“Low-discrepancy blue noise sampling”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Low-discrepancy blue noise sampling
Session/Category Title:
- All About Sampling
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
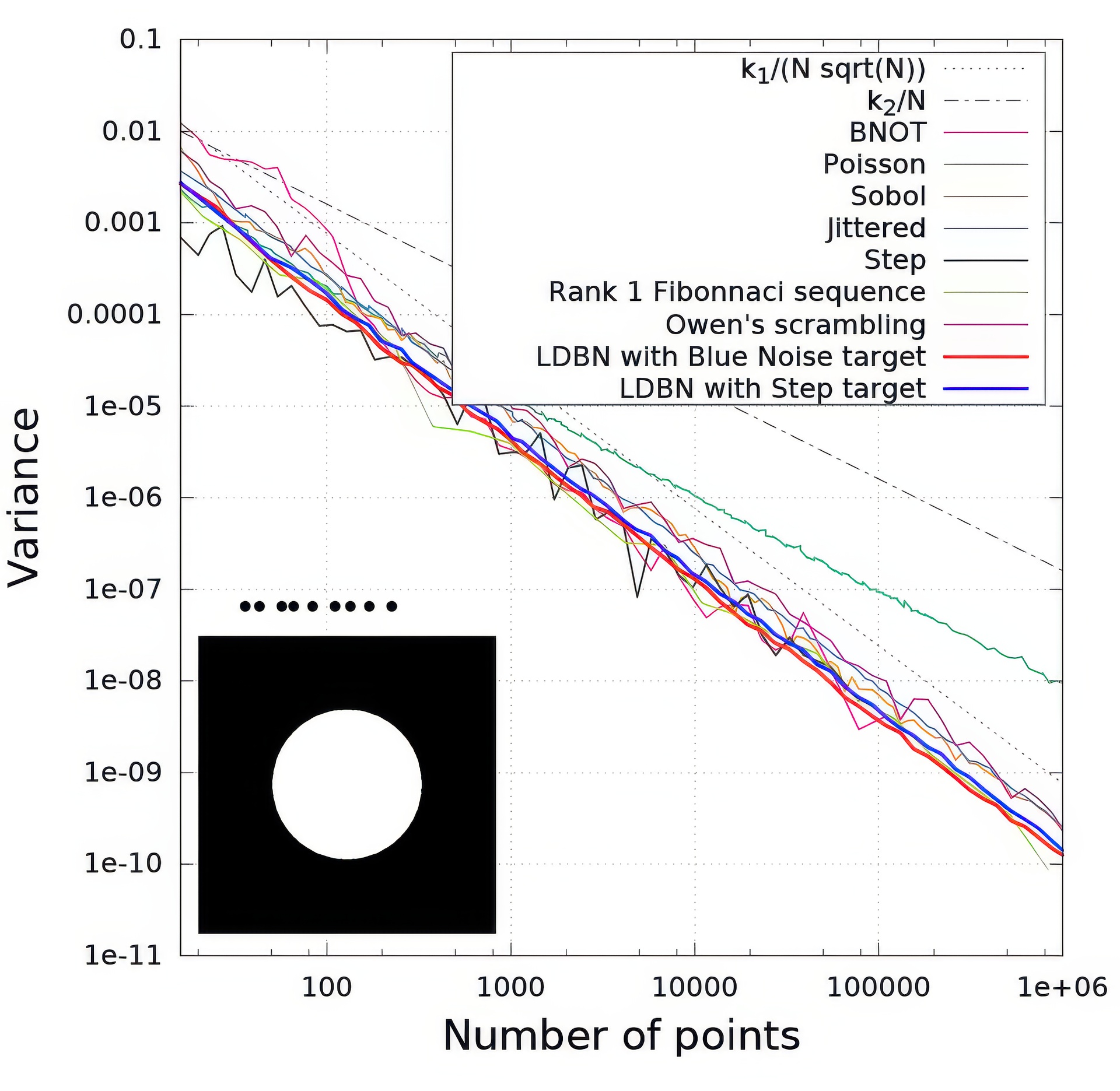
We present a novel technique that produces two-dimensional low-discrepancy (LD) blue noise point sets for sampling. Using one-dimensional binary van der Corput sequences, we construct two-dimensional LD point sets, and rearrange them to match a target spectral profile while preserving their low discrepancy. We store the rearrangement information in a compact lookup table that can be used to produce arbitrarily large point sets. We evaluate our technique and compare it to the state-of-the-art sampling approaches.
References:
1. Ahmed, A. G. M., Huang, H., and Deussen, O. 2015. AA patterns for point sets with controlled spectral properties. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6, 212:1–212:8.
2. Balzer, M., Schlömer, T., and Deussen, O. 2009. Capacity-constrained point distributions: A variant of Lloyd’s method. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3, 86:1–8.
3. Chen, Z., Yuan, Z., Choi, Y.-K., Liu, L., and Wang, W. 2012. Variational blue noise sampling. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 18, 10, 1784–1796.
4. Cohen, M., Shade, J., Hiller, S., and Deussen, O. 2003. Wang tiles for image and texture generation. ACM Trans. Graphics 22, 3, 287–294.
5. Cook, R. L. 1986. Stochastic sampling in computer graphics. ACM Trans. Graph. 5, 1, 51–72.
6. Dammertz, S. 2009. Rank-1 lattices in computer graphics. University of Ulm, PhD Thesis.
7. de Goes, F., Breeden, K., Ostromoukhov, V., and Desbrun, M. 2012. Blue noise through optimal transport. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6, 171:1–171:11.
8. Dippé, M. A. Z., and Wold, E. H. 1985. Antialiasing through stochastic sampling. In ACM SIGGRAPH, 69–78.
9. Dunbar, D., and Humphreys, G. 2006. A spatial data structure for fast Poisson-disk sample generation. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 3, 503–508.
10. Durand, F. 2011. A frequency analysis of Monte-Carlo and other numerical integration schemes. MIT CSAIL Tech. rep. TR-2011-052.
11. Ebeida, M. S., Davidson, A. A., Patney, A., Knupp, P. M., Mitchell, S. A., and Owens, J. D. 2011. Efficient maximal Poisson-disk sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 49:1–49:12.
12. Fattal, R. 2011. Blue-noise point sampling using kernel density model. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 3, 48:1–48:12.
13. Faure, H. 1982. Discrépances de suites associées à un système de numération (en dimension s). Acta Arithmetica 41, 4, 337–351. Cross Ref
14. Halton, J. H. 1960. On the efficiency of certain quasi-random sequences of points in evaluating multi-dimensional integrals. Numerische Mathematik 2, 1, 84–90.
15. Hammersley, J. M. 1960. Monte Carlo methods for solving multivariable problems. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 86, 3, 844–874. Cross Ref
16. Heck, D., Schlömer, T., and Deussen, O. 2013. Blue noise sampling with controlled aliasing. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 3, 25:1–25:12.
17. Hlawka, E. 1961. Funktionen von beschränkter Variation in der Theorie der Gleichverteilung. Annali di Matematica Pura ed Applicata 54, 1, 325–333.
18. Jiang, M., Zhou, Y., Wang, R., Southern, R., and Zhang, J. J. 2015. Blue noise sampling using an sph-based method. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6, 211:1–211:11.
19. Keller, A. 2004. Stratification by rank-1 lattices. Monte Carlo and Quasi-Monte Carlo Methods 2002, 299–313.
20. Keller, A. 2012. Quasi-Monte Carlo image synthesis in a nutshell. Monte Carlo and Quasi-Monte Carlo Methods, 213–252.
21. Kensler, A. 2013. Correlated multi-jittered sampling. Pixar Technical Memo 13-01 7, 86–112.
22. Kollig, T., and Keller, A. 2002. Efficient multidimensional sampling. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 21, 557–563. Cross Ref
23. Kopf, J., Cohen-Or, D., Deussen, O., and Lischinski, D. 2006. Recursive Wang tiles for real-time blue noise. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 3, 509–518.
24. Kuhn, H. W. 1955. The Hungarian Method for the assignment problem. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly 2, 83–97. Cross Ref
25. Kuipers, L., and Niederreiter, H. 1974. Uniform Distribution of Sequences. Pure and applied mathematics. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
26. Lagae, A., and Dutré, P. 2006. An alternative for Wang tiles: Colored edges versus colored corners. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 4, 1442–1459.
27. Lagae, A., and Dutré, P. 2008. A comparison of methods for generating Poisson disk distributions. Computer Graphics Forum 27, 1, 114–129. Cross Ref
28. Lemieux, C. 2009. Monte Carlo and Quasi Monte Carlo Sampling. Springer-Verlag New York.
29. Lloyd, S. 1982. Least squares quantization in PCM. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 28, 2, 129–137.
30. Matoušek, J. 1998. On the L2-discrepancy for anchored boxes. Journal of Complexity 14, 4, 527–556.
31. McCool, M., and Fiume, E. 1992. Hierarchical Poisson disk sampling distributions. In Proc. Graphics Interface ’92, 94–105.
32. Mitchell, D. P., and Netravali, A. N. 1988. Reconstruction filters in computer-graphics. In ACM Siggraph Computer Graphics, vol. 22, ACM, 221–228.
33. Mitchell, D. 1991. Spectrally optimal sampling for distributed ray tracing. In Proc. SIGGRAPH ’91, vol. 25, 157–164.
34. Niederreiter, H. 1988. Low-discrepancy and low-dispersion sequences. Journal of Number Theory 30, 1, 51–70. Cross Ref
35. Niederreiter, H. 1992. Random Number Generation and quasi-Monte Carlo Methods. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, PA, USA.
36. Ostromoukhov, V., Donohue, C., and Jodoin, P.-M. 2004. Fast hierarchical importance sampling with blue noise properties. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3, 488–495.
37. Ostromoukhov, V. 2007. Sampling with polyominoes. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3, 78:1–78:6.
38. Owen, A. B. 1995. Randomly permuted (t,m,s)-nets and (t, s)-sequences. MCQMC in Scientific Computing. Lecture Notes in Statistics, Vol. 106, 299–317. Cross Ref
39. Owen, A. 2003. Variance and discrepancy with alternative scrambling. ACM Trans Model Comput Simul 13, 363–378.
40. Öztireli, A. C., and Gross, M. 2012. Analysis and synthesis of point distributions based on pair correlation. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6, 174:1–174:6.
41. Pharr, M., and Humphreys, G. 2010. Physically Based Rendering, Second Edition: From Theory To Implementation, 2nd ed. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.
42. Pilleboue, A., Singh, G., Coeurjolly, D., Kazhdan, M., and Ostromoukhov, V. 2015. Variance analysis for Monte Carlo integration. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4, 124:1–124:14.
43. Ramamoorthi, R., Anderson, J., Meyer, M., and Nowrouzezahrai, D. 2012. A theory of monte carlo visibility sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 5, 121.
44. Reinert, B., Ritschel, T., Seidel, H.-P., and Georgiev, I. 2016. Projective blue-noise sampling. Computer Graphics Forum 35, 1, 285–295.
45. Saka, Y., Gunzburger, M., and Burkardt, J. 2007. Latinized, improved LHS, and CVT point sets in hypercubes. International Journal of Numerical Analysis and Modeling 4, 3-4, 729–743.
46. Schlömer, T., Heck, D., and Deussen, O. 2011. Farthest-point optimized point sets with maximized minimum distance. In Symp. on High Performance Graphics, 135–142.
47. Schmaltz, C., Gwosdek, P., Bruhn, A., and Weickert, J. 2010. Electrostatic halftoning. Comput. Graph. Forum 29, 8, 2313–2327. Cross Ref
48. Shirley, K. C. P., and Wang, C. 1994. Multi-jittered sampling. Graphics Gems IV 4, 370.
49. Shirley, P. 1991. Discrepancy as a quality measure for sample distributions. In Proc. Eurographics ’91, 183–194.
50. Sobol’, I. M. 1967. On the distribution of points in a cube and the approximate evaluation of integrals. Zhurnal Vychislitel’noi Matematiki i Matematicheskoi Fiziki 7, 4, 784–802.
51. Tezuka, S. 1994. A generalization of Faure sequences and its efficient implementation. Tech. rep., RT0105, IBM Research, Tokyo.
52. Torralba, A., and Oliva, A. 2003. Statistics of natural image categories. Network (Bristol, England) 14, 3, 391–412.
53. Ulichney, R. 1988. Dithering with blue noise. Proceedings of the IEEE 76, 1, 56–79. Cross Ref
54. van der Corput, J. 1935. Verteilungsfunktionen. Proceedings of the Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen, 38, 813–821.
55. Wachtel, F., Pilleboue, A., Coeurjolly, D., Breeden, K., Singh, G., Cathelin, G., de Goes, F., Desbrun, M., and Ostromoukhov, V. 2014. Fast tile-based adaptive sampling with user-specified Fourier spectra. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4, 56:1–56:11.
56. Wei, L.-Y., and Wang, R. 2011. Differential domain analysis for non-uniform sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4, 50:1–50:10.
57. Xu, Y., Liu, L., Gotsman, C., and Gortler, S. J. 2011. Capacity-constrained Delaunay triangulation for point distributions. Computers & Graphics 35, 3, 510 — 516.
58. Yuksel, C. 2015. Sample elimination for generating Poisson disk sample sets. Comput. Graph. Forum 34, 2, 25–32.
59. Zhou, Y., Huang, H., Wei, L.-Y., and Wang, R. 2012. Point sampling with general noise spectrum. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4, 76:1–76:11.