“Cache-Friendly Micro-Jittered Sampling”
Conference:
Type(s):
Entry Number: 36
Title:
- Cache-Friendly Micro-Jittered Sampling
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
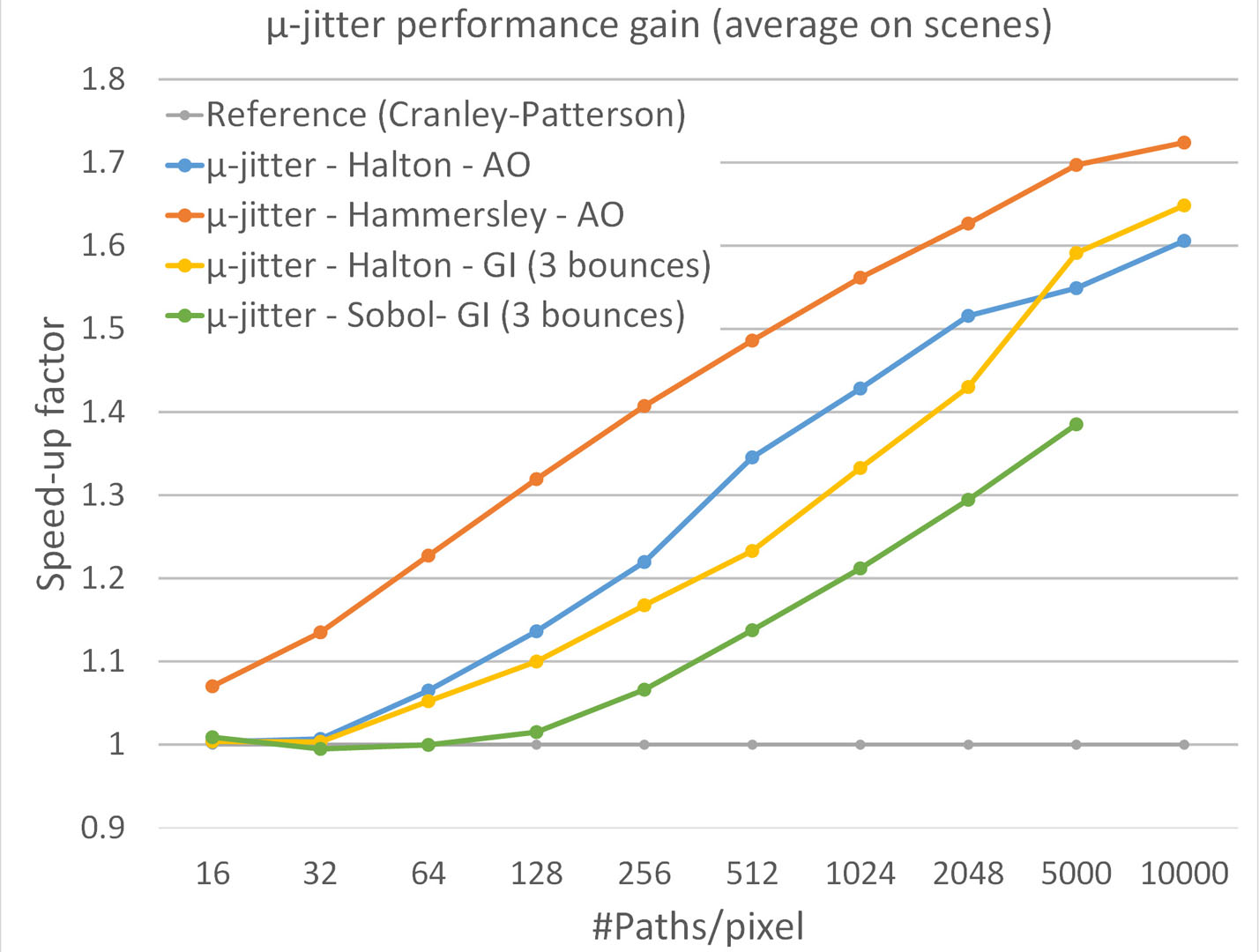
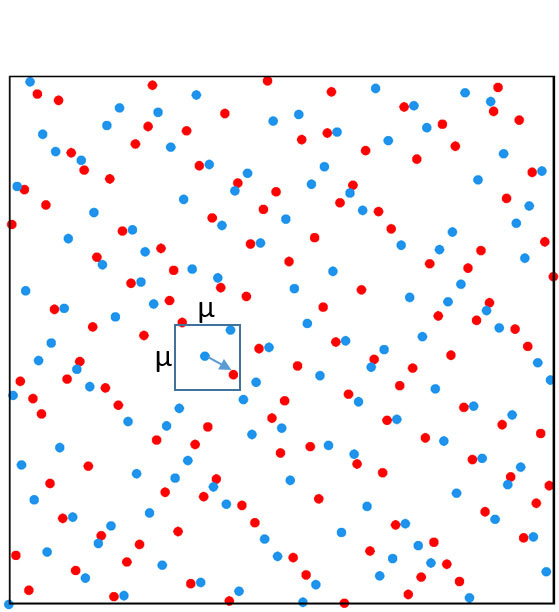
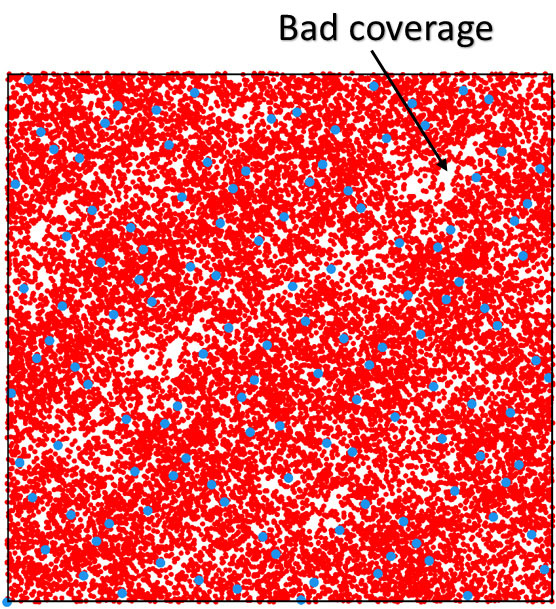
Monte-Carlo integration techniques for global illumination are popular on GPUs thanks to their massive parallel architecture, but efficient implementation remains challenging. The use of randomly decorrelated low-discrepancy sequences in the path-tracing algorithm allows faster visual convergence. However, the parallel tracing of incoherent rays often results in poor memory cache utilization, reducing the ray bandwidth efficiency. Interleaved sampling [Keller et al. 2001] partially solves this problem, by using a small set of distributions split in coherent ray-tracing passes, but the solution is prone to structured noise. On the other hand, ray-reordering methods [Pharr et al. 1997] group stochastic rays into coherent ray packets but their implementation add an additional sorting cost on the GPU [Moon et al. 2010] [Garanzha and Loop 2010].
References:
Garanzha, K., and Loop, C. 2010. Fast ray sorting and breadth-first packet traversal for gpu ray tracing. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 29, Wiley Online Library, 289298.Google Scholar
Keller, A., Keller, E., and Heidrich, W. 2001. Interleaved sampling. In Rendering Techniques 2001 (Proc. 12th Eurographics Workshop on Rendering, Springer, 269–276. Google ScholarDigital Library
Kollig, T., and Keller, A. 2002. Efficient multidimensional sampling. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 21, Wiley Online Library, 557–563.Google Scholar
Moon, B., Byun, Y., Kim, T.-J., Claudio, P., Kim, H.-S., Ban, Y.-J., Nam, S. W., and Yoon, S.-E. 2010. Cache-oblivious ray reordering. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 3 (July), 28:1–28:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
Pharr, M., Kolb, C., Gershbein, R., and Hanrahan, P. 1997. Rendering complex scenes with memory-coherent ray tracing. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., New York, NY, USA, SIGGRAPH ’97, 101–108. Google ScholarDigital Library
Ramamoorthi, R., Anderson, J., Meyer, M., and Nowrouzezahrai, D. 2012. A theory of monte-carlo visibility sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 5 (Sept.), 121:1–121:16.
Keyword(s):
Acknowledgements:
We would like to thank Gael Sourimant for its implementation and ̈ experimentations of the micro-jittering method in a SSAO context. We also thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and feedback.
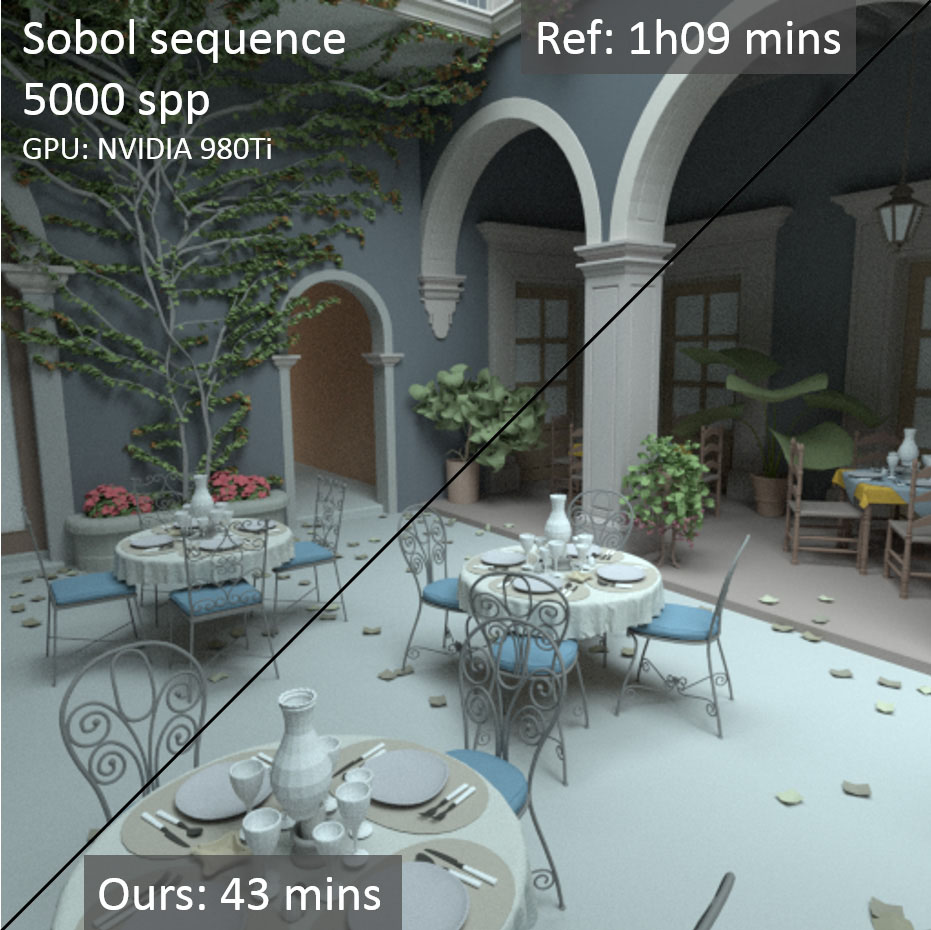
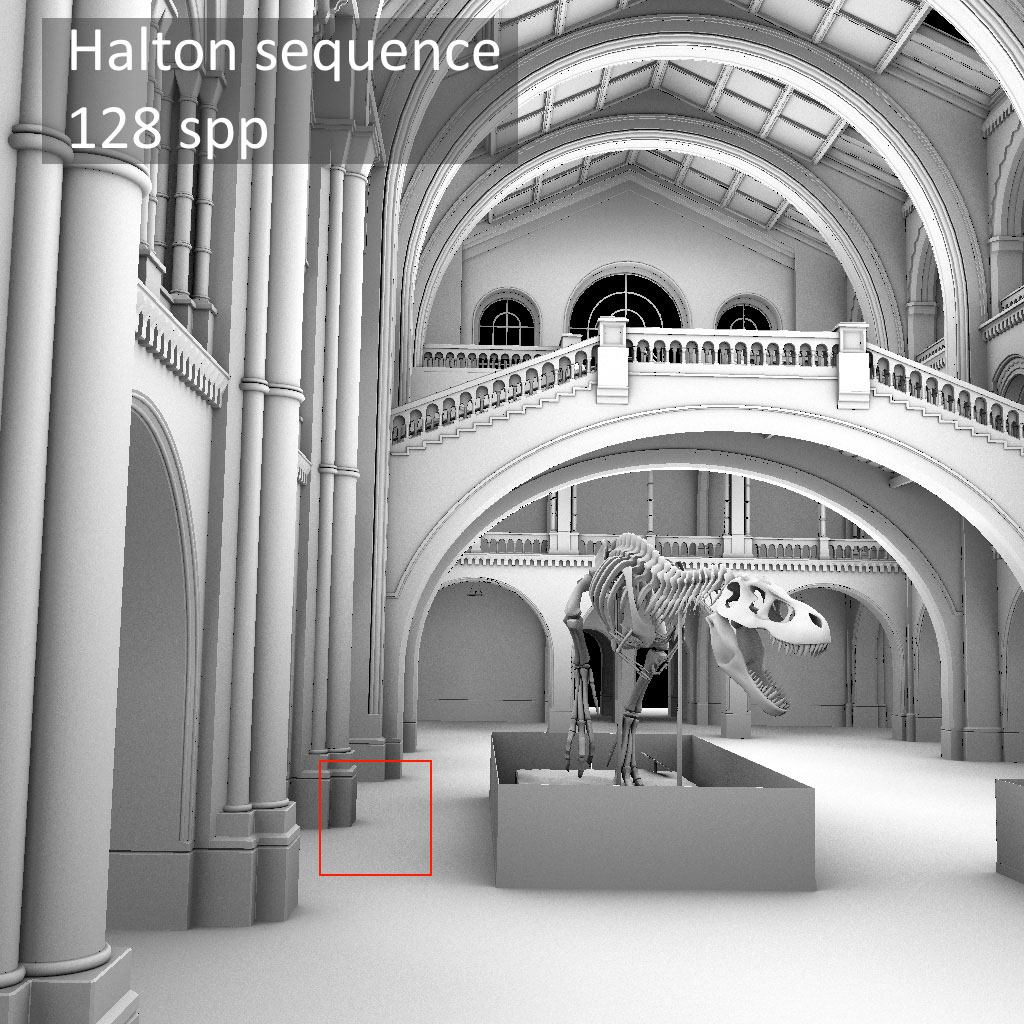
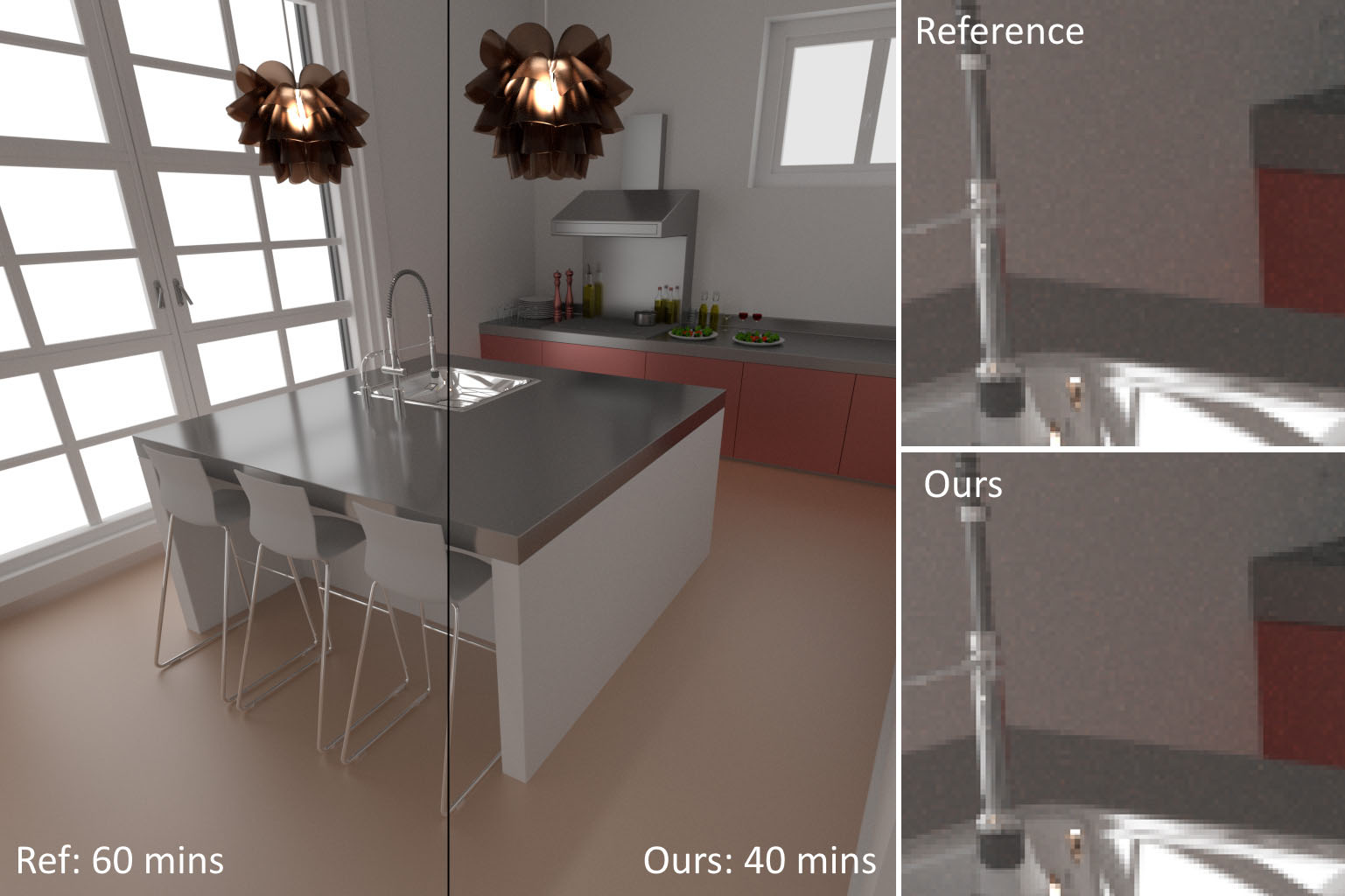
Scene credits: the San-Miguel scene in teaser-left was modeled by Guillermo M. Leal Llaguno. The London NH museum in mid- dle was modeled by Alvaro Luna Bautista and Joel Andersdon. The interior 3D model from figure 3 comes from Chocofur store: store.chocofur.com.