“Interactive Teaching Aids Design for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology–Using Bones and Muscles as Example” by Chen, Chen, Chang, Yu, Chou, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Interactive Teaching Aids Design for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology–Using Bones and Muscles as Example
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Entry Number:
- 23
Abstract:
Learning essentials of anatomy and physiology[R. Richardson et al. 2018] can make students knowing more about the connection between bones and muscles of human bodies. In the past, we can only use books, pictures, videos or fixed bone model to teach. This kind of teaching may suit for student over 15. But, for student under 15, it’s hard to increase their interest or studying time for learning. If there are some models that can be assembled during the class, as Alison James[A. James et al. 2014] said, building LEGO helps us to think more about the 3D shape of the object. Can also increase student’s interest of learning.
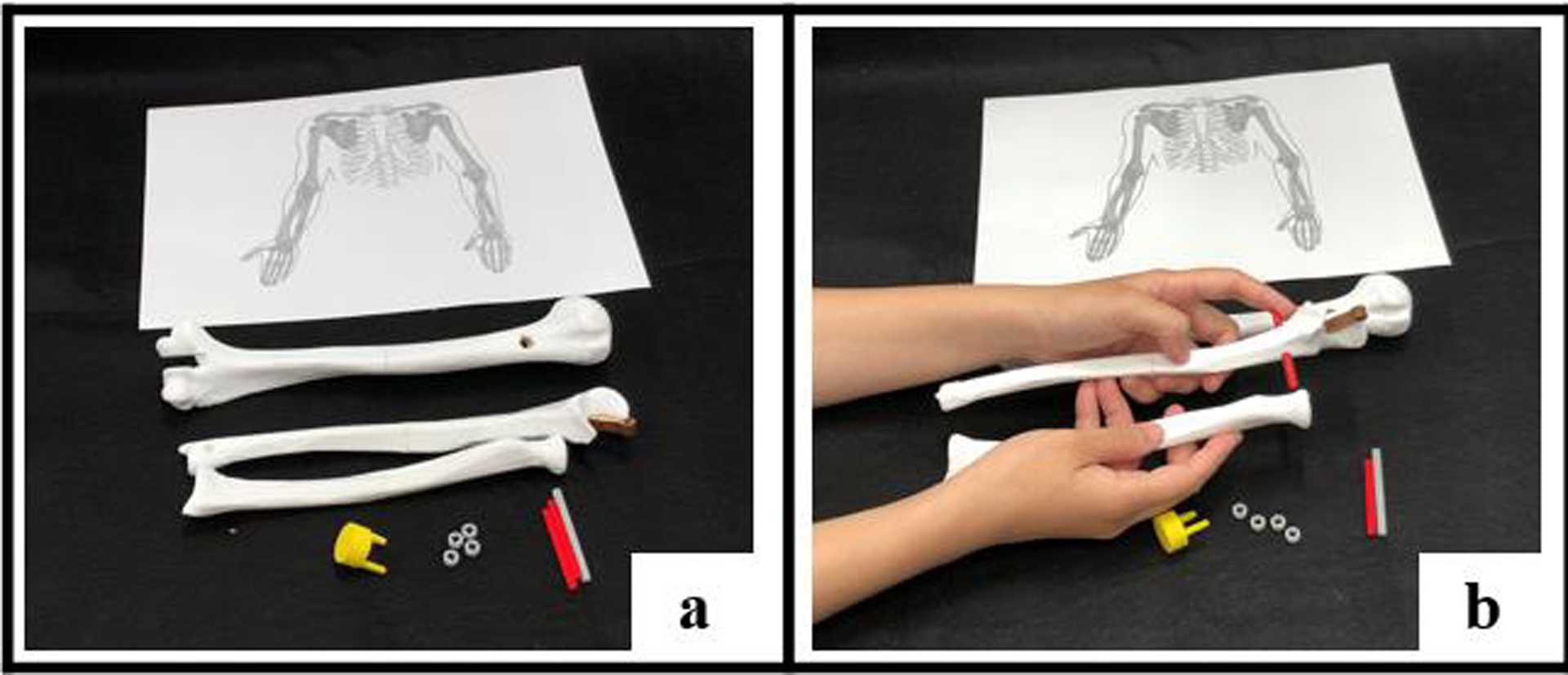
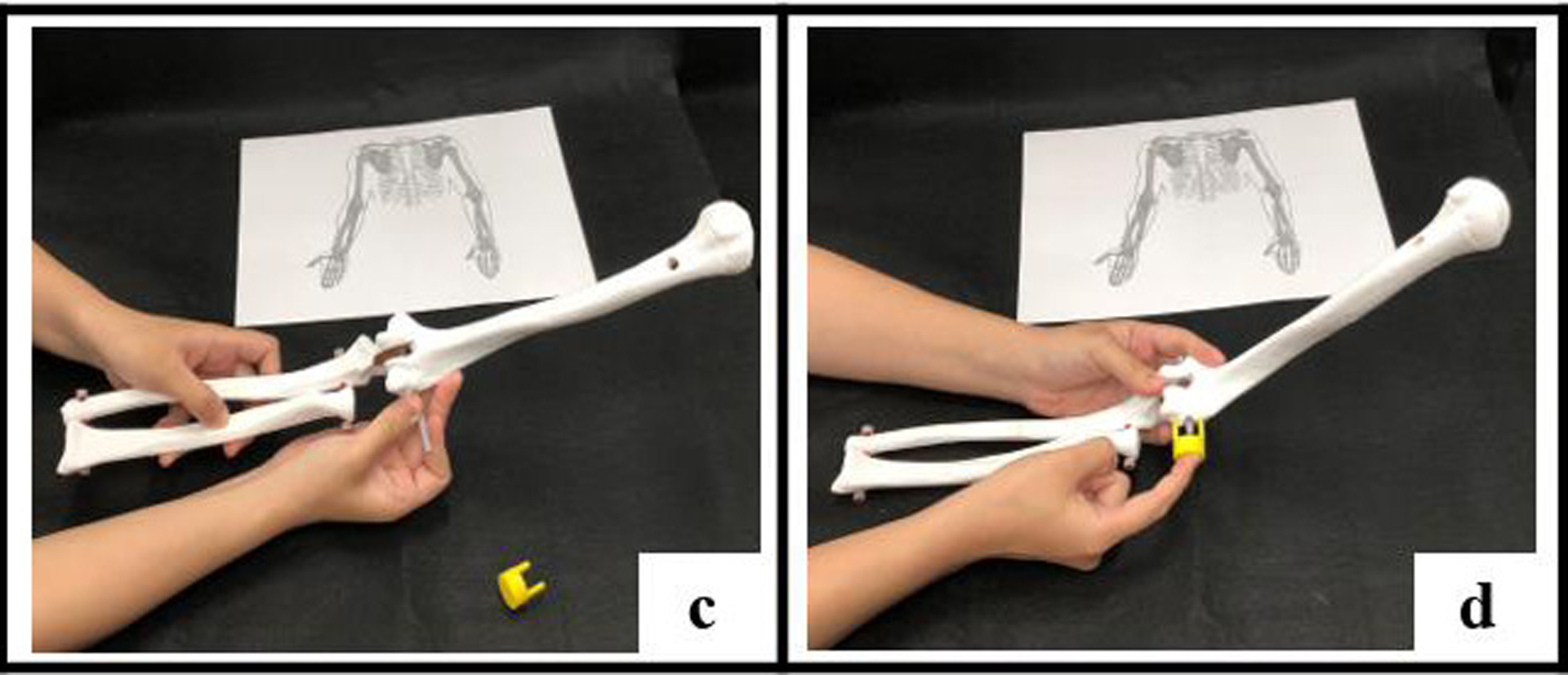
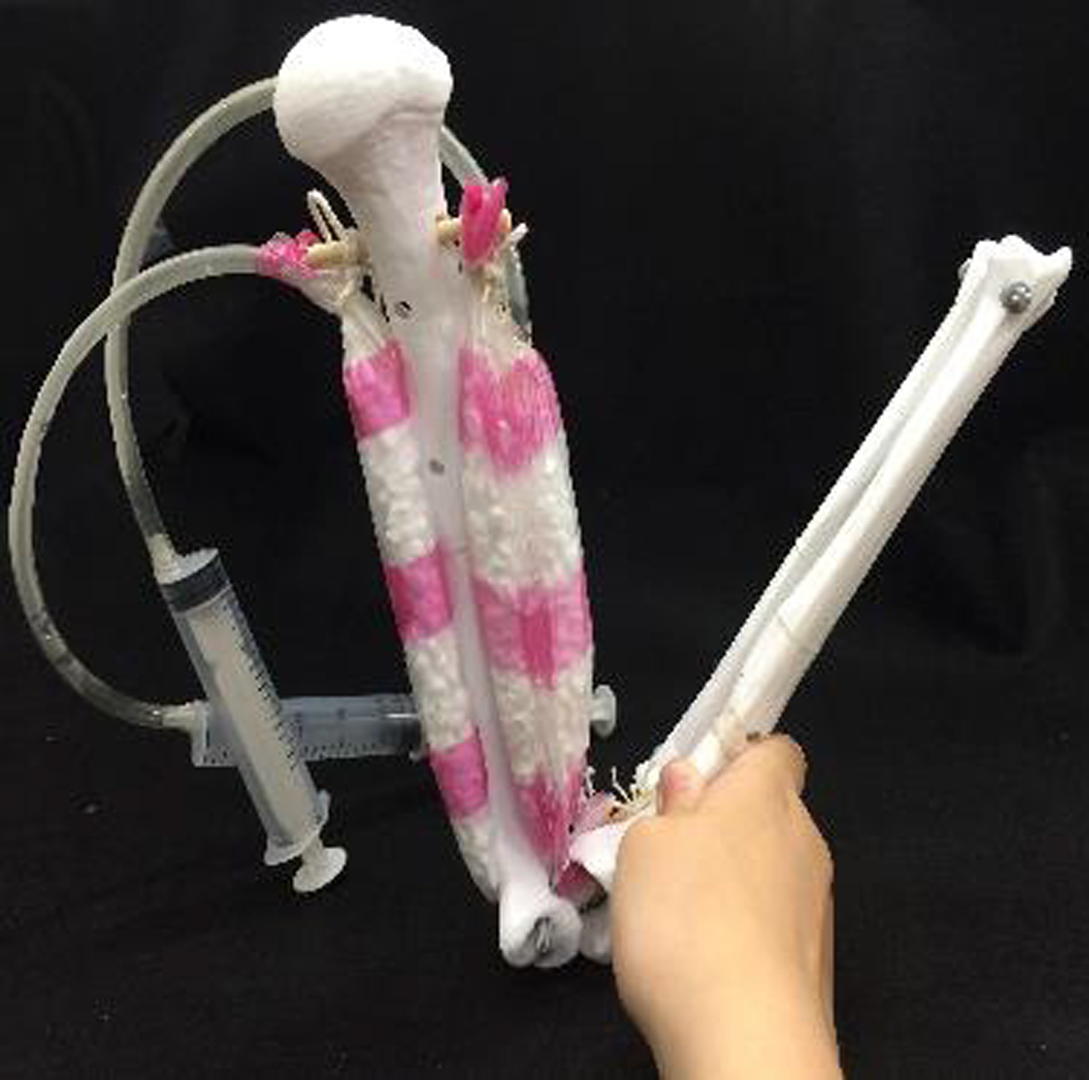
In this study, we design a set of interactive teaching aids for essentials of anatomy and physiology to student under 15. The aids include two parts, assembled real working model and interactive augment reality.
In assembled model part, student can assembled 3D-printed bones and muscle-liked plastic bag with syringe and rubber bands. By assembled them, students can learn more about how bones are connected with muscles. The other part, the interactive augment reality is design for the assembled working model. Showing how muscles really works on the screen of device. In this way, student can memorize it easier and deeper.
References:
- R. Richardson, The Making of Mr. Gray’s Anatomy. Publish by Oxford University Press, 2008.
- A. James, “Learning in Three Dimensions: Using Lego Serious Play for Creative and Critical Reflection across Time and Space,” Global Innovation of Teaching and Learning in Higher Education, 2014, pp 275-294.
Keyword(s):
Additional Images:
- 2018 Posters: Chen_Interactive Teaching Aids Design for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology?Using Bones and Muscles as Example
- 2018 Posters: Chen_Interactive Teaching Aids Design for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology?Using Bones and Muscles as Example