“Random-access rendering of general vector graphics”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Random-access rendering of general vector graphics
Session/Category Title:
- Texture
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
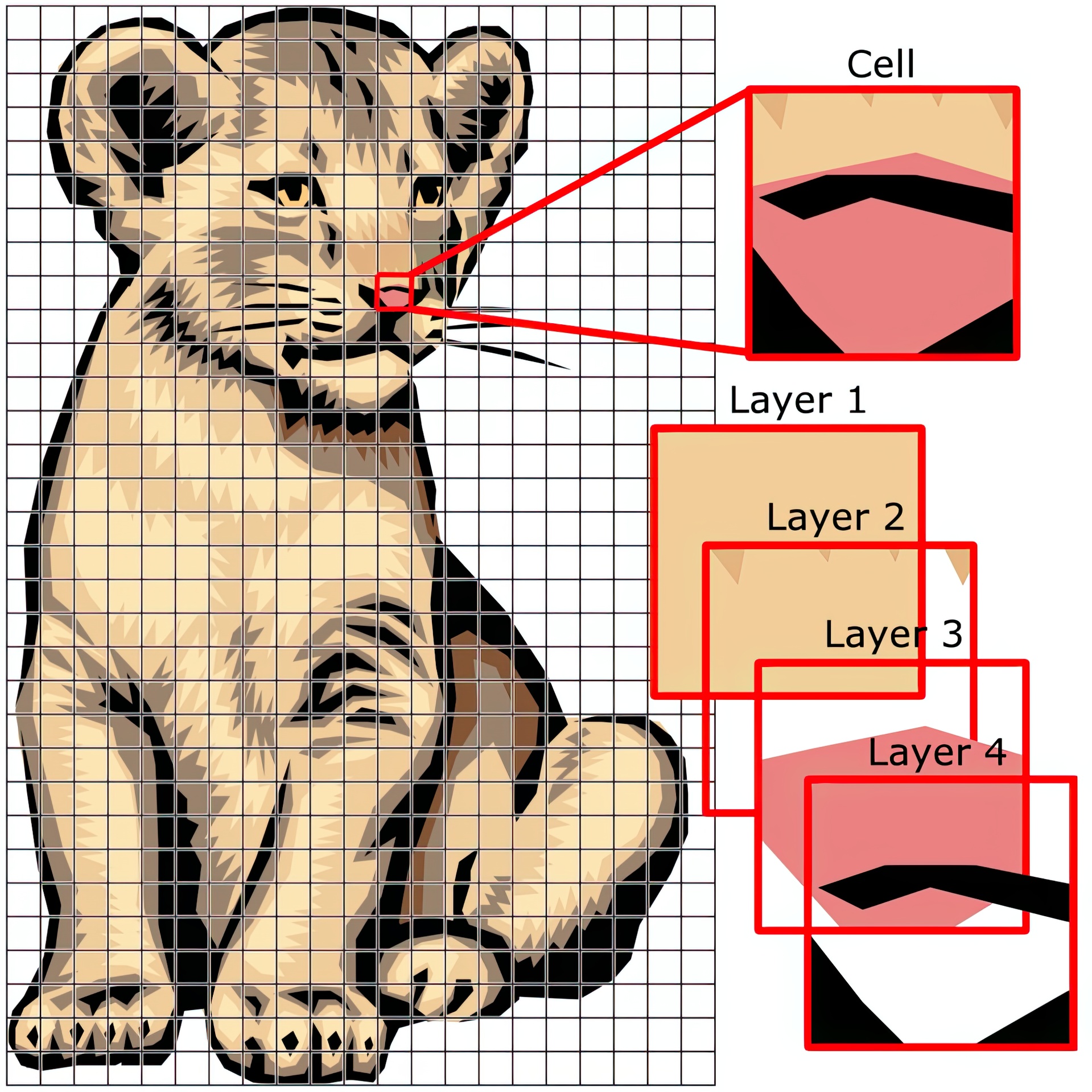
We introduce a novel representation for random-access rendering of antialiased vector graphics on the GPU, along with efficient encoding and rendering algorithms. The representation supports a broad class of vector primitives, including multiple layers of semitransparent filled and stroked shapes, with quadratic outlines and color gradients. Our approach is to create a coarse lattice in which each cell contains a variable-length encoding of the graphics primitives it overlaps. These cell-specialized encodings are interpreted at runtime within a pixel shader. Advantages include localized memory access and the ability to map vector graphics onto arbitrary surfaces, or under arbitrary deformations. Most importantly, we perform both prefiltering and supersampling within a single pixel shader invocation, achieving inter-primitive antialiasing at no added memory bandwidth cost. We present an efficient encoding algorithm, and demonstrate high-quality real-time rendering of complex, real-world examples.
References:
1. Blinn J. 1998. A ghost in a snowstorm, IEEE CG&A, 18(1), 79–84. Google Scholar
2. Blinn J. 2006. How to solve a cubic equation, Part 2: The 11 Case. IEEE CG&A, 26(4), 90–100. Google Scholar
3. Carpenter L. 1984. The A-buffer, an antialiased hidden surface method. ACM SIGGRAPH, 103–108. Google Scholar
4. Foley J., van Dam A., Feiner S., and Hughes J. 1990. Computer Graphics: Principles and Practice. Addison Wesley. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Frisken S., Perry R., Rockwood A., and Jones T. 2000. Adaptively sampled distance fields: A general representation of shape for computer graphics. ACM SIGGRAPH, 249–254. Google Scholar
6. Goldman R., Sederberg T., and Anderson D. 1984. Vector elimination: A technique for the implicitization, inversion, and intersection of planar parametric rational polynomial curves. CAGD 1, 327–356.Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Greiner G., and Hormann K. 1998. Efficient clipping of arbitrary polygons. ACM TOG 17(2), 71–83. Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Gupta S., and Sproull R. 1981. Filtering edges for gray-scale displays. ACM SIGGRAPH. Google Scholar
9. Heckbert P. 1989. Fundamentals of texture mapping and image warping. M.S. Thesis, UC Berkeley, Dept of EECS.Google Scholar
10. Laine S., and Aila T. 2006. A weighted error metric and optimization method for antialiasing patterns. Eurographics, 83–94.Google Scholar
11. Mitchell D., and Netravali A. 1988. Reconstruction filters in computer graphics. ACM SIGGRAPH, 221–228. Google Scholar
12. Lefebvre S., and Hoppe H. 2006. Perfect spatial hashing. ACM SIGGRAPH, 579–588. Google Scholar
13. Lefohn A., Kniss J., Strzodka R., Sengupta S., and Owens J. 2006. Glift: Generic efficient random-access GPU data structures, ACM TOG 25(1), 1–37. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Loop C., and Blinn J. 2005. Resolution-independent curve rendering using programmable graphics hardware. ACM SIGGRAPH, 1000–1009. Google Scholar
15. Loviscach J. 2005. Efficient magnification of bi-level textures. ACM SIGGRAPH Sketches. Google Scholar
16. Nehab D., and Hoppe H. 2007. Texel programs for random-access antialiased vector graphics. Microsoft Research Technical Report MSR-TR-2007-95, July 2007.Google Scholar
17. Parilov E., and Zorin D. 2008. Real-time rendering of textures with feature curves. ACM TOG, 27(1). Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Qin Z., McCool M., and Kaplan C. 2006. Real-time texture-mapped vector glyphs. Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games, 125–132. Google Scholar
19. Qin Z., McCool M., and Kaplan C. 2008. Precise vector textures for real-time 3D rendering. Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games. Google Scholar
20. Ramanarayanan G., Bala K., and Walter B. 2004. Feature-based textures. Symposium on Rendering, 65–73. Google Scholar
21. Ray N., Cavin X., and Lévy B. 2005. Vector texture maps on the GPU. Technical Report ALICE-TR-05-003.Google Scholar
22. Persson E. 2007. Selective supersampling. Shader X5, 177–183.Google Scholar
23. Sen P., Cammarano M., and Hanrahan P. 2003. Shadow silhouette maps. ACM SIGGRAPH, 521–526. Google Scholar
24. Sen P. 2004. Silhouette maps for improved texture magnification. Symposium on Graphics Hardware, 65–73. Google Scholar
25. Stokes M., Anderson M., Chandrasekar S. and Motta R. 1996. A standard default color space for the Internet — sRGB http://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.htmlGoogle Scholar
26. Sutherland I., and Hodgman G. 1974. Reentrant polygon clipping. Communications of the ACM 17(1), 32–42. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Tarini M., and Cignoni P. 2005. Pinchmaps: Textures with customizable discontinuities. Eurographics, 557–568.Google Scholar
28. Tumblin J., and Choudhury P. 2004. Bixels: Picture samples with sharp embedded boundaries. Symposium on Rendering, 186–194. Google Scholar
29. Warnock J. 1969. A hidden surface algorithm for computer generated halftone pictures. PhD Thesis, University of Utah. Google Scholar
30. Winner S., Kelley M., Pease B., Rivard B., and Yen A. 1997. Hardware accelerated rendering of antialiasing using a modified A-buffer algorithm. ACM SIGGRAPH, 307–316. Google Scholar