“PCCD: parallel continuous collision detection” by Kim, Heo and Yoon
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- PCCD: parallel continuous collision detection
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
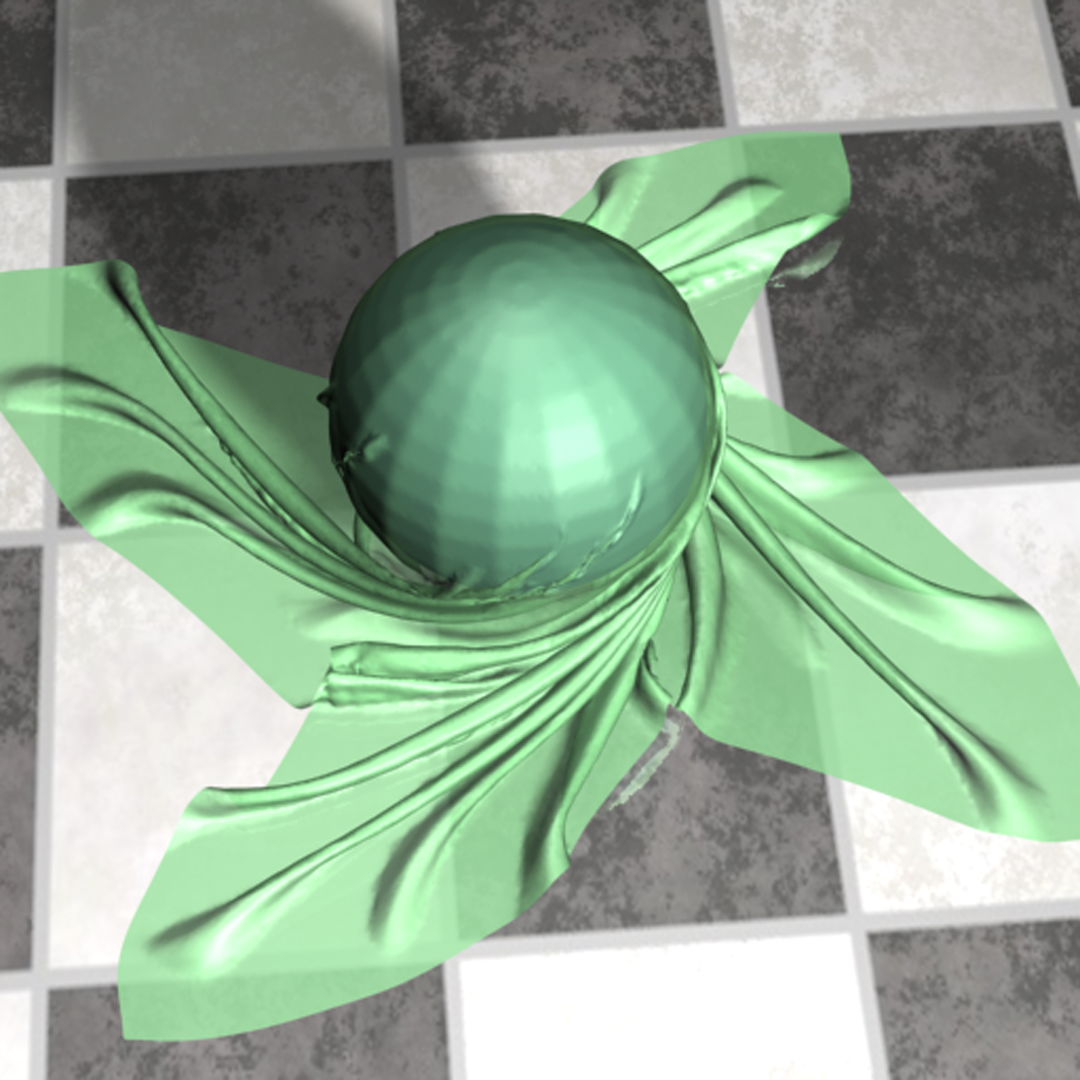
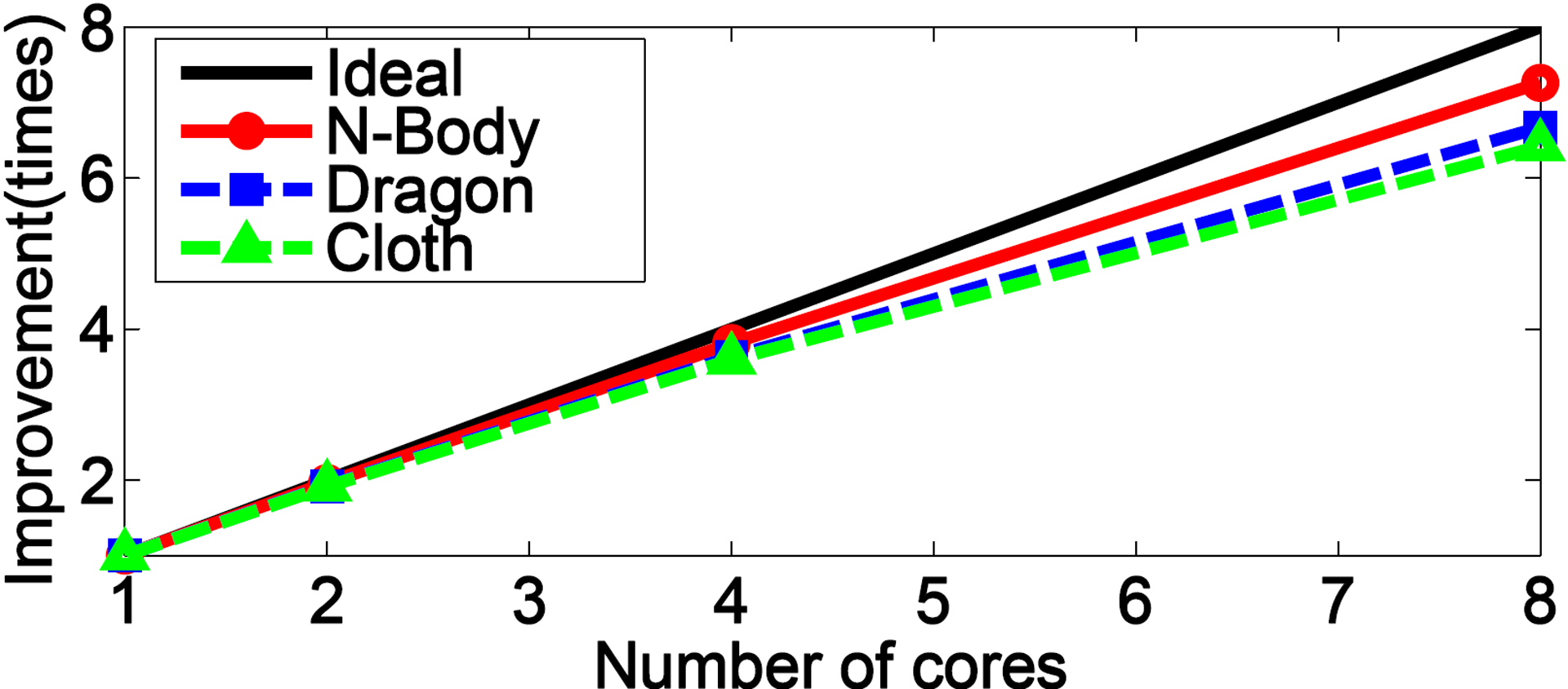
Collision detection between deformable models is one of fundamental tools of various applications including games. Collision detection can be classified into two categories: discrete and continuous collision detection methods. Discrete collision detection (DCD) has been demonstrated to show the interactive performance by using bounding volume hierarchies (BVHs). However, some colliding primitives may be missed since DCD methods find intersecting primitives only at discrete time steps. This issue can be a very serious problem in physical based simulation, CAD/CAM applications and etc. On the other hand, continuous collision detection (CCD) identifies the first time of contact of colliding primitives during a time interval between two discrete time steps.
References:
1. Asanovic, K., R., Catanzaro, B., Gebis, J., Husbands, P., K., Patterson, D., Plishker, W., Shalf, J., Williams, S., and Yelick, K. 2006. The landscape of parallel computing research: A view from Berkeley. Tech. Rep. UCB/EECS-2006-183, EECS Dept., Univ. of California, Berkeley.
2. Curtis, S., Tamstorf, R., and Manocha, D. 2008. Fast collision detection for deformable models using representative-triangles. Symp. on Interactive 3D Graphics, 61–69.
3. Sud, A., Govindaraju, N., Gayle, R., Kabul, I., and Manocha, D. 2006. Fast proximity computation among deformable models using discrete voronoi diagrams. Proc. of ACM SIGGRAPH, 1144–1153.