“Making Small Spaces Feel Large: Infinite Walking in Virtual Reality” by Suma, Azmandian, Grechkin, Phan and Bolas
Notice: Pod Template PHP code has been deprecated, please use WP Templates instead of embedding PHP. has been deprecated since Pods version 2.3 with no alternative available. in /data/siggraph/websites/history/wp-content/plugins/pods/includes/general.php on line 518
Conference:
- SIGGRAPH 2015
-
More from SIGGRAPH 2015:
Notice: Array to string conversion in /data/siggraph/websites/history/wp-content/plugins/siggraph-archive-plugin/src/next_previous/source.php on line 345

Notice: Array to string conversion in /data/siggraph/websites/history/wp-content/plugins/siggraph-archive-plugin/src/next_previous/source.php on line 345

Type(s):
Entry Number: 16
Title:
- Making Small Spaces Feel Large: Infinite Walking in Virtual Reality
Presenter(s):
Description:
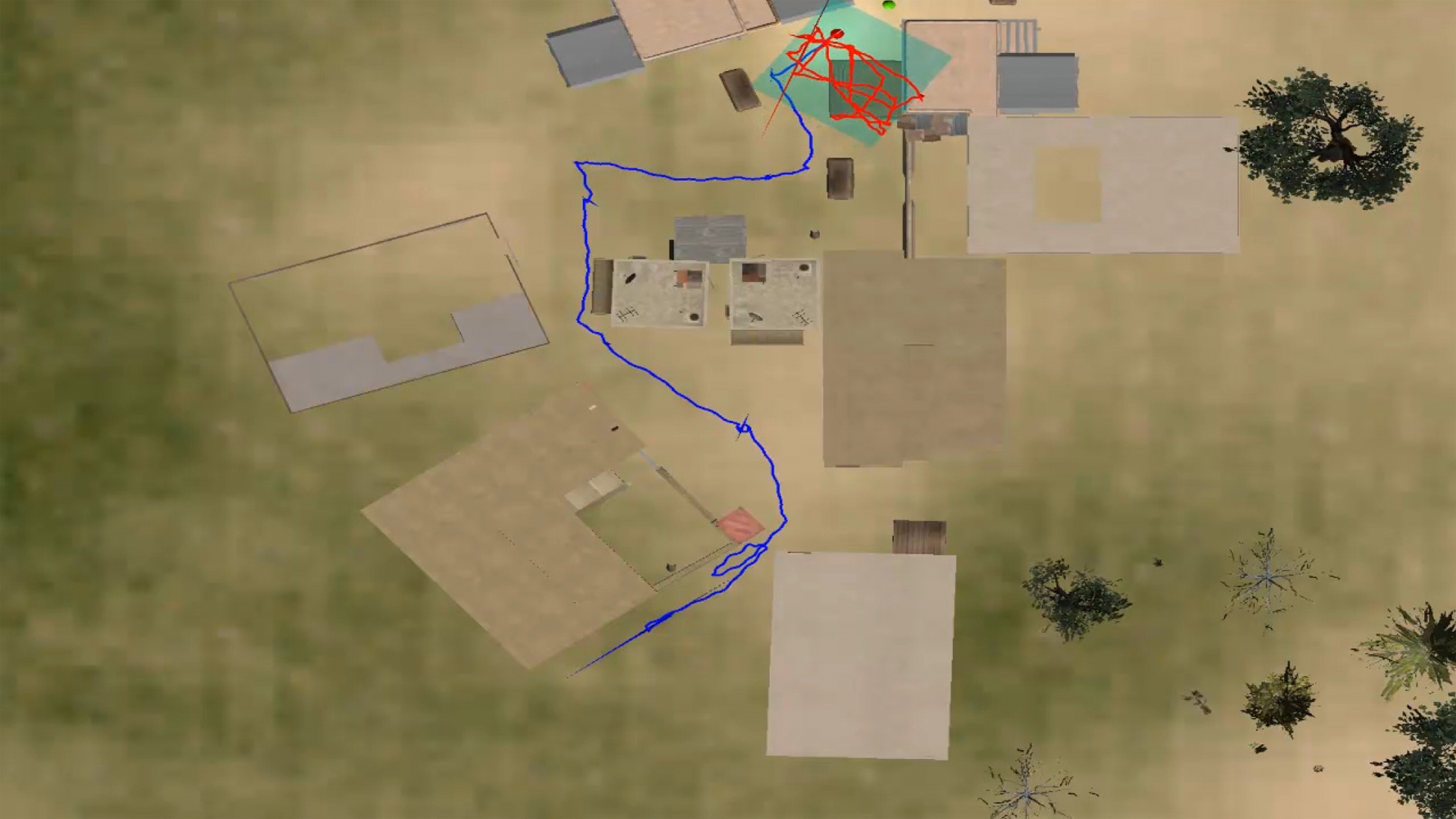
Over the past few years, virtual reality has experienced a resurgence. Fueled by a proliferation of consumer-level head-mounted display and motion tracking devices, an unprecedented quantity of immersive experiences and content are available for both desktop and mobile platforms. However, natural locomotion in immersive virtual environments remains a significant challenge. Many of the VR applications available to date require seated use or limit body movement within a small area, instead relying a gamepad or mouse/keyboard for movement within the virtual world. Lacking support for natural walking, these virtual reality experiences do not fully replicate the physical and perceptual cues from the real world, and often fall short in maintaining the illusion that the user has been transported to another place.
We present a virtual reality demonstration that supports infinite walking within a confined physical space. This is achieved using redirected walking, a class of techniques that introduce subtle discrepancies between physical and virtual motions [Razzaque et al. 2001]. When employed properly, redirected walking can be stunningly effective. Previous research has made users believe that they walked in a straight line when they actually traveled in a wide circle, or that they walked between waypoints in a long virtual hallway when in fact they went back and forth between the same two points in the real world. While perceptually compelling, redirected walking is challenging to employ effectively in an unconstrained scenario because users’ movements may often be unpredictable. Therefore, our recent research has focused on dynamic planning and optimization of redirected walking techniques, enabling the system to intelligently apply redirection as users explore virtual environments of arbitrary size and shape [Azmandian et al. 2014b] [Azmandian et al. 2014a].
References:
AZMANDIAN, M., BOLAS, M., AND SUMA, E. 2014. Countering user deviation during redirected walking. In ACM Symposium on Applied Perception, 129.
AZMANDIAN, M., YAHATA, R., BOLAS, M., AND SUMA, E. 2014. An enhanced steering algorithm for redirected walking in virtual environments. In IEEE Virtual Reality, 65–66.
RAZZAQUE, S., KOHN, Z., AND WHITTON, M. C. 2001. Redirected Walking. In Eurographics (Short Presentation).