“Sparse cholesky updates for interactive mesh parameterization” by Herholz and Sorkine-Hornung
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Sparse cholesky updates for interactive mesh parameterization
Session/Category Title:
- Digital Geometry Processing
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
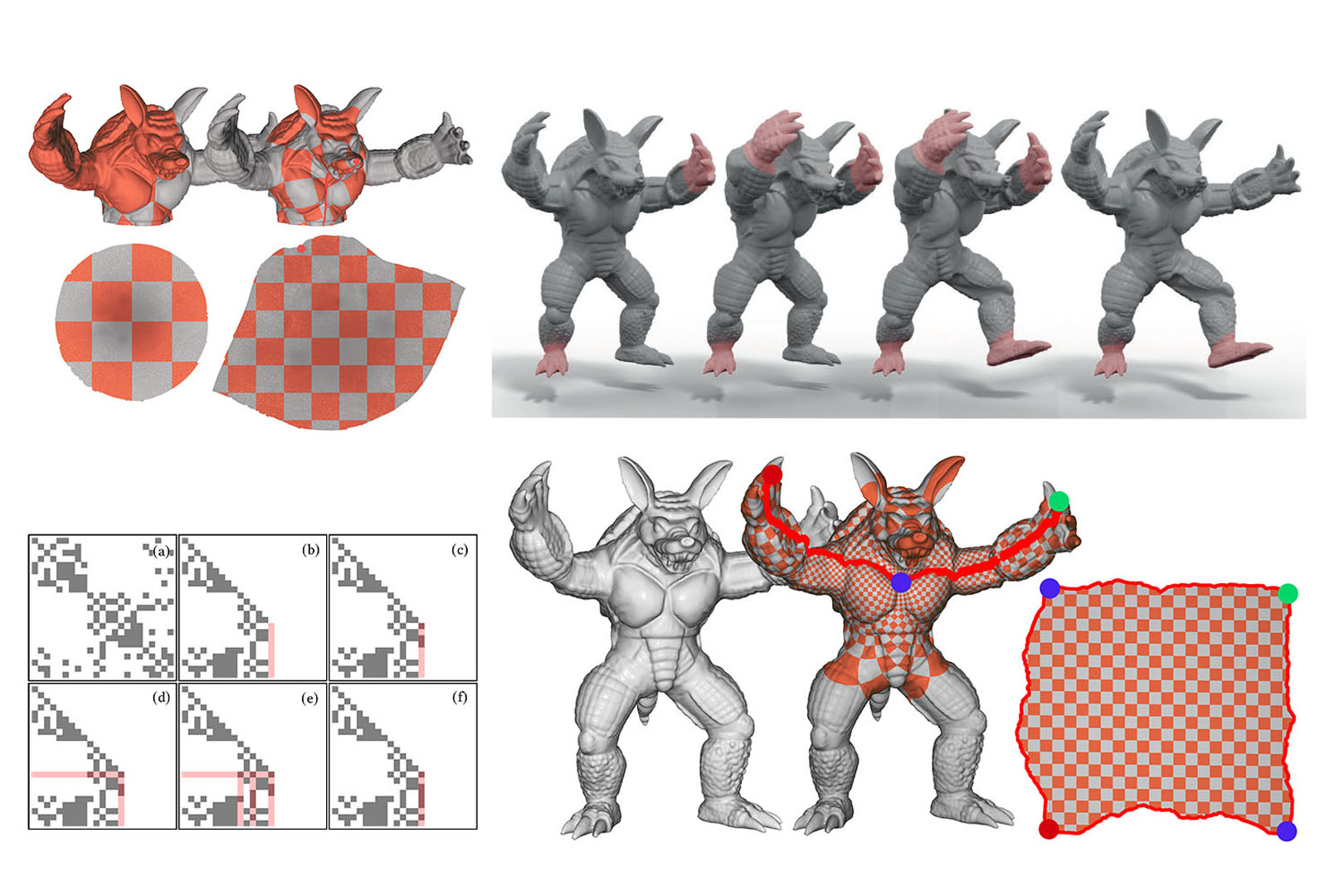
We present a novel linear solver for interactive parameterization tasks. Our method is based on the observation that quasi-conformal parameterizations of a triangle mesh are largely determined by boundary conditions. These boundary conditions are typically constructed interactively by users, who have to take several artistic and geometric constraints into account while introducing cuts on the geometry. Commonly, the main computational burden in these methods is solving a linear system every time new boundary conditions are imposed. The core of our solver is a novel approach to efficiently update the Cholesky factorization of the linear system to reflect new boundary conditions, thereby enabling a seamless and interactive workflow even for large meshes consisting of several millions of vertices.
References:
1. Noam Aigerman, Shahar Z. Kovalsky, and Yaron Lipman. 2017. Spherical Orbifold Tutte Embeddings. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4, Article 90 (July 2017), 13 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Mario Botsch and Olga Sorkine. 2008a. On Linear Variational Surface Deformation Methods. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 14, 1 (Jan 2008), 213–230. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Mario Botsch and Olga Sorkine. 2008b. On linear variational surface deformation methods. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 14, 1 (2008), 213–230.Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Yanqing Chen, Timothy A. Davis, William W. Hager, and Sivasankaran Rajamanickam. 2008. Algorithm 887: CHOLMOD, Supernodal Sparse Cholesky Factorization and Update/Downdate. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 35, 3, Article 22 (Oct. 2008), 14 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Jieyu Chu, Nafees Bin Zafar, and Xubo Yang. 2017. A Schur Complement Preconditioner for Scalable Parallel Fluid Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 5, Article 163 (July 2017), 11 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Timothy A. Davis. 2004. Algorithm 832: UMFPACK V4.3—an Unsymmetric-Pattern Multifrontal Method. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 30, 2 (June 2004), 196–199. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Timothy A. Davis. 2006. Direct Methods for Sparse Linear Systems. SIAM, Philadelphia, PA.Google Scholar
8. Timothy A. Davis and W. Hager. 1999. Modifying a Sparse Cholesky Factorization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 20, 3 (1999), 606–627. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Timothy A. Davis and William W. Hager. 2000. Multiple-Rank Modifications of a Sparse Cholesky Factorization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 22, 4 (July 2000), 997–1013. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Timothy A. Davis and William W. Hager. 2005. Row Modifications of a Sparse Cholesky Factorization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 26, 3 (2005), 621–639. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Timothy A. Davis and William W. Hager. 2009. Dynamic Supernodes in Sparse Cholesky Update/Downdate and Triangular Solves. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 35, 4, Article 27 (Feb. 2009), 23 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Timothy A Davis, Sivasankaran Rajamanickam, and Wissam M Sid-Lakhdar. 2016. A survey of direct methods for sparse linear systems. Acta Numerica 25 (2016), 383–566.Google ScholarCross Ref
13. Robert D. Falgout, Jim E. Jones, and Ulrike Meier Yang. 2006. The Design and Implementation of hypre, a Library of Parallel High Performance Preconditioners. In Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations on Parallel Computers, Are Magnus Bruaset and Aslak Tveito (Eds.). Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, 267–294.Google Scholar
14. Phillip E. Gill, Gene H. Golub, Walter A. Murray, and Michael A. Saunders. 1972. Methods for Modifying Matrix Factorizations. Technical Report. Stanford, CA, USA.Google Scholar
15. Gaël Guennebaud, Benoît Jacob, et al. 2010. Eigen v3. http://eigen.tuxfamily.org.Google Scholar
16. Florian Hecht, Yeon Jin Lee, Jonathan R. Shewchuk, and James F. O’Brien. 2012. Updated Sparse Cholesky Factors for Corotational Elastodynamics. ACM Transactions on Graphics 31, 5 (oct 2012), 123:1–13. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Philipp Herholz and Marc Alexa. 2018. Factor Once: Reusing Cholesky Factorizations on Sub-Meshes. ACM Transaction on Graphics (Proc. of Siggraph Asia) 37, 6 (2018), 9. Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Philipp Herholz and Marc Alexa. 2019. Efficient Computation of Smoothed Exponential Maps. Computer Graphics Forum 38, 6 (2019), 79–90. Google ScholarCross Ref
19. Philipp Herholz, Timothy A. Davis, and Marc Alexa. 2017. Localized Solutions of Sparse Linear Systems for Geometry Processing. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 6, Article 183 (Nov. 2017), 8 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Intel. 2009. Intel Math Kernel Library. Reference Manual.Google Scholar
21. George Karypis and Vipin Kumar. 1998. A Fast and High Quality Multilevel Scheme for Partitioning Irregular Graphs. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 20, 1 (1998), 359–392. Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Haixiang Liu, Nathan Mitchell, Mridul Aanjaneya, and Eftychios Sifakis. 2016. A Scalable Schur-Complement Fluids Solver for Heterogeneous Compute Platforms. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 6, Article 201 (Nov. 2016), 12 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Haggai Maron, Meirav Galun, Noam Aigerman, Miri Trope, Nadav Dym, Ersin Yumer, Vladimir G. Kim, and Yaron Lipman. 2017. Convolutional Neural Networks on Surfaces via Seamless Toric Covers. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4, Article 71 (July 2017), 10 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Matthias Müller and Markus Gross. 2004. Interactive Virtual Materials. In Proceedings of Graphics Interface 2004 (London, Ontario, Canada) (GI ’04). Canadian HumanComputer Communications Society, Waterloo, CAN, 239–246.Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Jorge Nocedal and Stephen Wright. 2006. Numerical optimization. Springer Science & Business Media.Google Scholar
26. Rohan Sawhney and Keenan Crane. 2017. Boundary First Flattening. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 1, Article 5 (Dec. 2017), 14 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Olga Sorkine and Marc Alexa. 2007. As-rigid-as-possible Surface Modeling. In Proceedings of the Fifth Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing (Barcelona, Spain) (SGP ’07). Eurographics Association, Aire-la-Ville, Switzerland, Switzerland, 109–116.Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Olga Sorkine, Daniel Cohen-Or, Dror Irony, and Sivan Toledo. 2005. Geometry-Aware Bases for Shape Approximation. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 11, 2 (2005), 171–180.Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Yu-Hong Yeung, Jessica Crouch, and Alex Pothen. 2016. Interactively Cutting and Constraining Vertices in Meshes Using Augmented Matrices. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 2, Article 18 (Feb. 2016), 17 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Yu-Hong Yeung, Alex Pothen, and Jessica Crouch. 2018. AMPS: A Real-time Mesh Cutting Algorithm for Surgical Simulations. arXiv:1811.00328 [cs.CE]Google Scholar