“Incendiary reflection: evoking emotion through deformed facial feedback” by Yoshida, Sakurai, Narumi, Tanikawa and Hirose
Conference:
Experience Type(s):
Title:
- Incendiary reflection: evoking emotion through deformed facial feedback
Entry Number: 08
Organizer(s)/Presenter(s):
Description:
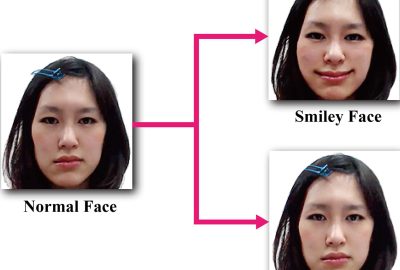
Incendiary reflection aims to create computer-generated emotion by letting people recognize pseudo-generated facial expressions as changes to their own facial expressions (Figure 1, left).
With conventional human-computer interactions, the manipulation subjective elements of experienced emotion is not possible. Thus, emotional experience may not be properly conveyed in such contexts. Emotion is assumed to result from perceiving stimulation from the external environment, such as behaviors or situations, and handling this stimulation internally. Bodily responses, such as heart rate and facial expressions, have been thought to consequently change via an evoked emotion. However, the internal processing mechanisms for evoking an emotion by a relevant stimulus have not been fully clarified. Therefore, evoking emotions by reproducing this process through engineering techniques is extremely difficult.
However, in the field of cognitive science, some researchers argue that recognition of changes within bodily responses unconsciously evokes an emotion. William James best expressed this phenomenon: “We don’t laugh because we’re happy – we’re happy because we laugh.” [James. 1950] For example, the facial feedback hypothesis [Tomkins. 1962] indicates that changes to facial expressions affect emotional experience: smiling enhances pleasant feelings while attenuating unpleasant feelings.
We focus on the effect of facial expressions on evoked emotion. We propose a method for manipulating emotional states through feedback of deformed facial expressions in real time.
References:
JAMES, W., The principles of psychology, vol. 2. Dover Publications, New York, 1950.
TOMKINS, S., Affect, imagery, and consciousness: The Positive affects; Springer, New York, vol.1, 1962.
SHAEFER, S. et al., Image deformation using moving least squares, ACM Trans. Graph, vol.25, no.3, pp.533-540, 2006.
YOSHIDA, S. et al., Manipulation of an Emotional Experience by Real-time Deformed Facial Feedback, In Proc of the 4th Augmented Human International Conference, pp.35-42, 2013.
Additional Images:
- 2013 ETech Yoshida: Incendiary reflection: evoking emotion through deformed facial feedback
- 2013 ETech Yoshida: Incendiary reflection: evoking emotion through deformed facial feedback