“Image-based bidirectional scene reprojection”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Image-based bidirectional scene reprojection
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
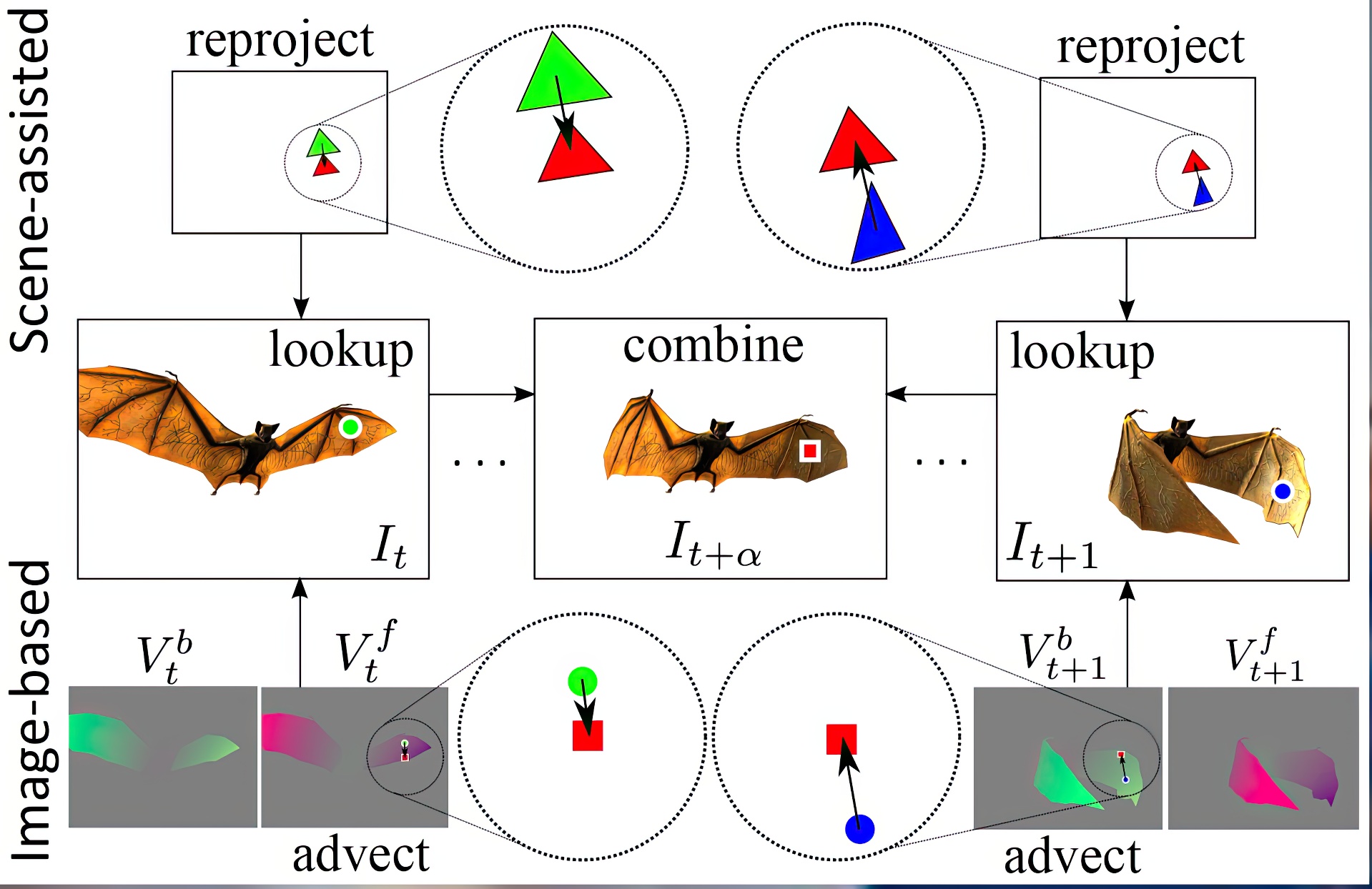
We introduce a method for increasing the framerate of real-time rendering applications. Whereas many existing temporal upsampling strategies only reuse information from previous frames, our bidirectional technique reconstructs intermediate frames from a pair of consecutive rendered frames. This significantly improves the accuracy and efficiency of data reuse since very few pixels are simultaneously occluded in both frames. We present two versions of this basic algorithm. The first is appropriate for fill-bound scenes as it limits the number of expensive shading calculations, but involves rasterization of scene geometry at each intermediate frame. The second version, our more significant contribution, reduces both shading and geometry computations by performing reprojection using only image-based buffers. It warps and combines the adjacent rendered frames using an efficient iterative search on their stored scene depth and flow. Bidirectional reprojection introduces a small amount of lag. We perform a user study to investigate this lag, and find that its effect is minor. We demonstrate substantial performance improvements (3–4x) for a variety of applications, including vertex-bound and fill-bound scenes, multi-pass effects, and motion blur.
References:
1. Andreev, D. 2010. Real-time framerate up-conversion for video games. In SIGGRAPH 2010 Talks. Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Badt, Jr., S. 1988. Two algorithms for taking advantage of temporal coherence in ray tracing. The Visual Computer, 4(3):123–132.Google ScholarCross Ref
3. Beier, T. and Neely, S. 1992. Feature-based image metamorphosis. SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph., 26(2):35–42. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Chen, S. E. and Williams, L. 1993. View interpolation for image synthesis. In Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH 93, pages 279–288. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. d’Eon, E. and Luebke, D. 2007. Advanced techniques for realistic real-time skin rendering. In GPU Gems 3, Addison-Wesley.Google Scholar
6. Didyk, P., Eisemann, E., Ritschel, T., Myszkowski, K., and Seidel, H.-P. 2010. Perceptually-motivated real-time temporal upsampling of 3D content for high-refresh-rate displays. Computer Graphics Forum, 29(2).Google Scholar
7. Didyk, P., Ritschel, T., Eisemann, E., Myszkowski, K., and Seidel, H.-P. 2010. Adaptive image-space stereo view synthesis. In Vision, Modeling, and Visualization.Google Scholar
8. Eisemann, M., De Decker, B., Magnor, M., Bekaert, P., De Aguiar, E., Ahmed, N., Theobalt, C., and Sellent, A. 2008. Floating textures. Computer Graphics Forum, 27(2).Google Scholar
9. Fitzgibbon, A., Wexler, Y., and Zisserman, A. 2005. Image-based rendering using image-based priors. International Journal of Computer Vision, 63(2):141–151. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Herzog, R., Eisemann, E., Myszkowski, K., and Seidel, H.-P. 2010. Spatio-temporal upsampling on the GPU. In Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games, ACM. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Mahajan, D., Huang, F.-C., Matusik, W., Ramamoorthi, R., and Belhumeur, P. 2009. Moving gradients: a path-based method for plausible image interpolation. ACM Trans. Graph., 28(3):1–11. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Mark, W. R., McMillan, L., and Bishop, G. 1997. Postrendering 3D warping. In Proc. Symposium of Interactive 3D Graphics, pages 7–16. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Mattausch, O., Scherzer, D., and Wimmer, M. 2010. High-quality screen-space ambient occlusion using temporal coherence. Computer Graphics Forum, 29(8):2492–2503.Google ScholarCross Ref
14. McMillan, L. and Bishop, G. 1995. Plenoptic modeling: an image-based rendering system. In Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH 95. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Nehab, D., Sander, P. V., Lawrence, J., Tatarchuk, N., and Isidoro, J. R. 2007. Accelerating real-time shading with reverse reprojection caching. In Graphics Hardware, pages 25–35. Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Pajak, D., Herzog, R., Eisemann, E., Myszkowski, K., and Seidel, H.-P. 2011. Scalable remote rendering with depth and motion-flow augmented streaming. Comp. Graph. Forum, 30(2).Google Scholar
17. Scherzer, D., Jeschke, S., and Wimmer, M. 2007. Pixel-correct shadow maps with temporal reprojection and shadow test confidence. In Eurograph. Symp. Rendering, pages 45–50. Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Scherzer, D., Schwärzler, M., Mattausch, O., and Wimmer, M. 2009. Real-time soft shadows using temporal coherence. LNCS (Proc. ISVC), 5876:13–24. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Scherzer, D., Yang, L., Mattausch, O., Nehab, D., Sander, P. V., Wimmer, M., and Eisemann, E. 2011. A survey on temporal coherence methods in real-time rendering. In Eurographics State of the Art Reports.Google Scholar
20. Seitz, S. M. and Dyer, C. R. 1996. View morphing. In Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH 96, ACM, pages 21–30. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Sitthi-amorn, P., Lawrence, J., Yang, L., Sander, P. V., and Nehab, D. 2008. An improved shading cache for modern GPUs. In Proc. of Graphics Hardware, pages 95–101. Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Sitthi-amorn, P., Lawrence, J., Yang, L., Sander, P. V., Nehab, D., and Xi, J. 2008. Automated reprojection-based pixel shader optimization. ACM Trans. Graph., 27(5):127. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Stich, T., Linz, C., Albuquerque, G., and Magnor, M. 2008. View and time interpolation in image space. Computer Graphics Forum (Proc. of Pacific Graphics), 27(7):1781–1787.Google ScholarCross Ref
24. Stich, T., Linz, C., Wallraven, C., Cunningham, D., and Magnor, M. 2008. Perception-motivated interpolation of image sequences. In Proc. Appl. Percept. Graph. Visul., pages 97–106. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Sullivan, G. J. and Wiegand, T. 2005. Video compression from concepts to the H.264-AVC standard. In Proceedings of the IEEE.Google Scholar
26. Vedula, S., Baker, S., and Kanade, T. 2002. Spatio-temporal view interpolation. In Eurograph. Workshop on Rendering. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Wang, Z., Bovik, A. C., Sheikh, H. R., and Simoncelli, E. P. 2004. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Proc., 13(4):600–612. Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Wiegand, T., Sullivan, G. J., Bj ontegaard, G., and Luthra, A. 2003. Overview of the H.264-AVC video coding standard. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Tech., 13. Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Yang, L., Nehab, D., Sander, P. V., Sitthi-amorn, P., Lawrence, J., and Hoppe, H. 2009. Amortized supersampling. ACM Trans. Graph., 28(5):135. Google ScholarDigital Library