“Centroidal power diagrams with capacity constraints: computation, applications, and extension” by Xin, Lévy, Chen, Chu, Yu, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Centroidal power diagrams with capacity constraints: computation, applications, and extension
Session/Category Title:
- Tessellations
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
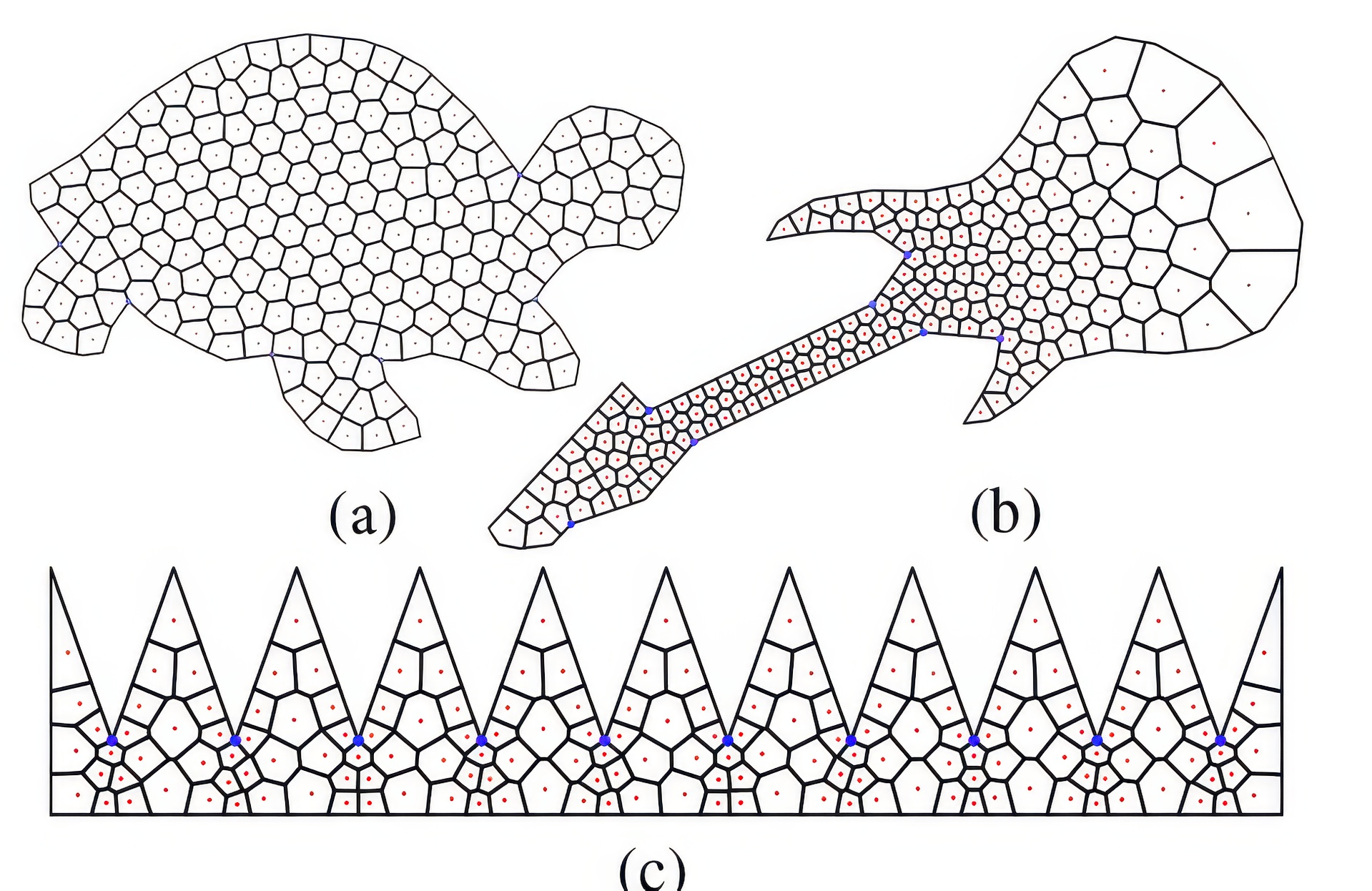
This article presents a new method to optimally partition a geometric domain with capacity constraints on the partitioned regions. It is an important problem in many fields, ranging from engineering to economics. It is known that a capacity-constrained partition can be obtained as a power diagram with the squared L2 metric. We present a method with super-linear convergence for computing optimal partition with capacity constraints that outperforms the state-of-the-art in an order of magnitude. We demonstrate the efficiency of our method in the context of three different applications in computer graphics and geometric processing: displacement interpolation of function distribution, blue-noise point sampling, and optimal convex decomposition of 2D domains. Furthermore, the proposed method is extended to capacity-constrained optimal partition with respect to general cost functions beyond the squared Euclidean distance.
References:
1. Abramson, I. S. 1982. On bandwidth variation in kernel estimates-a square root law. Annals of Statistics 10, 4, 1217–1223. Cross Ref
2. Agueh, M., and Carlier, G. Barycenters in the Wasserstein space. SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis 43, 2, 904–924.
3. Atkinson, K. E. 2008. An introduction to numerical analysis. John Wiley & Sons.
4. Aurenhammer, F., and Klein, R. 2000. Voronoi diagrams. Handbook of computational geometry 5, 201–290.
5. Aurenhammer, F., Hoffmann, F., and Aronov, B. 1998. Minkowski-type theorems and least-squares clustering. Algorithmica 20, 1, 61–76. Cross Ref
6. Aurenhammer, F. 1987. Power diagrams: properties, algorithms and applications. SIAM Journal on Computing 16, 1, 78–96.
7. Balzer, M., and Heck, D. 2008. Capacity-constrained Voronoi diagrams in finite spaces. In Voronoi Diagrams in Science and Engineering.
8. Balzer, M., Deussen, O., and Lewerentz, C. 2005. Voronoi treemaps for the visualization of software metrics. In Proceedings of the 2005 ACM symposium on Software visualization, 165–172.
9. Balzer, M., Schlömer, T., and Deussen, O. 2009. Capacity-constrained point distributions: A variant of Lloyd’s method. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3, 86:1–8.
10. Benamou, J., Froese, B. D., and Oberman, A. M. 2014. Numerical solution of the optimal transportation problem using the Monge-Ampère equation. J. Comput. Physics 260, 107–126.
11. Benamou, J.-D., Carlier, G., Cuturi, M., Nenna, L., and Peyré, G. 2015. Iterative bregman projections for regularized transportation problems. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 37, 2, A1111–A1138.
12. Bonneel, N., Van De Panne, M., Paris, S., and Heidrich, W. 2011. Displacement interpolation using Lagrangian mass transport. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 6, 158.
13. Bonneel, N., Rabin, J., Peyré, G., and Pfister, H. 2015. Sliced and radon Wasserstein barycenters of measures. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision 51, 1, 22–45.
14. Borgwardt, A., Brieden, A., and Gritzmann, P. 2014. Geometric clustering for the consolidation of farmland and woodland. Mathematical Intelligencer 36, 2, 37–44. Cross Ref
15. Bourne, D., and Roper, S. 2014. Centroidal power diagrams, Lloyd’s algorithm and applications to optimal location problems. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.2786.
16. Bourne, D., Peletier, M., and Roper, S. 2014. Hexagonal patterns in a simplified model for block copolymers. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics 74, 5, 1315–1337. Cross Ref
17. Brenier, Y. 1991. Polar factorization and monotone rearrangement of vector-valued functions. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics 44, 4, 375–417. Cross Ref
18. Chen, Z., Yuan, Z., Choi, Y.-K., Liu, L., and Wang, W. 2012. Variational blue noise sampling. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 18, 10, 1784–1796.
19. Cortés, J. 2010. Coverage optimization and spatial load balancing by robotic sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 55, 3, 749–754. Cross Ref
20. Crane, K., Weischedel, C., and Wardetzky, M. 2013. Geodesics in heat: A new approach to computing distance based on heat flow. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 5, 13–15.
21. Cuturi, M., and Doucet, A. 2013. Fast computation of Wasserstein barycenters. arXiv preprint arXiv:1310.4375.
22. de Goes, F., Breeden, K., Ostromoukhov, V., and Desbrun, M. 2012. Blue noise through optimal transport. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6, 171.
23. Dobrovolsky, V. A. 1972. Sur l’histoire de la classification des points singuliers des équations différentielles. Revue d’histoire des sciences 25, 1, 3–11.
24. Du, Q., Faber, V., and Gunzburger, M. 1999. Centroidal Voronoi tessellations: applications and algorithms. SIAM Rev. 41, 4, 637–676.
25. Fedkiw, R., Stam, J., and Jensen, H. W. 2001. Visual simulation of smoke. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 2001, 15–22.
26. Gangbo, W., and Cann, R. M. 1996. The geometry of optimal transportation. Acta Mathematica.
27. Ghosh, M., Amato, N. M., Lu, Y., and Lien, J. M. 2013. Fast approximate convex decomposition using relative concavity. Computer-Aided Design 45, 2, 494–504.
28. Greene, D. H. 1983. The decomposition of polygons into convex parts. Computational Geometry 1, 235–259.
29. Gu, X., Luo, F., Sun, J., and Yau, S. T. 2013. Variational principles for Minkowski type problems, discrete optimal transport, and discrete Monge-Ampère equations. Mathematical Methods in Solid State & Superfluid Theory 61, 5, 1–45.
30. Jobson, D. J., Rahman, Z.-u., and Woodell, G. A. 1996. Retinex image processing: Improved fidelity to direct visual observation. In Color and Imaging Conference, Society for Imaging Science and Technology, 124–125.
31. Kantorovich, L., and Gavurin, M. 1949. Application of mathematical methods to problems of analysis of freight flows. Problems of raising the efficiency of transport performance, 110–138.
32. Kartch, D. 2000. Efficient Rendering and Compression for Full-Parallax Computer-Generated Holographic Stereograms. PhD thesis, Cornell University.
33. Kitagawa, J., Mérigot, Q., and Thibert, B. 2016. A Newton algorithm for semi-discrete optimal transport. CoRR abs/1603.05579.
34. Landis, H., 2002. Global illumination in production. ACM SIGGRAPH 2002 Course #16 Notes.
35. Lasdon, L. S., Fox, R. L., and Ratner, M. W. 1974. Nonlinear optimization using the generalized reduced gradient method. RAIRO – Operations Research – Recherche Opérationnelle 8, 3, 73–103.
36. Leal, L. G. 2007. Advanced transport phenomena: fluid mechanics and convective transport processes. Scitech Book News, 3.
37. Levoy, M., Pulli, K., Curless, B., Rusinkiewicz, S., Koller, D., Pereira, L., Ginzton, M., Anderson, S., Davis, J., Ginsberg, J., Shade, J., and Fulk, D. 2000. The digital michelangelo project. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 2000, 131–144.
38. Lévy, B. 2014. A numerical algorithm for l2 semi-discrete optimal transport in 3D. Esaim Mathematical Modelling & Numerical Analysis 49, 6.
39. Li, H., Nehab, D., Wei, L.-Y., Sander, P. V., and Fu, C.-W. 2010. Fast capacity constrained Voronoi tessellation. In Proceedings of the 2010 ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games, I3D ’10, 13:1–13:1.
40. Liu, D. C., and Nocedal, J. 1989. On the limited memory BFGS method for large scale optimization. Mathematical Programming: Series A and B 45, 3, 503–528.
41. Liu, Y., Wang, W., Lévy, B., Sun, F., Yan, D.-M., Lu, L., and Yang, C. 2009. On centroidal Voronoi tessellation: energy smoothness and fast computation. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 4, 101:1–101:17.
42. Lloyd, S. 2006. Least squares quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor. 28, 2, 129–137.
43. Lu, L., Choi, Y.-K., Wang, W., and Kim, M.-S. 2007. Variational 3D shape segmentation for bounding volume computation. Computer Graphics Forum 26, 3, 329–338. Cross Ref
44. Lu, L., Sharf, A., Zhao, H., Wei, Y., Fan, Q., Chen, X., Savoye, Y., Tu, C., Cohen-Or, D., and Chen, B. 2014. Build-to-last: strength to weight 3D printed objects. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4, 70–79.
45. Ma, X.-N., Trudinger, S. N., and Wang, X.-J. 2005. Regularity of potential functions of the optimal transportation problem. Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 177, 2, 151–183. Cross Ref
46. McCann, R., and Guillen, N. 2010. Five lectures on optimal transportation: Geometry, regularity and applications. In Summer School: New Vistas in Image Processing and Partial Differential Equations.
47. Mérigot, Q. 2011. A multiscale approach to optimal transport. Computer Graphics Forum 30, 5, 1583–1592. Cross Ref
48. Milgrom, P., and Segal, I. 2002. Envelope Theorems for Arbitrary Choice Sets. Econometrica 70, 2, 583–601. Cross Ref
49. Monge, G. 1781. Mémoire sur la théorie des déblais et des remblais. De l’Imprimerie Royale.
50. Moré, J. J., and Thuente, D. J. 1994. Line search algorithms with guaranteed sufficient decrease. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 20, 3, 286–307.
51. Oberman, A., and Ruan, Y. 2015. An efficient linear programming method for optimal transportation. arXiv:1509.03668.
52. Okabe, A., Boots, B., and Sugihara, K. 1992. Spatial Tessellations: Concepts and Applications of Voronoi Diagrams. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY, USA.
53. Park, S. W., Linsen, L., Kreylos, O., Owens, J. D., and Hamann, B. 2006. Discrete Sibson interpolation. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 12, 2, 243–253.
54. Parke, F. I., and Waters, K. 1996. Computer Facial Animation. A. K. Peters.
55. Patel, R., Frasca, P., and Bullo, F. 2014. Centroidal area-constrained partitioning for robotic networks. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control 136, 3, 031024. Cross Ref
56. Pellacini, F., Vidimče, K., Lefohn, A., Mohr, A., Leone, M., and Warren, J. 2005. Lpics: a hybrid hardware-accelerated relighting engine for computer cinematography. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3, 464–470.
57. Pogorelov, A. V. 1994. Generalized solutions of Monge-Ampère equations of elliptic type. In A tribute to Ilya Bakelman, volume 3 of Discrourses Math. Appl, 47–50.
58. Rabin, J., Peyré, G., Delon, J., and Bernot, M. 2011. Wasserstein barycenter and its application to texture mixing. In Scale Space and Variational Methods in Computer Vision. Springer, 435–446.
59. Sako, Y., and Fujimura, K. 2000. Shape similarity by homotropic deformation. The Visual Computer 16, 1, 47–61.
60. Santambrogio, F. 2015. Optimal Transport for Applied Mathematicians. Springer International Publishing.
61. Solomon, J., De Goes, F., Peyré, G., Cuturi, M., Butscher, A., Nguyen, A., Du, T., and Guibas, L. 2015. Convolutional Wasserstein distances: Efficient optimal transportation on geometric domains. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4, 66.
62. Su, Z., Wang, Y., Shi, R., Zeng, W., Sun, J., Luo, F., and Gu, X. 2015. Optimal mass transport for shape matching and comparison. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence 37, 11, 2246–2259.
63. Su, K., Chen, W., Lei, N., Cui, L., Jiang, J., and Gu, X. D. 2016. Measure controllable volumetric mesh parameterization. Computer-Aided Design 78, 188–198.
64. Surazhsky, V., and Surazhsky, T. 2005. Fast exact and approximate geodesics on meshes. ACM Trans. Graph 24, 553–560.
65. Villani, C. 2008. Optimal transport: old and new, vol. 338. Springer Science & Business Media.
66. Xin, S.-Q., and Wang, G.-J. 2009. Improving Chen and Han’s algorithm on the discrete geodesic problem. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 4, 104.
67. Xin, S.-Q., Wang, X., Xia, J., Mueller-Wittig, W., Wang, G.-J., and He, Y. 2013. Parallel computing 2D Voronoi diagrams using untransformed sweepcircles. Computer-Aided Design 45, 2, 483–493.
68. Yan, D.-M., Guo, J.-W., Wang, B., Zhang, X.-P., and Wonka, P. 2015. A survey of blue-noise sampling and its applications. Journal of Computer Science and Technology 30, 3, 439–452. Cross Ref
69. Yee, Y. L. H. 2000. Spatiotemporal sensistivity and visual attention for efficient rendering of dynamic environments. Master’s thesis, Cornell University.
70. Ying, X., Wang, X., and He, Y. 2013. Saddle vertex graph (svg): A novel solution to the discrete geodesic problem. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 6, 2504–2507.
71. Ying, X., Xin, S. Q., and He, Y. 2013. Parallel Chen-Han (PCH) algorithm for discrete geodesics. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 1, 57–76.
72. Zhang, S., Guo, J., Zhang, H., Jia, X., Yan, D. M., Yong, J., and Wonka, P. 2016. Capacity constrained blue-noise sampling on surfaces. Computers & Graphics 55, C, 44–54.
73. Zhao, X., Su, Z., Gu, X. D., Kaufman, A., Sun, J., Gao, J., and Luo, F. 2013. Area-preservation mapping using optimal mass transport. IEEE Transactions on Visualization & Computer Graphics 19, 12, 2838–47.
74. Zhou, Y., Ju, L., and Wang, S. 2015. Multiscale superpixels and supervoxels based on hierarchical edge-weighted centroidal voronoi tessellation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 24, 11, 3834–45. Cross Ref