“RigMesh: automatic rigging for part-based shape modeling and deformation”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- RigMesh: automatic rigging for part-based shape modeling and deformation
Session/Category Title:
- Skinning
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
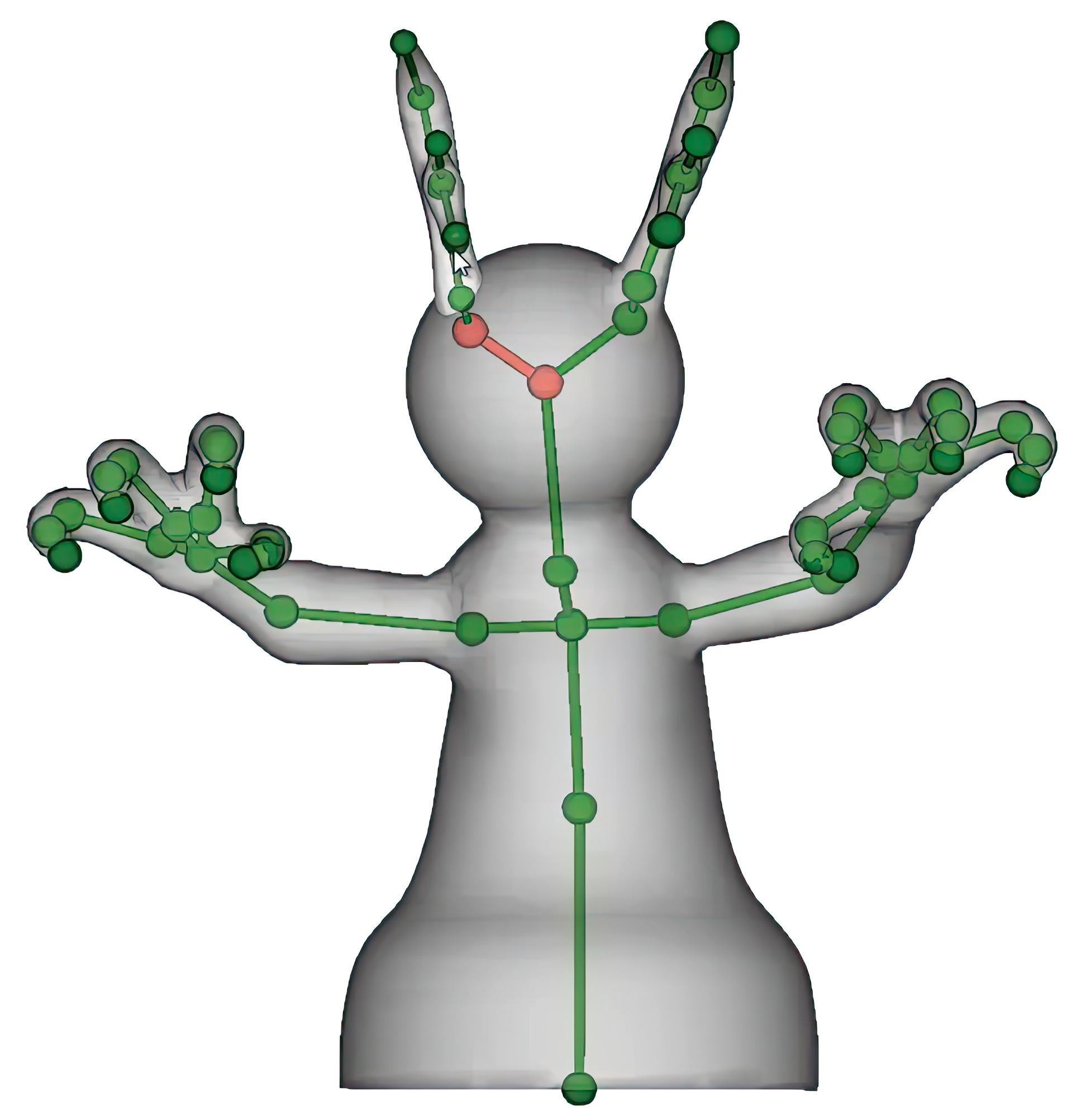
The creation of a 3D model is only the first stage of the 3D character animation pipeline. Once a model has been created, and before it can be animated, it must be rigged. Manual rigging is laborious, and automatic rigging approaches are far from real-time and do not allow for incremental updates. This is a hindrance in the real world, where the shape of a model is often revised after rigging has been performed. In this paper, we introduce algorithms and a user-interface for sketch-based 3D modeling that unify the modeling and rigging stages of the 3D character animation pipeline. Our algorithms create a rig for each sketched part in real-time, and update the rig as parts are merged or cut. As a result, users can freely pose and animate their shapes and characters while rapidly iterating on the base shape. The rigs are compatible with the state-of-the-art character animation pipeline; they consist of a low-dimensional skeleton along with skin weights identifying the surface with bones of the skeleton.
References:
1. Alexe, A., Barthe, L., Cani, M.-P., and Gaildrat, V. 2005. Shape modeling by sketching using convolution surfaces. In Proceedings of Pacific Graphics, Short paper.
2. Allègre, R., Galin, E., Chaine, R., and Akkouche, S. 2006. The hybridtree: mixing skeletal implicit surfaces, triangle meshes, and point sets in a free-form modeling system. Graph. Models 68, 1 (Jan.), 42–64.
3. Au, O. K.-C., Tai, C.-L., Chu, H.-K., Cohen-Or, D., and Lee, T.-Y. 2008. Skeleton extraction by mesh contraction. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3 (Aug.), 44:1–44:10.
4. Autodesk, 2012. 3ds Max. http://www.autodesk.com/3dsmax.
5. Autodesk, 2012. Fbx. http://usa.autodesk.com/fbx.
6. Autodesk, 2012. Maya. http://www.autodesk.com/maya.
7. Baran, I., and Popović, J. 2007. Automatic rigging and animation of 3D characters. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3 (July).
8. Bernhardt, A., Pihuit, A., Cani, M.-P., and Barthe, L. 2008. Matisse: Painting 2D regions for modeling free-form shapes. In Eurographics Workshop on Sketch-Based Interfaces and Modeling (SBIM), 57–64.
9. Biederman, I. 1987. Recognition-by-components: A theory of human image understanding. Psychological Review 94, 115–147.
10. Bloomenthal, J. 2002. Medial-based vertex deformation. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (SCA), 147–151.
11. Chaudhuri, S., Kalogerakis, E., Guibas, L., and Koltun, V. 2011. Probabilistic reasoning for assembly-based 3D modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4.
12. Cherlin, J. J., Samavati, F., Sousa, M. C., and Jorge, J. A. 2005. Sketch-based modeling with few strokes. In Proceedings of the Spring Conference on Computer Graphics, 137–145.
13. Chew, L. P. 1989. Constrained delaunay triangulations. Algorithmica 4, 1, 97–108.
14. Cordier, F., Seo, H., Park, J., and Noh, J. Y. 2011. Sketching of mirror-symmetric shapes. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 17, 11 (Nov.), 1650–1662.
15. Cornea, N. D., Silver, D., and Min, P. 2007. Curve-skeleton properties, applications, and algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 13 (May), 530–548.
16. Douglas, D. H., and Peucker, T. K. 1973. Algorithms for the reduction of the number of points required to represent a line or its caricature. The Canadian Cartographer 10, 2, 112–122.
17. Funkhouser, T., Kazhdan, M., Shilane, P., Min, P., Kiefer, W., Tal, A., Rusinkiewicz, S., and Dobkin, D. 2004. Modeling by example. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (Aug.), 652–663.
18. Gingold, Y., Igarashi, T., and Zorin, D. 2009. Structured annotations for 2D-to-3D modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 28 (December), 148:1–148:9.
19. Grochow, K., Martin, S. L., Hertzmann, A., and Popović, Z. 2004. Style-based inverse kinematics. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (Aug.), 522–531.
20. Hecker, C., Raabe, B., Enslow, R. W., DeWeese, J., Maynard, J., and van Prooijen, K. 2008. Real-time motion retargeting to highly varied user-created morphologies. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3 (Aug.), 27:1–27:11.
21. Igarashi, T., Matsuoka, S., and Tanaka, H. 1999. Teddy: A sketching interface for 3D freeform design. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH, 409–416.
22. Karpenko, O. A., and Hughes, J. F. 2006. SmoothSketch: 3D free-form shapes from complex sketches. ACM Trans. Graph. 25 (July), 589–598.
23. Kavan, L., Collins, S., Žára, J., and O’Sullivan, C. 2008. Geometric skinning with approximate dual quaternion blending. ACM Trans. Graph. 27 (November), 105:1–105:23.
24. Kraevoy, V., Julius, D., and Sheffer, A. 2007. Model composition from interchangeable components. In Proceedings of Pacific Graphics, 129–138.
25. Kry, P. G., James, D. L., and Pai, D. K. 2002. Eigenskin: real time large deformation character skinning in hardware. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (SCA), 153–159.
26. Lewis, J. P., and Anjyo, K. 2009. Identifying salient points. In ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2009 Sketches, 41:1–41:1.
27. Lewis, J. P., Cordner, M., and Fong, N. 2000. Pose space deformation: a unified approach to shape interpolation and skeleton-driven deformation. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH, 165–172.
28. Magnenat-Thalmann, N., Laperrière, R., and Thalmann, D. 1988. Joint-dependent local deformations for hand animation and object grasping. In Proceedings of Graphics Interface, 26–33.
29. Maxis, 2008. Spore creature creator. http://www.spore.com/.
30. Mi, X., DeCarlo, D., and Stone, M. 2009. Abstraction of 2D shapes in terms of parts. In Proceedings of NPAR, 15–24.
31. Miller, C., Arikan, O., and Fussell, D. 2010. Frankenrigs: building character rigs from multiple sources. In ACM Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics (I3D), 31–38.
32. Mohr, A., and Gleicher, M. 2003. Building efficient, accurate character skins from examples. ACM Trans. Graph. 22 (July), 562–568.
33. Nealen, A., Sorkine, O., Alexa, M., and Cohen-Or, D. 2005. A sketch-based interface for detail-preserving mesh editing. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3 (July), 1142–1147.
34. Nealen, A., Igarashi, T., Sorkine, O., and Alexa, M. 2007. FiberMesh: Designing freeform surfaces with 3D curves. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3 (July).
35. Nealen, A., Pett, J., Alexa, M., and Igarashi, T. 2009. GridMesh: Fast and high quality 2D mesh generation for interactive 3D shape modeling. In Shape Modeling International (SMI), 155–162.
36. Nielsen, J. 1993. Usability Engineering. Morgan Kaufmann publishers Inc.
37. Olsen, L., Samavati, F., Sousa, M., and Jorge, J. 2009. Sketch-based modeling: A survey. Computers & Graphics 33, 85–103.
38. Pan, J., Yang, X., Xie, X., Willis, P., and Zhang, J. J. 2009. Automatic rigging for animation characters with 3D silhouette. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 20, 23 (June), 121–131.
39. Pihuit, A., Cani, M.-P., and Palombi, O. 2010. Sketch-based modeling of vascular systems: a first step towards interactive teaching of anatomy. In Eurographics Workshop on Sketch-Based Interfaces and Modeling (SBIM), 151–158.
40. Pixologic, 2012. ZBrush. http://www.pixologic.com/zbrush/.
41. Prasad, L. 1997. Morphological analysis of shapes. CNLS Newsletter 139, 1–18.
42. Schmidt, R., and Singh, K. 2010. meshmixer: an interface for rapid mesh composition. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2010 Talks, 6:1–6:1.
43. Schmidt, R., Wyvill, B., Sousa, M. C., and Jorge, J. A. 2005. ShapeShop: Sketch-based solid modeling with blob-Trees. In Eurographics Workshop on Sketch-Based Interfaces and Modeling (SBIM), 53–62.
44. Sharf, A., Blumenkrants, M., Shamir, A., and Cohen-Or, D. 2006. SnapPaste: an interactive technique for easy mesh composition. Vis. Comput. 22, 9 (Sept.), 835–844.
45. Sharf, A., Lewiner, T., Shamir, A., and Kobbelt, L. 2007. On-the-fly curve-skeleton computation for 3D shapes. Computer Graphics Forum 26, 3 (october), 323–328.
46. Sherstyuk, A. 1999. Interactive shape design with convolution surfaces. In Shape Modeling International (SMI), 56–65.
47. Shukan, Z. 2012. Personal communication.
48. Sorkine, O., and Cohen-Or, D. 2004. Least-squares meshes. In Shape Modeling International (SMI), 191–199.
49. Sugihara, M., de Groot, E., Wyvill, B., and Schmidt, R. 2008. A sketch-based method to control deformation in a skeletal implicit surface modeler. In Eurographics Workshop on Sketch-Based Interfaces and Modeling (SBIM), 65–72.
50. Tai, C.-L., Zhang, H., and Fong, J. C.-K. 2004. Prototype modeling from sketched silhouettes based on convolution surfaces. Computer Graphics Forum 23, 1, 71–83.
51. Thacker, J. 2012. Rigmesh: putting the fun back into rigging. http://www.cgchannel.com/2012/05/rigmesh-putting-the-fun-back-into-rigging/.
52. Wang, R. Y., Pulli, K., and Popović, J. 2007. Real-time enveloping with rotational regression. ACM Trans. Graph. 26 (July).
53. Wareham, R., and Lasenby, J. 2008. Bone glow: An improved method for the assignment of weights for mesh deformation. In Proceedings of the 5th international conference on Articulated Motion and Deformable Objects, AMDO ’08, 63–71.
54. Watt, A., and Watt, M. 1991. Advanced animation and rendering techniques.
55. Weber, O., Sorkine, O., Lipman, Y., and Gotsman, C. 2007. Context-aware skeletal shape deformation. Computer Graphics Forum 26, 3.
56. Wyvill, B., Guy, A., and Galin, E. 1999. Extending the CSG tree: Warping, blending and boolean operations in an implicit surface modeling system. Computer Graphics Forum 18, 2, 149–158.
57. Yang, R., and Wünsche, B. C. 2010. Life-sketch: a framework for sketch-based modelling and animation of 3D objects. In Proceedings of the Eleventh Australasian Conference on User Interface – Volume 106, 61–70.