“A polynomial particle-in-cell method” by Fu, Guo, Gast, Jiang and Teran
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- A polynomial particle-in-cell method
Session/Category Title:
- Fluids in Particular
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
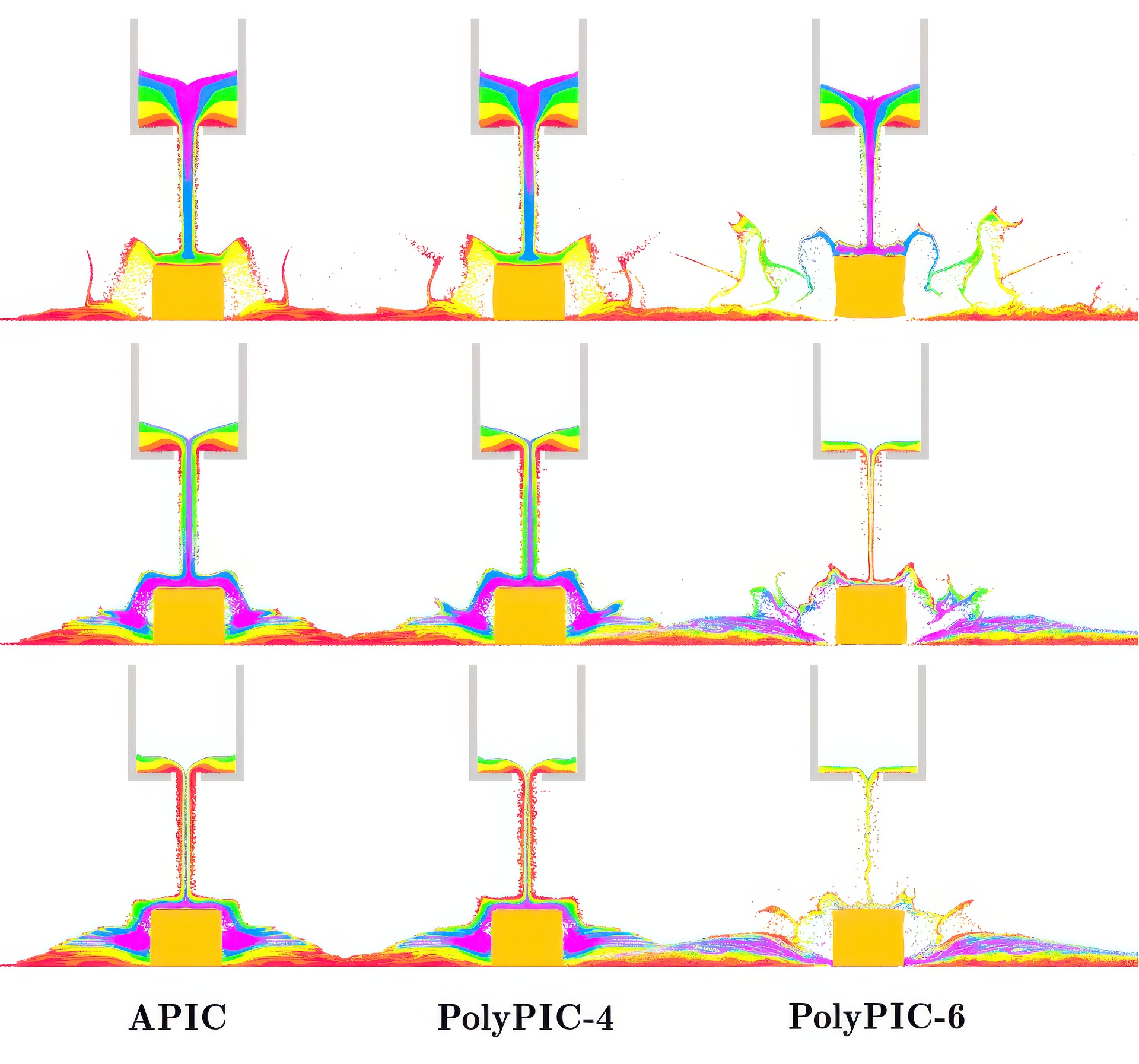
Recently the Affine Particle-In-Cell (APIC) Method was proposed by Jiang et al.[2015; 2017b] to improve the accuracy of the transfers in Particle-In-Cell (PIC) [Harlow 1964] techniques by augmenting each particle with a locally affine, rather than locally constant description of the velocity. This reduced the dissipation of the original PIC without suffering from the noise present in the historic alternative, Fluid-Implicit-Particle (FLIP) [Brackbill and Ruppel 1986]. We present a generalization of APIC by augmenting each particle with a more general local function. By viewing the grid-to-particle transfer as a linear and angular momentum conserving projection of the particle-wise local grid velocities onto a reduced basis, we greatly improve the energy and vorticity conservation over the original APIC. Furthermore, we show that the cost of the generalized projection is negligible over APIC when using a particular class of local polynomial functions. Lastly, we note that our method retains the filtering property of APIC and PIC and thus has similar robustness to noise.
References:
1. R. Ando, N. Thuerey, and C. Wojtan. 2015. A Stream Function Solver for Liquid Simulations. ACM Trans Graph 34 (2) (August 2015), 8.
2. R. Ando, N. Thurey, and R. Tsuruno. 2012. Preserving Fluid Sheets with Adaptively Sampled Anisotropic Particles. IEEE Trans Vis Comp Graph 18, 8 (Aug. 2012), 1202–1214.
3. R. Ando, N. Thurey, and C. Wojtan. 2013. Highly adaptive liquid simulations on tetrahedral meshes. ACM Trans Graph 32, 4 (2013), 103:1–103:10.
4. R. Ando and R. Tsuruno. 2011. A particle-based method for preserving fluid sheets. In Proc ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp Comp Anim (SCA ’11). 7–16.
5. C. Batty, F. Bertails, and R. Bridson. 2007. A fast variational framework for accurate solid-fluid coupling. ACM Trans Graph 26, 3 (2007).
6. C. Batty and R. Bridson. 2008. Accurate viscous free surfaces for buckling, coiling, and rotating liquids. Proc ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurograph Symp Comp Anim (2008), 219–228.
7. L. Boyd and R. Bridson. 2012. MultiFLIP for energetic two-phase fluid simulation. ACM Trans Graph 31, 2 (2012), 16:1–16:12.
8. J. Brackbill. 1988. The ringing instability in Particle-In-Cell calculations of low-speed flow. J Comp Phys 75, 2 (1988), 469–492.
9. J. Brackbill and H. Ruppel. 1986. FLIP: A method for adaptively zoned, Particle-In-Cell calculations of fluid flows in two dimensions. J Comp Phys 65 (1986), 314–343.
10. N. Chentanez and M. Muller. 2014. Coupling 3D Eulerian, height field and particle methods for the simulation of large scale liquid phenomena. In Proc ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurograph Symp Comp Anim (SCA ’14).
11. G. Daviet and F. Bertails-Descoubes. 2016. A Semi-implicit Material Point Method for the Continuum Simulation of Granular Materials. ACM Trans Graph 35, 4 (2016), 102:1–102:13.
12. M. Desbrun and M. Cani. 1996. Smoothed Particles: A new paradigm for animating highly deformable bodies. In Eurographics Workshop on Computer Animation and Simulation (EGCAS), R. Boulic and G. Hegron (Eds.). Springer-Verlag, 61–76.
13. E. Edwards and R. Bridson. 2012. A high-order accurate Particle-In-Cell method. Int J Numer Meth Eng 90 (2012), 1073–1088. Cross Ref
14. Y. Fan, J. Litven, D. Levin, and D. Pai. 2013. Eulerian-on-lagrangian Simulation. ACM Trans Graph 32, 3 (2013), 22:1–22:9.
15. F. Ferstl, R. Ando, C. Wojtan, R. Westermann, and N. Thuerey. 2016. Narrow Band FLIP for Liquid Simulations. Comp Graph For 35 (2) (May 2016), 8.
16. N. Foster and D. Metaxas. 1996. Realistic animation of liquids. Graph Mod Imag Proc 58 (1996), 471–483.
17. C. Fu, Q. Guo, T. Gast, C. Jiang, and J. Teran. 2014. Material Point Method for Coupled Hydromechanical Problems. Supplementary Technical Document (2014).
18. Y. Gao, C. Li, S. Hu, and B. Barsky. 2009. Simulating gaseous fluids with low and high speeds. Comp Graph Forum 28, 28 (2009), 1845–1852. Cross Ref
19. D. Gerszewski and A. Bargteil. 2013. Physics-based Animation of Large-scale Splashing Liquids. ACM Trans Graph 32, 6 (2013), 185:1–185:6.
20. O. Gonzalez and A. Stuart. 2008. A first course in continuum mechanics. Cambridge University Press.
21. C. Gritton and M. Berzins. 2017. Improving accuracy in the MPM method using a null space filter. Comp Part Mech 4, 1 (2017), 131–142. Cross Ref
22. C. Hammerquist and J. Nairn. 2017. A new method for material point method particle updates that reduces noise and enhances stability. Comp Meth App Mech Eng 318 (2017), 724 — 738. Cross Ref
23. F. Harlow. 1964. The particle-in-cell method for numerical solution of problems in fluid dynamics. Meth Comp Phys 3 (1964), 319–343.
24. F. Harlow and E. Welch. 1965. Numerical Calculation of Time Dependent Viscous Flow of Fluid with a Free Surface. Phys Fluid 8, 12 (1965), 2182–2189. Cross Ref
25. W. Hong, D. House, and J. Keyser. 2008. Adaptive particles for incompressible fluid simulation. Vis Comp 24, 7 (2008), 535–543.
26. W. Hong, D. House, and J. Keyser. 2009. An adaptive sampling approach to incompressible particle-based fluid. Theory Pract Comp Graph (2009), 69–76.
27. C. Jiang, T. Gast, and J. Teran. 2017a. Anisotropic elastoplasticity for cloth, knit and hair frictional contact. ACM Trans Graph 36, 4 (2017).
28. C. Jiang, C. Schroeder, A. Selle, J. Teran, and A. Stomakhin. 2015. The Affine Particle-In-Cell Method. ACM Trans Graph 34, 4 (2015), 51:1–51:10.
29. C. Jiang, C. Schroeder, and J. Teran. 2017b. An angular momentum conserving affine-particle-in-cell method. J Comp Phys 338 (2017), 137 — 164.
30. G. Klár, T. Gast, A. Pradhana, C. Fu, C. Schroeder, C. Jiang, and J. Teran. 2016. Drucker-prager Elastoplasticity for Sand Animation. ACM Trans Graph 35, 4 (2016), 103:1–103:12.
31. E. Larionov, C. Batty, and R. Bridson. 2017. Variational Stokes: A Unified Pressure-Viscosity Solver for Accurate Viscous Liquids. ACM Trans Graph 36, 4 (2017).
32. H. Lee, J. Hong, and C. Kim. 2009. Interchangeable SPH and level set method in multiphase fluids. Vis Comp 25, 5 (2009), 713–718.
33. D. Levin, J. Litven, G. Jones, S. Sueda, and D. Pai. 2011. Eulerian Solid Simulation with Contact. ACM Trans Graph 30, 4 (2011), 36:1–36:10.
34. F. Losasso, J. Talton, N. Kwatra, and R. Fedkiw. 2008. Two-way coupled SPH and Particle Level Set fluid simulation. IEEE Trans Vis Comp Graph 14 (2008), 797–804.
35. A. McAdams, A. Selle, K. Ward, E. Sifakis, and J. Teran. 2009. Detail Preserving Continuum Simulation of Straight Hair. ACM Trans Graph 28, 3 (2009), 62:1–62:6.
36. O. Mercier, C. Beauchemin, N. Thuerey, T. Kim, and D. Nowrouzezahrai. 2015. Surface Turbulence for Particle-Based Liquid Simulations. ACM Trans Graph 34 (6) (Nov 2015), 10.
37. R. Narain, A. Golas, S. Curtis, and M. Lin. 2009. Aggregate Dynamics for Dense Crowd Simulation. ACM Trans Graph 28, 5 (2009), 122:1–122:8.
38. R. Narain, A. Golas, and M. Lin. 2010. Free-flowing granular materials with two-way solid coupling. ACM Trans Graph 29, 6 (2010), 173:1–173:10.
39. D. Ram, T. Gast, C. Jiang, C. Schroeder, A. Stomakhin, J. Teran, and P. Kavehpour. 2015. A material point method for viscoelastic fluids, foams and sponges. In Proc ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurograph Symp Comp Anim. 157–163.
40. K. Raveendran, C. Wojtan, and G. Turk. 2011. Hybrid SPH. In Proc 2011 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurograp Symp Comp Anim (SCA ’11). 33–42.
41. Wolfram Research. 2016. Mathematica 11.0. (2016).
42. M. Steffen, R. Kirby, and M. Berzins. 2008. Analysis and reduction of quadrature errors in the material point method (MPM). Int J Numer Meth Eng 76, 6 (2008), 922–948. Cross Ref
43. A. Stomakhin, C. Schroeder, L. Chai, J. Teran, and A. Selle. 2013. A Material Point Method for snow simulation. ACM Trans Graph 32, 4 (2013), 102:1–102:10.
44. A. Stomakhin, C. Schroeder, C. Jiang, L. Chai, J. Teran, and A. Selle. 2014. Augmented MPM for phase-change and varied materials. ACM Trans Graph 33, 4 (2014), 138:1–138:11.
45. D. Sulsky, Z. Chen, and H. Schreyer. 1994. A particle method for history-dependent materials. Comp Meth App Mech Eng 118, 1 (1994), 179–196. Cross Ref
46. D. Sulsky, S. Zhou, and H. Schreyer. 1995. Application of a particle-in-cell method to solid mechanics. Comp Phys Comm 87, 1 (1995), 236–252. Cross Ref
47. A. P. Tampubolon, T. Gast, G. Klár, C. Fu, J. Teran, C. Jiang, and K. Museth. 2017. Multi-species simulation of porous sand and water mixtures. ACM Trans Graph 36, 4 (2017).
48. Y. Teng, D. Levin, and T. Kim. 2016. Eulerian Solid-fluid Coupling. ACM Trans Graph 35, 6 (2016), 200:1–200:8.
49. N. Thuerey and T. Pfaff. 2016. MantaFlow. (2016). http://mantaflow.com.
50. K. Um, S. Baek, and J. Han. 2014. Advanced hybrid particle-grid method with sub-grid particle correction. Comp Graph Forum 33 (2014), 209–218.
51. P. Wallstedt and J. Guilkey. 2007. Improved velocity projection for the material point method. Comp Mod in Eng and Sci 19, 3 (2007), 223.
52. Y. Yue, B. Smith, C. Batty, C. Zheng, and E. Grinspun. 2015. Continuum foam: a material point method for shear-dependent flows. ACM Trans Graph 34, 5 (2015), 160:1–160:20.
53. X. Zhang, M. Li, and R. Bridson. 2016. Resolving fluid boundary layers with particle strength exchange and weak adaptivity. ACM Trans Graph (TOG) 35, 4 (2016), 76.
54. B. Zhu, X. Yang, and Y. Fan. 2010. Creating and preserving vortical details in SPH fluid. Comp Graph Forum 29, 7 (2010), 2207–2214. Cross Ref
55. F. Zhu, J. Zhao, S. Li, Y. Tang, and G. Wang. 2016. Dynamically Enriched MPM for Invertible Elasticity. In Comp Graph For. Wiley Online Library.
56. Y. Zhu and R. Bridson. 2005. Animating sand as a fluid. ACM Trans Graph 24, 3 (2005), 965–972.