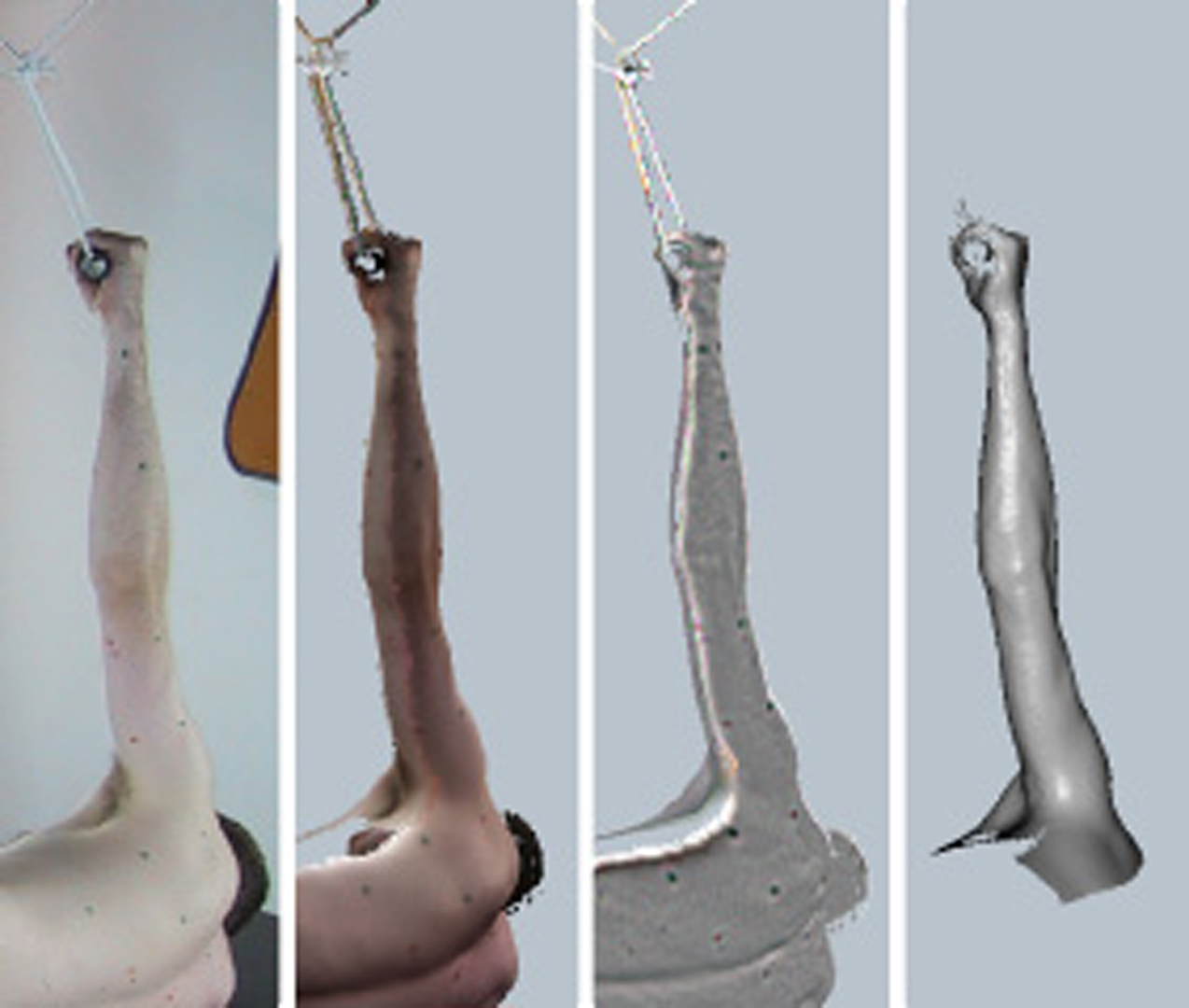
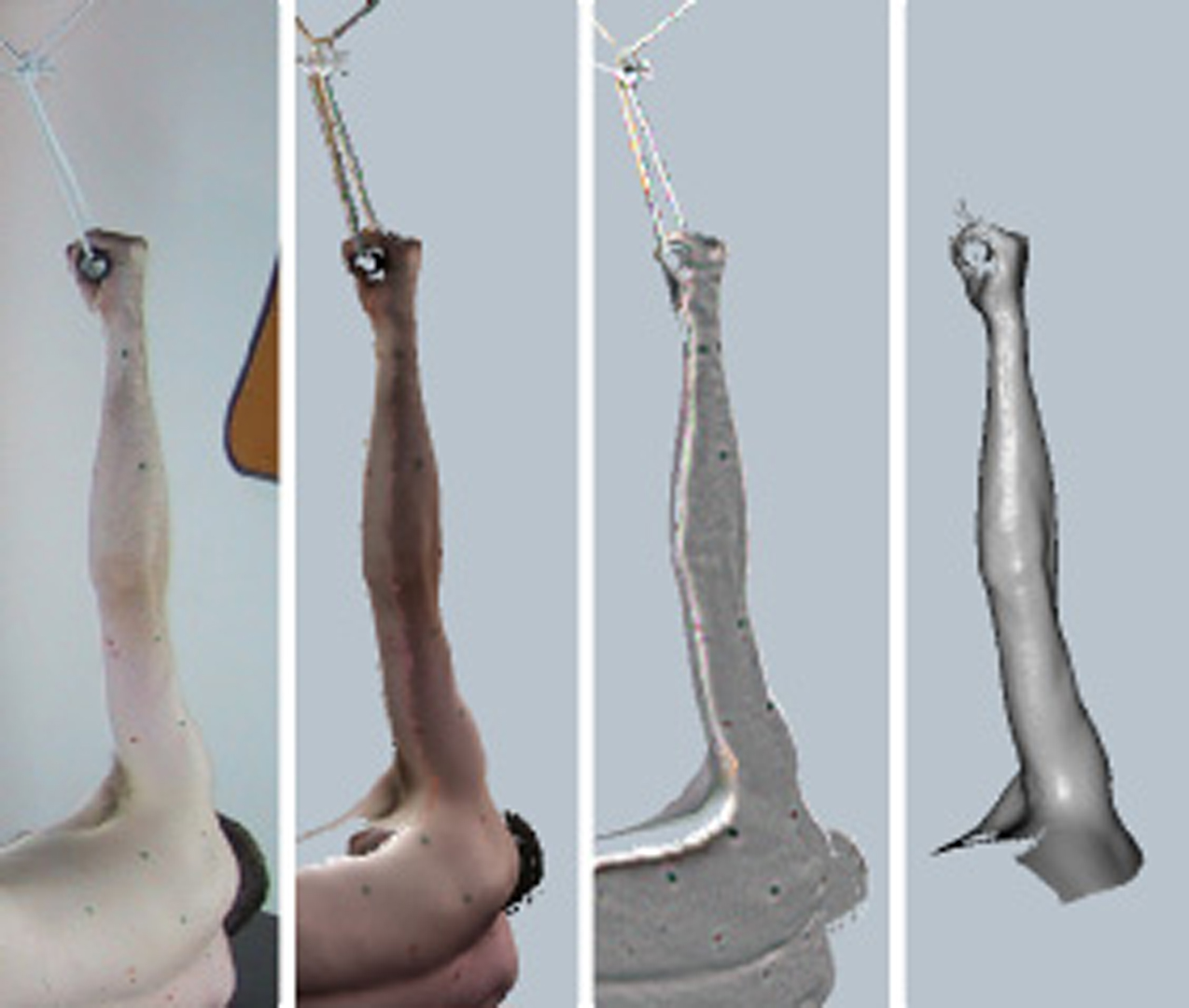
“Articulated body deformation from range scan data” by Allen, Curless and Popovic
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Articulated body deformation from range scan data
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
This paper presents an example-based method for calculating skeleton-driven body deformations. Our example data consists of range scans of a human body in a variety of poses. Using markers captured during range scanning, we construct a kinematic skeleton and identify the pose of each scan. We then construct a mutually consistent parameterization of all the scans using a posable subdivision surface template. The detail deformations are represented as displacements from this surface, and holes are filled smoothly within the displacement maps. Finally, we combine the range scans using k-nearest neighbor interpolation in pose space. We demonstrate results for a human upper body with controllable pose, kinematics, and underlying surface shape.
References:
1. AUBEL, A., AND THALMANN, D. 2001. Interactive modeling of the human musculature. In Proc. of Computer Animation 2001.]]Google Scholar
2. BLANZ, V., AND VETTER, T. 1999. A morphable model for the synthesis of 3D faces. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 99, Addison Wesley, New York, A. Rockwood, Ed., Annual Conference Series, 187-194.]] Google Scholar
3. BUEHLER, C., BOSSE, M., MCMILLAN, L., GORTLER, S. J., AND COHEN, M. F. 2001. Unstructured lumigraph rendering. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 2001, ACM Press / ACM SIGGRAPH, E. Fiume, Ed., Annual Conference Series, ACM, 425-432.]] Google Scholar
4. CATMULL, E., AND CLARK, J. 1978. Recursively generated B-spline surfaces on arbitrary topological meshes. Computer-Aided Design 10 (Sept.), 350-355.]]Google Scholar
5. CHADWICK, J. E., HAUMANN, D. R., AND PARENT, R. E. 1989. Layered construction for deformable animated characters. Computer Graphics (Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 89) 23, 3, 243-252.]] Google Scholar
6. CURLESS, B., AND LEVOY, M. 1995. Better optical triangulation through spacetime analysis. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 987-994.]] Google Scholar
7. CURLESS, B., AND LEVOY, M. 1996. A volumetric method for building complex models from range images. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 96, ACM Press / ACM SIGGRAPH / Addison Wesley Longman, K. Akeley, Ed., Annual Conference Series, ACM, 303-312.]] Google Scholar
8. GILL, P. E., MURRAY, W., AND WRIGHT, M. H. 1989. Practical Optimization. Academic Press.]]Google Scholar
9. GOLD, S., AND RANGARAJAN, A. 1996. A graduated assignment algorithm for graph matching. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 18, 4, 377-388.]] Google Scholar
10. GOWITZKE, B. A., AND MILNER, M. 1988. Scientific Bases of Human Movement, third ed. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD.]]Google Scholar
11. GUENTER, B., GRIMM, C., WOOD, D., MALVAR, H., AND PIGHIN, F. 1998. Making faces. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 98, Addison Wesley, M. Cohen, Ed., Annual Conference Series, ACM, 55-66.]] Google Scholar
12. HERDA, L., FUA, P., PLÄNKERS, R., BOULIC, R., AND THALMANN, D. 2001. Using skeleton-based tracking to increase the reliability of optical motion capture. Human Movement Science Journal 20, 313-341.]]Google Scholar
13. KRISHNAMURTHY, V., AND LEVOY, M. 1996. Fitting smooth surfaces to dense polygon meshes. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 96, Addison Wesley, H. Rushmeier, Ed., Annual Conference Series, ACM, 313-324.]] Google Scholar
14. LEE, A., MORETON, H., AND HOPPE, H. 2000. Displaced subdivision surfaces. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 2000, ACM Press / ACM SIGGRAPH / Addison Wesley Longman, K. Akeley, Ed., ACM, 85-94.]] Google Scholar
15. LEWIS, J. P., CORDNER, M., AND FONG, N. 2000. Pose space deformations: A unified approach to shape interpolation and skeleton-driven deformation. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 2000, ACM Press / ACM SIGGRAPH / Addison Wesley Longman, K. Akeley, Ed., Annual Conference Series, ACM, 165-172.]] Google Scholar
16. LUTTGENS, K., AND WELLS, K. F. 1982. Kinesiology: scientific basis of human motion, seventh ed. CBS College Publishing, New York, NY.]]Google Scholar
17. MAGNENAT-THALMANN, N., LAPERRIERE, R., AND THALMANN, D. 1988. Joint-dependent local deformations for hand animation and object grasping. In Proc. Graphics Interface, 26-33.]] Google Scholar
18. NG-THOW-HING, V. 1999. Physically based anatomic modeling for construction of musculoskeletal systems. In Proceedings of the 1999 SIGGRAPH annual conference: Conference abstracts and applications, ACM Press, New York, NY 10036, USA, Computer Graphics, ACM, 264-264.]] Google Scholar
19. PIGHIN, F., HECKER, J., LISCHINSKI, D., SZELISKI, R., AND SALESIN, D. H. 1998. Synthesizing realistic facial expressions from photographs. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 98, Addison Wesley, M. Cohen, Ed., Annual Conference Series, ACM, 75-84.]] Google Scholar
20. PRAUN, E., SWELDENS, W., AND SCHRÖDER, P. 2001. Consistent mesh parameterizations. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 2001, ACM Press / ACM SIGGRAPH, E. Fiume, Ed., Annual Conference Series, ACM, 179-184.]] Google Scholar
21. ROSE, C., COHEN, M. F., AND BODENHEIMER, B. 1998. Verbs and adverbs: Multidimensional motion interpolation. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications 18, 5 (Sept./Oct.), 32-41.]] Google Scholar
22. SCHEEPERS, F., PARENT, R. E., CARLSON, W. E., AND MAY, S. F. 1997. Anatomy-based modeling of the human musculature. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 97, T. Whitted, Ed., Annual Conference Series, ACM, 163-172.]] Google Scholar
23. SHEN JIANHUA, THALMANN, N. M., AND THALMANN, D. 1994. Human skin deformation from cross-sections. In Computer Graphics Int. ’94.]]Google Scholar
24. SILAGHI, M.-C., PLÄNKERS, R., BOULIC, R., FUA, P., AND THALMANN, D. 1998. Local and global skeleton fitting techniques for optical motion capture. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Modelling and Motion Capture Techniques for Virtual Environments (CAPTECH-98), Springer, Berlin, N. Magnenat-Thalmann and D. Thalmann, Eds., vol. 1537 of LNAI, 26-40.]] Google Scholar
25. SLOAN, P.-P., ROSE, C., AND COHEN, M. F. 2001. Shape by example. In Proceedings of 2001 Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics.]] Google Scholar
26. TALBOT, J. 1998. Accurate Characterization of Skin Deformations Using Range Data. Master’s thesis, Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto.]]Google Scholar
27. TURK, G., AND LEVOY, M. 1994. Zippered polygon meshes from range images. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 94, ACM Press, vol. 28 of Annual Conference Series, ACM, 311-318.]] Google Scholar
28. WILHELMS, J., AND GELDER, A. V. 1997. Anatomically based modeling. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 97, T. Whitted, Ed., Annual Conference Series, ACM, 173-180.]] Google Scholar
29. ZHU, C., BYRD, R. H., LU, P., AND NOCEDAL, J. 1997. Algorithm 778. L-BFGS-B: Fortran subroutines for Large-Scale bound constrained optimization. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 23, 4 (Dec.), 550-560.]] Google Scholar