“Retinal 3D: augmented reality near-eye display via pupil-tracked light field projection on retina”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Retinal 3D: augmented reality near-eye display via pupil-tracked light field projection on retina
Session/Category Title:
- Displays
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
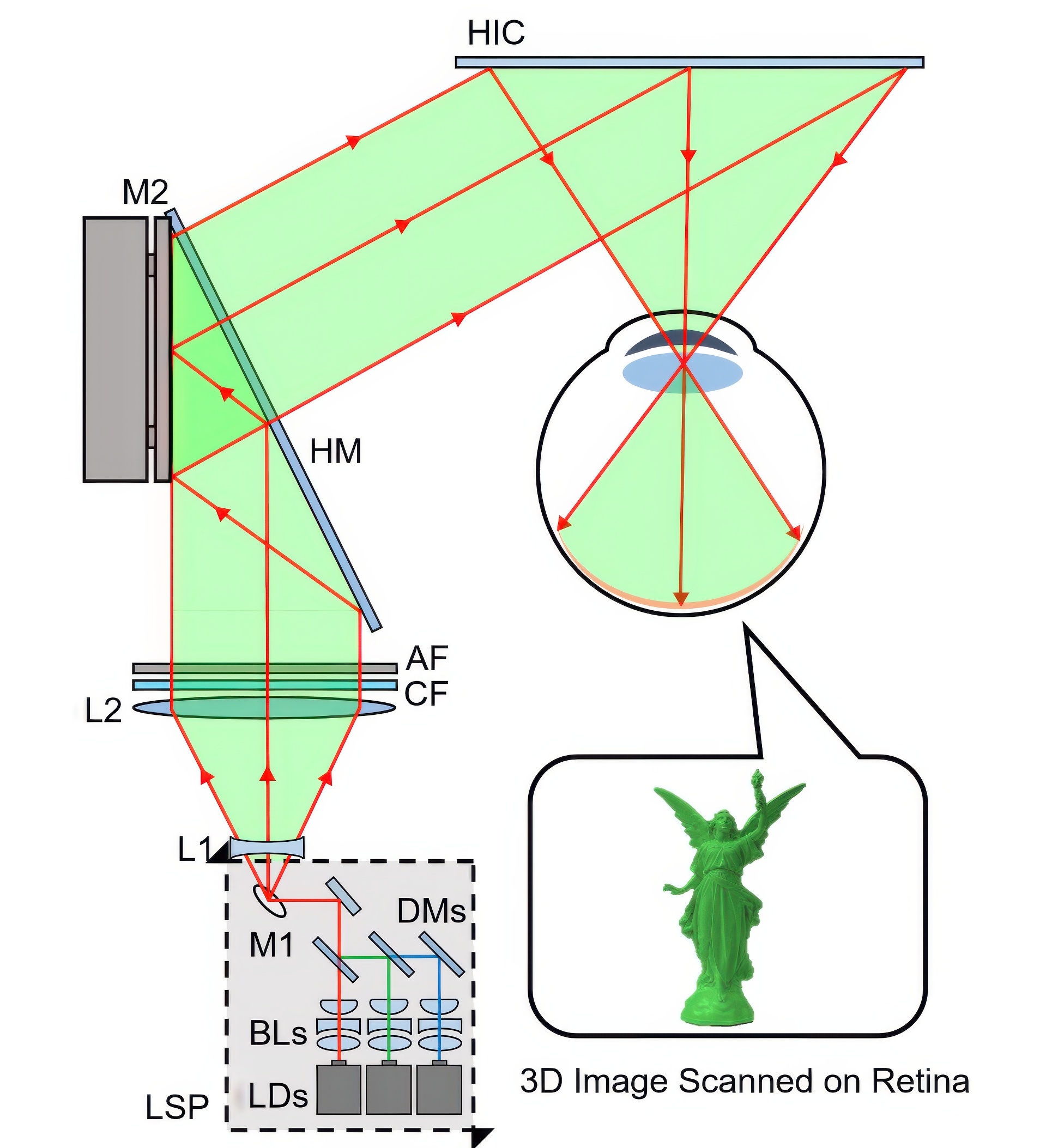
We introduce an augmented reality near-eye display dubbed “Retinal 3D.” Key features of the proposed display system are as follows: Focus cues are provided by generating the pupil-tracked light field that can be directly projected onto the retina. Generated focus cues are valid over a large depth range since laser beams are shaped for a large depth of field (DOF). Pupil-tracked light field generation significantly reduces the needed information/computation load. Also, it provides “dynamic eye-box” which can be a break-through that overcome the drawbacks of retinal projection-type displays. For implementation, we utilized a holographic optical element (HOE) as an image combiner, which allowed high transparency with a thin structure. Compared with current augmented reality displays, the proposed system shows competitive performances of a large field of view (FOV), high transparency, high contrast, high resolution, as well as focus cues in a large depth range. Two prototypes are presented along with experimental results and assessments. Analysis on the DOF of light rays and validity of focus cue generation are presented as well. Combination of pupil tracking and advanced near-eye display technique opens new possibilities of the future augmented reality.
References:
1. Richard A. Abrains, David E. Meyer, and Sylvan Kornblum. 1989. Speed and accuracy of saccadic eye movements: characteristics of impulse variability in the oculomotor system. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 15, 3 (1989), 529–543. Cross Ref
2. R. T. Azuma. 1997. A survey of augmented reality. Presence: Teleoperators and virtual environments 6, 4 (1997), 335–385.
3. T. Blum, M. Wieczorek, A. Aichert, R. Tibrewal, and N. Navab. 2010. The effect of out-of-focus blur on visual discomfort when using stereo displays. In In Proceedings of the IEEE Science and Technology International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality. IEEE, Los Alamitos, CA.
4. Peter D. Burns. 2000. Slanted-Edge MTF for digital camera and scanner analysis. Proc. IS&T 2000 PICS Conference (2000), 135–138.
5. D. H. Close. 1975. Holographic optical elements. Opt. Eng. 14, 5 (1975), 145402. Cross Ref
6. Hans J. Coufal, Demetri Psaltis, and Glenn T. Sincerbox. 2000. Holographic Data Storage. Springer-Verlag.
7. U. Hofmann, J. Janes, and H. J. Quenzer. 2012. High-Q MEMS resonators for laser beam scanning displays. Micromachines 3 (2012), 509–528. Cross Ref
8. K. Hong, J. Yeom, C. Jang, J. Hong, and B. Lee. 2014. Full color lens-array holographic optical element for three dimensional optical see-through augmented reality. Opt. Lett. 39, 1 (Jan. 2014), 127–130. Cross Ref
9. Mei-Li Hsieh and Ken Y. Hsu. 2001. Grating detuning effect on holographic memory in photopolymers. Opt. Eng. 40, 10 (2001), 2125–2133. Cross Ref
10. Hong Hua and Bahram Javidi. 2014. A 3d integral imaging optical see-through head-mounted display. Opt. Express 22, 11 (June 2014), 13484–13492. Cross Ref
11. Fu-Chung Huang, Kevin Chen, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2015. The light field stereoscope immersive computer graphics via factored near-eye light field displays with focus cues. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4 (2015), 60.
12. F.-C. Huang, G. Wetzstein, B. A. Barsky, and R. Raskar. 2014. Eyeglasses-free display: Towards correcting visual aberrations with computational light field displays. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (2014), 59:1–59:12.
13. C. Jang, C.-K. Lee, J. Jeong, G. Li, S. Lee, J. Yeom, K. Hong, and B. Lee. 2016. Recent progress in see-through three-dimensional displays using holographic optical elements. Appl. Opt. 55, 3 (Jan. 2016), A71–A85. Cross Ref
14. D.-W. Kim, Y.-M. Kwon, Q.-H. Park, and S.-K. Kim. 2011. Analysis of a head-mounted display-type multifocus display system using a laser scanning method. Opt. Eng. 50, 3 (2011), 034006. Cross Ref
15. Joel Kollin. 1993. A retinal display for virtual-environment applications. SID International Symposium Digest of Technical Papers 24 (1993), 827.
16. Bernard Kress and Thad Starner. 2013. A review of head-mounted displays (HMD) technologies and applications for consumer electronics. In Proceedings of SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, International Society for Optics and Photonics 87200A (2013). Cross Ref
17. M. Lambooij, Marten. Fortuin, Ingrid Heynderickx, and Wijnand IJsselsteijn. 2009. Visual discomfort and visual fatigue of stereoscopic displays: a review. J. Imaging Sci. Technol. 53, 3 (2009), 30201–1. Cross Ref
18. Seungjae Lee, Changwon Jang, Seokil Moon, Jaebum Cho, and Byoungho Lee. 2016. Additive Light Field displays: Realization of Augmented Reality with Holographic Optical Elements. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 4 (July 2016), 60.
19. Laure Leroy, Philippe Fuchs, and Guillaume Moreau. 2012. Real-time adaptive blur for reducing eye strain in stereoscopic displays. ACM Transactions on Applied Perception (TAP) 9, 2, Article 9 (June 2012).
20. Sheng Liu and Hong Hua. 2010a. A novel prototype for an optical see-through head-mounted display with addressable focus cues. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 16, 3 (2010), 381–393.
21. Sheng Liu and Hong Hua. 2010b. A systematic method for designing depth-fused multi-focal plane three-dimensional displays. Opt. Express 18, 11 (2010), 11562–11573. Cross Ref
22. Andrew Maimone, Andreas Georgiou, and Joel S. Kollin. 2017. Holographic Near-Eye Displays for Virtual and Augmented Reality. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (July 2017), 85:1–85:16.
23. Steven Mathews and Philip B. Kruger. 1994. Spatiotemporal transfer function of human accommodation. Vision Research 34, 15 (Aug. 1994), 1965–1980. Cross Ref
24. S.C. McQaide, E. J. Seibel, J. P. Kelly, B. T. Schowengerdt, and T. A. Furness. 2013. A retinal scanning display system that produces multiple focal planes with a deformable membrane mirror. Displays 24 (2013), 65–72. Cross Ref
25. R. Michael, O. Guevara, M. de la Paz, J. A. de Toledo, and R. I. Barraquer. 2011. Neural contrast sensitivity calculated from measured total contrast sensitivity and modulation transfer function. Acta ophthalmologica 89, 3 (2011), 278–283.
26. R. Narain, R. A. Albert, A. Bulbul, G. J. Ward, M. S. Banks, and J. F. O’Brien. 2015. Optimal presentation of imagery with focus cues on multi-plane displays. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4 (Aug. 2015), 59.
27. N. A. Polak and R. Jones. 1990. Dynamic interactions between accommodation and convergence. IEEE Trans on Biomed Eng. 37, 10 (Oct. 1990), 1011–1014. Cross Ref
28. Sowmya Ravikumar, Kurt Akeley, and Martin S. Banks. 2011. Creating effective focus cues in multi-plane 3D displays. Opt. Express 19, 21 (Oct. 2011), 20940–20952. Cross Ref
29. Bahaa E. A. Saleh and Malvin C. Teich. 1991. Fundamentals of Photonics. New York: Wiley.
30. Yasuhiro Takaki and Nichiyo Nago. 2010. Multi-projection of lenticular displays to construct a 256-view super multi-view display. Opt. Express 18, 9 (April 2010), 8824–8835. Cross Ref
31. Yasuhiro Takaki and Yuta Yamaguchi. 2015. Flat-panel see-through three-dimensional display based on integral imaging. Opt. Lett 40, 8 (April 2015), 1873–1876. Cross Ref
32. Marc von Waldkirch, Paul Lukowicz, and Gerhard Tröster. 2003. Defocusing simulations on a retinal scanning display for quasi accommodation free viewing. Opt. Express 11, 24 (2003), 3220. Cross Ref
33. M. Watanabe, T Haruhisa, A. Nobuaki, M Riki, and Y. Shoji. 2003. A retinal scanning display with a wavefront curvature modulator. Journal of the Society for Information Display 11, 3 (2003), 511–515. Cross Ref
34. Gerald Westheimer. 1966. The maxwellian view. Vision Research 6, 11–12 (Dec. 1966), 669–682. Cross Ref
35. G. Wetzstein, D. Lanman, W. Heidrich, and R. Raskar. 2011. Layered 3d: Tomographic image synthesis for attenuation-based light eld and high dynamic range displays. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4 (July 2011).
36. H. J. Yeom, H. J. Kim, S. B. Kim, H. Zhang, B. Li, Y. M. Ji, S. H. Kim, and J. H. Park. 2015. 3D holographic head mounted display using holographic optical elements with astigmatism aberration compensation. Opt. Express 23, 25 (Dec. 2015), 32025–32034. Cross Ref
37. Mo Zohrabi, Robert H. Cormack, and Juliet T. Gopinath. 2016. Wide-angle nonmechanical beam steering using liquid lenses. Opt. Express 24, 21 (2016), 23798–23809. Cross Ref