“Rendering near-field speckle statistics in scattering media” by Bar, Gkioulekas and Levin
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Rendering near-field speckle statistics in scattering media
Session/Category Title:
- Computational Holography
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
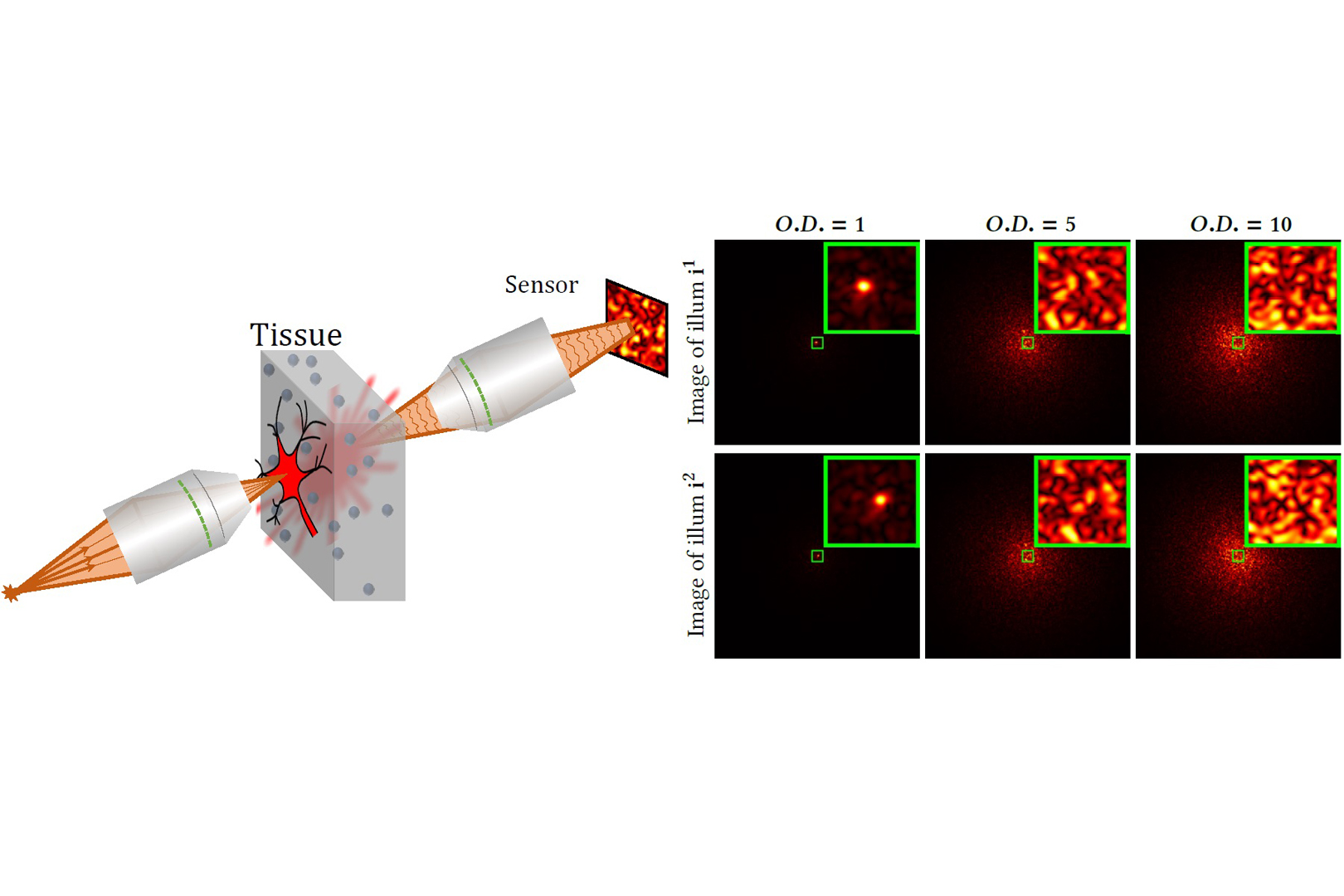
We introduce rendering algorithms for the simulation of speckle statistics observed in scattering media under coherent near-field imaging conditions. Our work is motivated by the recent proliferation of techniques that use speckle correlations for tissue imaging applications: The ability to simulate the image measurements used by these speckle imaging techniques in a physically-accurate and computationally-efficient way can facilitate the widespread adoption and improvement of these techniques. To this end, we draw inspiration from recently-introduced Monte Carlo algorithms for rendering speckle statistics under far-field conditions (collimated sensor and illumination). We derive variants of these algorithms that are better suited to the near-field conditions (focused sensor and illumination) required by tissue imaging applications. Our approach is based on using Gaussian apodization to approximate the sensor and illumination aperture, as well as von Mises-Fisher functions to approximate the phase function of the scattering material. We show that these approximations allow us to derive closed-form expressions for the focusing operations involved in simulating near-field speckle patterns. As we demonstrate in our experiments, these approximations accelerate speckle rendering simulations by a few orders of magnitude compared to previous techniques, at the cost of negligible bias. We validate the accuracy of our algorithms by reproducing ground truth speckle statistics simulated using wave-optics solvers, and real-material measurements available in the literature. Finally, we use our algorithms to simulate biomedical imaging techniques for focusing through tissue.
References:
1. David Abookasis and Joseph Rosen. 2004. NOISE 2 imaging system: seeing through scattering tissue with a reference point. Opt. Lett. (2004).Google Scholar
2. Eric Akkermans and Gilles Montambaux. 2007. Mesoscopic Physics of Electrons and Photons. Cambridge University Press.Google Scholar
3. Arindam Banerjee, Inderjit S. Dhillon, Joydeep Ghosh, and Suvrit Sra. 2005. Clustering on the unit hypersphere using von Mises-Fisher distributions. JMLR (2005).Google Scholar
4. Chen Bar, Marina Alterman, Ioannis Gkioulekas, and Anat Levin. 2019. A Monte Carlo Framework for Rendering Speckle Statistics in Scattering Media. ACM TOG (2019).Google Scholar
5. Chen Bar, Ioannis Gkioulekas, and Anat Levin. 2020. Project Website. https://github.com/chabner/gaussianBeam-field.Google Scholar
6. Brian A. Barsky and Todd J. Kosloff. 2008. Algorithms for Rendering Depth of Field Effects in Computer Graphics. ICCOMP (2008).Google Scholar
7. Mahed Batarseh, Sergey Sukhov, Zhean Shen, H. Gemar, Roxana Rezvani, and Aristide Dogariu. 2018. Passive sensing around the corner using spatial coherence. Nature Communications (2018).Google Scholar
8. Ibrahim Baydoun, Diego Baresch, Romain Pierrat, and Arnaud Derode. 2016. Radiative transfer of acoustic waves in continuous complex media: Beyond the Helmholtz equation. Physical Review E (2016).Google Scholar
9. Laurent Belcour, Kavita Bala, and Cyril Soler. 2014. A local frequency analysis of light scattering and absorption. ACM TOG (2014).Google Scholar
10. Stephan Bergmann, Mahsa Mohammadikaji, Stephan Irgenfried, Heinz Worn, Jürgen Beyerer, and Carsten Dachsbacher. 2016. A Phenomenological Approach to Integrating Gaussian Beam Properties and Speckle into a Physically-Based Renderer. VMV (2016).Google Scholar
11. Richard Berkovits and Shechao Feng. 1994. Correlations in coherent multiple scattering. Physics Reports (1994).Google Scholar
12. Bruce J. Berne and Robert Pecora. 2000. Dynamic light scattering: with applications to chemistry, biology, and physics. Courier Corporation.Google Scholar
13. Jacopo Bertolotti, Elbert G. Van Putten, Christian Blum, Ad Lagendijk, Willem L. Vos, and Allard P. Mosk. 2012. Non-invasive imaging through opaque scattering layers. Nature (2012).Google Scholar
14. Benedikt Bitterli, Srinath Ravichandran, Thomas Müller, Magnus Wrenninge, Jan Novák, Steve Marschner, and Wojciech Jarosz. 2018. A radiative transfer framework for non-exponential media. ACM TOG (2018).Google Scholar
15. David A. Boas and Arjun G. Yodh. 1997. Spatially varying dynamical properties of turbid media probed with diffusing temporal light correlation. JOSA A (1997).Google Scholar
16. Craig F. Bohren and Donald R. Huffman. 1983. Absorption and scattering of light by small particle. John Wiley & Sons.Google Scholar
17. Julie Chang and Gordon Wetzstein. 2018. Single-shot speckle correlation fluorescence microscopy in thick scattering tissue with image reconstruction priors. Journal of Biophotonics (2018).Google Scholar
18. Wai-Fung Cheong, Scott A. Prahl, and Ashley J. Welch. 1990. A review of the optical properties of biological tissues. IEEE JQE (1990).Google Scholar
19. Youngwoon Choi, Taeseok Daniel Yang, Christopher Fang-Yen, Pilsung Kang, Kyoung Jin Lee, Ramachandra R. Dasari, Michael S. Feld, and Wonshik Choi. 2011. Overcoming the Diffraction Limit Using Multiple Light Scattering in a Highly Disordered Medium. Phys. Rev. Lett. (2011).Google Scholar
20. Tom Cuypers, Tom Haber, Philippe Bekaert, Se Baek Oh, and Ramesh Raskar. 2012. Reflectance Model for Diffraction. ACM TOG (2012).Google Scholar
21. Eugene d’Eon. 2018. A reciprocal formulation of nonexponential radiative transfer. 1: Sketch and motivation. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Transport (2018).Google Scholar
22. Ronald L. Dougherty, Bruce J. Ackerson, Nafaa M. Reguigui, F. Dorri-Nowkoorani, and Ulf Nobbmann. 1994. Correlation transfer: Development and application. JQSRT (1994).Google Scholar
23. Turgut Durduran, Regine Choe, Wesley B. Baker, and Arjun G. Yodh. 2010. Diffuse optics for tissue monitoring and tomography. Reports on Progress in Physics (2010).Google Scholar
24. Eitan Edrei and Giuliano Scarcelli. 2016. Memory-effect based deconvolution microscopy for super-resolution imaging through scattering media. Scientific Reports (2016).Google Scholar
25. Robert K. Erf. 1978. Speckle Metrology. Elsevier.Google Scholar
26. Shechao Feng, Charles Kane, Patrick A. Lee, and A. Douglas Stone. 1988. Correlations and fluctuations of coherent wave transmission through disordered media. Phys. Rev. Lett. (1988).Google Scholar
27. Isaac Freund. 1990. Looking through walls and around corners. Physica A (1990).Google Scholar
28. Isaac Freund and Danny Eliyahu. 1992. Surface correlations in multiple-scattering media. Phys Rev A (1992).Google Scholar
29. David L. Fried. 1982. Anisoplanatism in adaptive optics. JOSA (1982).Google Scholar
30. Jeppe Revall Frisvad, Niels Jørgen Christensen, and Henrik Wann Jensen. 2007. Computing the scattering properties of participating media using Lorenz-Mie theory. ACM TOG (2007).Google Scholar
31. Ioannis Gkioulekas, Shuang Zhao, Kavita Bala, Todd Zickler, and Anat Levin. 2013. Inverse Volume Rendering with Material Dictionaries. ACM TOG (2013).Google Scholar
32. Walter I. Goldburg. 1999. Dynamic light scattering. American Journal of Physics (1999).Google Scholar
33. Joseph W. Goodman. 1968. Introduction to Fourier Optics. McGraw-Hill.Google Scholar
34. Joseph W. Goodman. 2007. Speckle Phenomena in Optics: Theory and Applications. Roberts and Company Pub.Google Scholar
35. Charles Han, Bo Sun, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and Eitan Grinspun. 2007. Frequency domain normal map filtering. ACM TOG (2007).Google Scholar
36. Roarke Horstmeyer, Haowen Ruan, and Changhuei Yang. 2015. Guidestar-assisted wavefront-shaping methods for focusing light into biological tissue. Nature Photonics (2015).Google Scholar
37. Pierre Jacquot and Jean-Marc Fournier. 2000. Interferometry in Speckle Light. Springer.Google ScholarCross Ref
38. Pierre Jacquot and Pramod K. Rastogi. 1979. Speckle motions induced by rigid-body movements in free-space geometry: an explicit investigation and extension to new cases. Appl. Opt. (1979).Google Scholar
39. Wenzel Jakob, Adam Arbree, Jonathan T. Moon, Kavita Bala, and Steve Marschner. 2010. A radiative transfer framework for rendering materials with anisotropic structure. ACM TOG (2010).Google Scholar
40. Michael L. Jakobsen, Hal T. Yura, and Steen G. Hanson. 2012. Spatial filtering velocimetry of objective speckles for measuring out-of-plane motion. Appl. Opt. (2012).Google Scholar
41. Adrian Jarabo, Carlos Aliaga, and Diego Gutierrez. 2018. A radiative transfer framework for spatially-correlated materials. ACM TOG (2018).Google Scholar
42. Henrik Wann Jensen, Stephen R. Marschner, Marc Levoy, and Pat Hanrahan. 2001. A practical model for subsurface light transport. ACM TOG (2001).Google Scholar
43. Benjamin Judkewitz, Roarke Horstmeyer, Ivo Vellekoop, and Changhuei Yang. 2014. Translation correlations in anisotropically scattering media. Nature Physics (2014).Google Scholar
44. Ori Katz, Yaron Bromberg, Eran Small, and Yaron Silberberg. 2010. Focusing and Compression of Ultrashort Pulses through Scattering Media. Nature Photonics (2010).Google Scholar
45. Ori Katz, Pierre Heidmann, Mathias Fink, and Sylvain Gigan. 2014. Non-invasive singleshot imaging through scattering layers and around corners via speckle correlation. Nature Photonics (2014).Google Scholar
46. Ori Katz, Eran Small, and Yaron Silberberg. 2012. Looking around corners and through thin turbid layers in real time with scattered incoherent light. Nature Photonics (2012).Google Scholar
47. Guillermo H. Kaufmann. 2011. Advances in Speckle Metrology and Related Techniques. Wiley.Google Scholar
48. Craig Kolb, Don Mitchell, and Pat Hanrahan. 1995. A Realistic Camera Model for Computer Graphics. ACM TOG (1995).Google Scholar
49. Puxiang Lai, Lidai Wang, Jian Wei Tay, and Lihong V. Wang. 2015. Photoacoustically guided wavefront shaping for enhanced optical focusing in scattering media. Nature Photonics (2015).Google Scholar
50. Yunzhe Li, Yujia Xue, and Lei Tian. 2018. Deep speckle correlation: a deep learning approach toward scalable imaging through scattering media. Optica (2018).Google Scholar
51. Qiang Lu, Xiaosong Gan, Min Gu, and Qingming Luo. 2004. Monte Carlo modeling of optical coherence tomography imaging through turbid media. Applied optics (2004).Google Scholar
52. Kanti Mardia and Peter Jupp. 2000. Directional statistics. John Wiley & Sons.Google Scholar
53. Jerome Mertz. 2019. Introduction to Optical Microscopy. Cambridge University Press.Google Scholar
54. Jerome Mertz, Hari Paudel, and Thomas G. Bifano. 2015. Field of view advantage of conjugate adaptive optics in microscopy applications. Applied Optics (2015).Google Scholar
55. Christopher A. Metzler, Felix Heide, Prasana Rangarajan, Muralidhar Madabhushi Balaji, Aparna Viswanath, Ashok Veeraraghavan, and Richard G. Baraniuk. 2020. Deep-inverse correlography: towards real-time high-resolution non-line-of-sight imaging. Optica (2020).Google Scholar
56. Christopher A. Metzler, Philip Schniter, Ashok Veeraraghavan, and Richard G Baraniuk. 2018. prDeep: Robust phase retrieval with a flexible deep network. ICML (2018).Google Scholar
57. Allard P. Mosk, Ad Lagendijk, Geoffroy Lerosey, and Mathias Fink. 2012. Controlling waves in space and time for imaging and focusing in complex media. Nature Photonics (2012).Google Scholar
58. Marco Mout, Michael Wick, F. Bociort, Joerg Petschulat, and Paul Urbach. 2016. Simulating multiple diffraction in imaging systems using a path integration method. Applied Optics (2016).Google Scholar
59. Srinivasa G. Narasimhan, Mohit Gupta, Craig Donner, Ravi Ramamoorthi, Shree K. Nayar, and Henrik Wann Jensen. 2006. Acquiring scattering properties of participating media by dilution. ACM TOG (2006).Google Scholar
60. Merlin Nimier-David, Sébastien Speierer, Benoît Ruiz, and Wenzel Jakob. 2020. Radiative backpropagation: an adjoint method for lightning-fast differentiable rendering. ACM TOG (2020).Google ScholarDigital Library
61. Micha Nixon, Ori Katz, Eran Small, Yaron Bromberg, Asher A. Friesem, Yaron Silberberg, and Nir Davidson. 2013. Real-time wavefront shaping through scattering media by all-optical feedback. Nature Photonics (2013).Google Scholar
62. Jan Novak, Iliyan Georgiev, Johannes Hanika, and Wojciech Jarosz. 2018. Monte Carlo Methods for Volumetric Light Transport Simulation. Computer Graphics Forum (2018).Google Scholar
63. Gerwin Osnabrugge, Roarke Horstmeyer, Ioannis N. Papadopoulos, Benjamin Judkewitz, and Ivo M. Vellekoop. 2017. Generalized optical memory effect. Optica (2017).Google Scholar
64. Yingtian Pan, Reginald Birngruber, Jürgen Rosperich, and Ralf Engelhardt. 1995. Low-coherence optical tomography in turbid tissue: theoretical analysis. Applied optics (1995).Google Scholar
65. David J. Pine, David A. Weitz, Paul M. Chaikin, and Eric Herbolzheimer. 1988. Diffusing wave spectroscopy. Physical review letters (1988).Google Scholar
66. Joseph Rosen and David Abookasis. 2003. Seeing through biological tissues using the fly eye principle. Optics Express (2003).Google ScholarCross Ref
67. Markus Rueckel, Julia A. Mack-Bucher, and Winfried Denk. 2006. Adaptive wavefront correction in two-photon microscopy using coherence-gated wavefront sensing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2006).Google ScholarCross Ref
68. Iman Sadeghi, Adolfo Munoz, Philip Laven, Wojciech Jarosz, Francisco Seron, Diego Gutierrez, and Henrik Jensen. 2012. Physically-Based Simulation of Rainbows. ACM TOG. (2012).Google Scholar
69. John Sawicki, Nikolas Kastor, and Min Xu. 2008. Electric field Monte Carlo simulation of coherent backscattering of polarized light by a turbid medium containing Mie scatterers. Optical Express (2008).Google ScholarCross Ref
70. Joseph M. Schmitt and A. Knüttel. 1997. Model of optical coherence tomography of heterogeneous tissue. JOSA A (1997).Google Scholar
71. Sam Schott, Jacopo Bertolotti, Jean-Francois Léger, Laurent Bourdieu, and Sylvain Gigan. 2015. Characterization of the angular memory effect of scattered light in biological tissues. Optics Express (2015).Google ScholarCross Ref
72. Brandon M. Smith, Pratham Desai, Vishal Agarwal, and Mohit Gupta. 2017. CoLux: Multi-object 3D Micro-motion Analysis Using Speckle Imaging. ACM TOG (2017).Google ScholarDigital Library
73. Cyril Soler, Kartic Subr, Frédo Durand, Nicolas Holzschuch, and François Sillion. 2009. Fourier Depth of Field. ACM TOG (2009).Google Scholar
74. Jos Stam. 1999. Diffraction shaders. ACM TOG (1999).Google Scholar
75. Frédéric Sur, Benoît Blaysat, and Michel Grédiac. 2018. Rendering deformed speckle images with a Boolean model. JMIV (2018).Google Scholar
76. Kevin T. Takasaki and Jason W. Fleischer. 2014. Phase-space measurement for depth-resolved memory-effect imaging. Optical Express (2014).Google Scholar
77. Bertrand Thierry, Xavier Antoine, Chokri Chniti, and Hasan Alzubaidi. 2015. μ-diff: An open-source Matlab toolbox for computing multiple scattering problems by disks. Computer Physics Communications (2015).Google Scholar
78. Bradley E. Treeby and Ben T. Cox. 2010. k-Wave: MATLAB toolbox for the simulation and reconstruction of photoacoustic wave-fields. JBO (2010).Google Scholar
79. Elbert G. van Putten, Duygu Akbulut, Jacopo Bertolotti, Willem. L. Vos, Ad Lagendijk, and Allard. P. Mosk. 2011. Scattering Lens Resolves Sub-100 nm Structures with Visible Light. Phys. Rev. Lett. (2011).Google Scholar
80. Ivo M. Vellekoop and Christof M. Aegerter. 2010. Scattered light fluorescence microscopy: imaging through turbid layers. Opt. Lett. (2010).Google Scholar
81. Ivo M. Vellekoop, Meng Cui, and Changhuei Yang. 2012. Digital optical phase conjugation of fluorescence in turbid tissue. Applied Physics Letters (2012).Google Scholar
82. Ivo M. Vellekoop, Aart Lagendijk, and Allard P. Mosk. 2010. Exploiting disorder for perfect focusing. Nature Photonics (2010).Google Scholar
83. Ivo M. Vellekoop and Allard P. Mosk. 2007. Focusing coherent light through opaque strongly scattering media. Opt. Lett. (2007).Google Scholar
84. Sebastian Werner, Zdravko Velinov, Wenzel Jakob, and Matthias B. Hullin. 2017. Scratch Iridescence: Wave-Optical Rendering of Diffractive Surface Structure. ACM TOG (2017).Google Scholar
85. Min Xu. 2004. Electric field Monte Carlo simulation of polarized light propagation in turbid media. Optical Express (2004).Google Scholar
86. Ling-Qi Yan, Miloš Hašan, Bruce Walter, Steve Marschner, and Ravi Ramamoorthi. 2018. Rendering specular microgeometry with wave optics. ACM TOG (2018).Google Scholar
87. Zahid Yaqoob, Demetri Psaltis, Michael Feld, and Changhuei Yang. 2008. Optical phase conjugation for turbidity suppression in biological samples. Nature photonics (2008).Google Scholar
88. Amnon Yariv. 1997. Optical electronics in modern communications. New York : Oxford University Press.Google Scholar
89. Kane Yee. 1966. Numerical solution of initial boundary value problems involving Maxwell’s equations in isotropic media. IEEE TAP (1966).Google Scholar
90. Hengchin Yeh, Ravish Mehra, Zhimin Ren, Lakulish Antani, Dinesh Manocha, and Ming Lin. 2013. Wave-ray Coupling for Interactive Sound Propagation in Large Complex Scenes. ACM TOG (2013).Google Scholar
91. Cheng Zhang, Bailey Miller, Kai Yan, Ioannis Gkioulekas, and Shuang Zhao. 2020. Path-space differentiable rendering. ACM TOG (2020).Google Scholar
92. Cheng Zhang, Lifan Wu, Changxi Zheng, Ioannis Gkioulekas, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and Shuang Zhao. 2019. A differential theory of radiative transfer. ACM TOG (2019).Google Scholar