49. Nobuyuki Umetani, Ryan Schmidt, and Jos Stam. 2015. Position-based elastic rods. In Proc. SCA’14. Eurographics Association, 21–30.
50. Josh Vekhter, Jiacheng Zhuo, Luisa F. Gil Fandino, Qixing Huang, and Etienne Vouga. 2019. Weaving geodesic foliations. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 4 (2019), 34:1–12.
51. Walter Wunderlich. 1951. Zur Differenzengeometrie der Flächen konstanter negativer Krümmung. Sitzungsber. Österr. Ak. Wiss. II 160 (1951), 39–77.
52. Walter Wunderlich. 1973. Drehsymmetrische Gleichgewichtsformen von Rhomben- und Sechsecknetzen. Zeitschrift Angew. Math. Mechanik 53 (1973), 593–600.