“Virtual Reality Mirror Therapy Rehabilitation For Post-Stroke Patients” by Sulimanov
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Virtual Reality Mirror Therapy Rehabilitation For Post-Stroke Patients
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Entry Number:
- 07
Abstract:
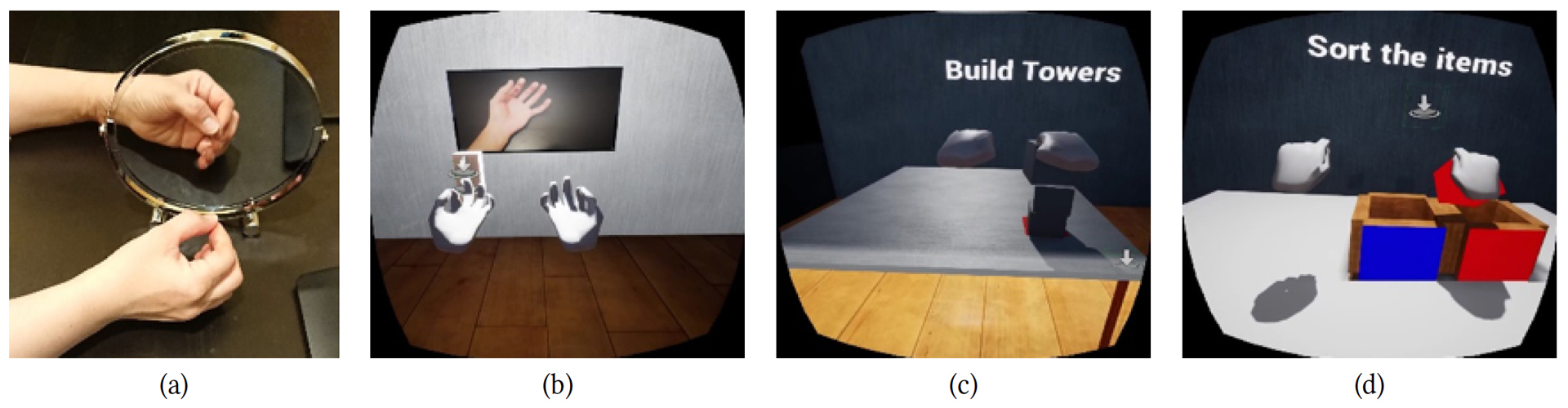
Strokes have a wide range of occurrence among people of all races and genders. The consequences of a stroke often include significant muscle weakness on one side of the body that must be physically exercised to attempt to restore its previous strength and mobility. In traditional mirror therapy, the partially disabled hand or leg is hidden by a mirror. The patient sees a reflection of the healthy side of their body where the disabled limb should be, in order to stimulate brain to operate the partially disabled hand/leg in the proper way. The patient will interact with mirror using unaffected hand and observe its reflection.
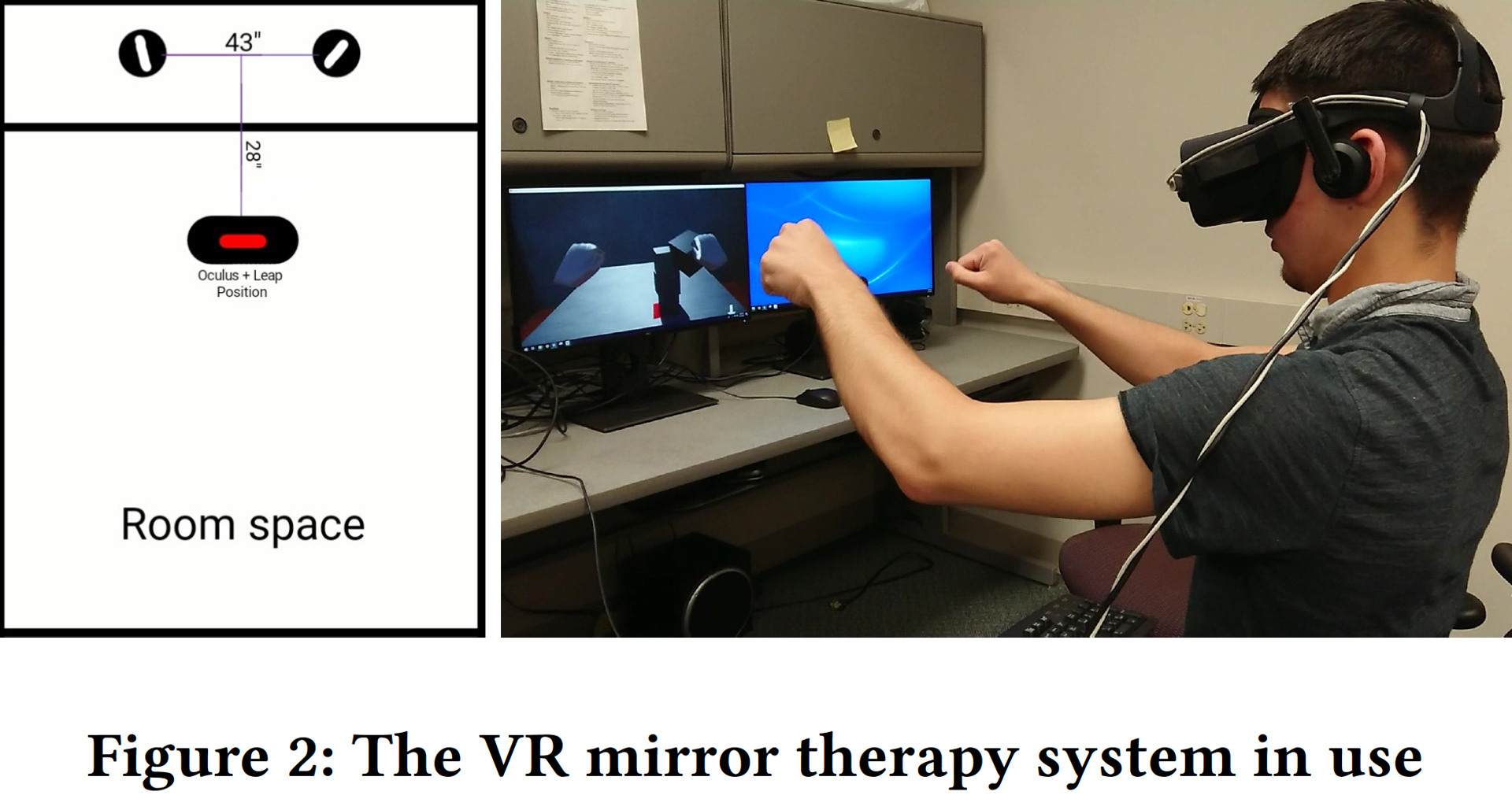
In this work, we recreate the techniques of Mirror Therapy in Virtual Reality (VR) video game environment. This approach provides completely unique sets of therapy uses with new capabilities that include richer exercise approaches and atmospheric customization. In contrast with physical environment, patients in Virtual Reality can use unlimited number of objects and other therapeutic resources for exercises, and proceed with abundant set of exercise movements. These features create both economical and usability advantage. Different environments with custom physics can now be presented to Mirror Therapy’s users and it can provide new rehabilitation techniques and practices.
Prior work in VR mirror therapy has focused primarily on pain management, using either sensors placed on the unaffected limb or a cyberglove [Ambron et al. 2018; Sato et al. 2010].
References:
- Elisabetta Ambron, Alexander Miller, Katherine J. Kuchenbecker, Laurel J. Buxbaum, and H. Branch Coslett. 2018. Immersive Low-Cost Virtual Reality Treatment for Phantom Limb Pain: Evidence from Two Cases. Frontiers in Neurology 9 (2018), 67.
- Jan Kaniewski. 2018. leap-ue4. Github Repository. (25 June 2018). https://github.com/ getnamo/leap-ue4
- Kenji Sato, Satoshi Fukumori, Takashi Matsusaki, Tomoko Maruo, Shinichi Ishikawa, Hiroyuki Nishie, Ken Takata, Hiroaki Mizuhara, Satoshi Mizobuchi, Hideki Nakatsuka, Masaki Matsumi, Akio Gofuku, Masataka Yokoyama, and Kiyoshi Morita. 2010. Nonimmersive Virtual Reality Mirror Visual Feedback Therapy and Its for the Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: An Open-Label Pilot Study. Pain Medicine 11 (2010), 622–629.
Keyword(s):
Acknowledgements:
Support for this work was provided, in part, by a gift from Epic Games.