“Higher-order finite elements for embedded simulation” by Longva, Löschner, Kugelstadt, Fernández-Fernández and Bender
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Higher-order finite elements for embedded simulation
Session/Category Title:
- Animation: Pretty Solid Physics Research
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
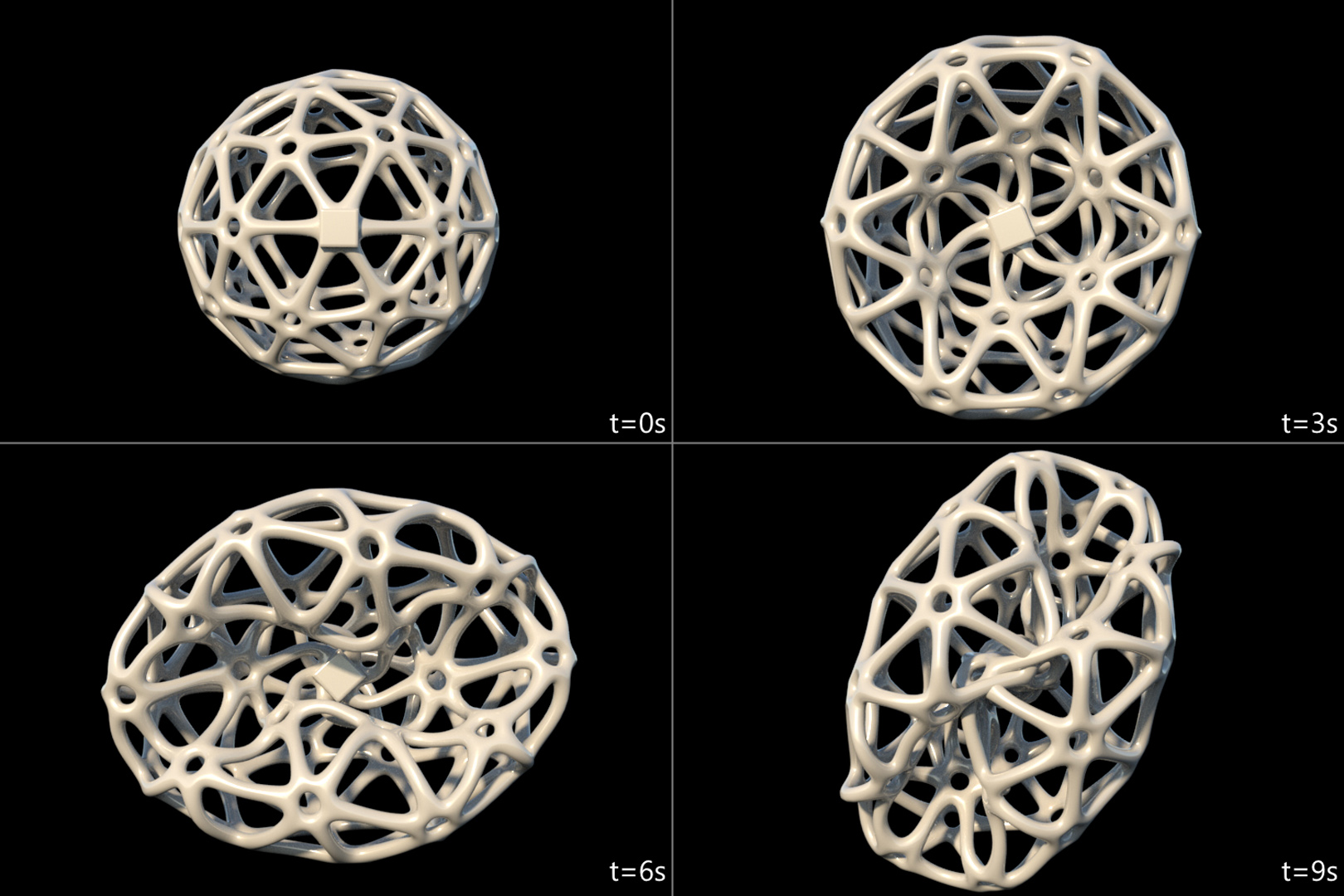
As demands for high-fidelity physics-based animations increase, the need for accurate methods for simulating deformable solids grows. While higherorder finite elements are commonplace in engineering due to their superior approximation properties for many problems, they have gained little traction in the computer graphics community. This may partially be explained by the need for finite element meshes to approximate the highly complex geometry of models used in graphics applications. Due to the additional perelement computational expense of higher-order elements, larger elements are needed, and the error incurred due to the geometry mismatch eradicates the benefits of higher-order discretizations. One solution to this problem is the embedding of the geometry into a coarser finite element mesh. However, to date there is no adequate, practical computational framework that permits the accurate embedding into higher-order elements.We develop a novel, robust quadrature generation method that generates theoretically guaranteed high-quality sub-cell integration rules of arbitrary polynomial accuracy. The number of quadrature points generated is bounded only by the desired degree of the polynomial, independent of the embedded geometry. Additionally, we build on recent work in the Finite Cell Method (FCM) community so as to tackle the severe ill-conditioning caused by partially filled elements by adapting an Additive-Schwarz-based preconditioner so that it is suitable for use with state-of-the-art non-linear material models from the graphics literature. Together these two contributions constitute a general-purpose framework for embedded simulation with higher-order finite elements.We finally demonstrate the benefits of our framework in several scenarios, in which second-order hexahedra and tetrahedra clearly outperform their first-order counterparts.
References:
1. Adam W. Bargteil and Elaine Cohen. 2014. Animation of Deformable Bodies with Quadratic Bézier Finite Elements. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 3, Article 27 (2014), 10 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Klaus-Jürgen Bathe. 2006. Finite element procedures. Klaus-Jurgen Bathe.Google Scholar
3. Max Budninskiy, Houman Owhadi, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2019. Operator-adapted wavelets for finite-element differential forms. J. Comput. Phys. 388 (2019), 144–177.Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Jiong Chen, Hujun Bao, Tianyu Wang, Mathieu Desbrun, and Jin Huang. 2018. Numerical Coarsening Using Discontinuous Shape Functions. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 120 (2018), 12 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Jiong Chen, Max Budninskiy, Houman Owhadi, Hujun Bao, Jin Huang, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2019. Material-Adapted Refinable Basis Functions for Elasticity Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 6, Article 161 (2019), 15 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Paolo Cignoni, Marco Callieri, Massimiliano Corsini, Matteo Dellepiane, Fabio Ganovelli, and Guido Ranzuglia. 2008. MeshLab: an Open-Source Mesh Processing Tool. In Eurographics Italian Chapter Conference. The Eurographics Association.Google Scholar
7. Sébastien Crozet et al. 2019. nalgebra: a linear algebra library for Rust. https://nalgebra.orgGoogle Scholar
8. Frits de Prenter, CV Verhoosel, and EH van Brummelen. 2019. Preconditioning immersed isogeometric finite element methods with application to flow problems. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 348 (2019), 604–631.Google ScholarCross Ref
9. Frits de Prenter, Clemens V Verhoosel, Gert J van Zwieten, and E Harald van Brummelen. 2017. Condition number analysis and preconditioning of the finite cell method. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 316 (2017), 297–327.Google ScholarCross Ref
10. Gilles Debunne, Mathieu Desbrun, Marie-Paule Cani, and Alan H. Barr. 2001. Dynamic Real-Time Deformations using Space & Time Adaptive Sampling. In ACM Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques. ACM, 31–36.Google Scholar
11. Sascha Duczek, Fabian Duvigneau, and Ulrich Gabbert. 2016. The finite cell method for tetrahedral meshes. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design 121 (2016), 18–32.Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Alexander Düster, Jamshid Parvizian, Zhengxiong Yang, and Ernst Rank. 2008. The finite cell method for three-dimensional problems of solid mechanics. Computer methods in applied mechanics and engineering 197, 45–48 (2008), 3768–3782.Google Scholar
13. P. Faloutsos, M. Van de Panne, and D. Terzopoulos. 1997. Dynamic free-form deformations for animation synthesis. IEEE Trans. on Vis. and Comp. Graph. 3, 3 (1997).Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Christian Hafner, Christian Schumacher, Espen Knoop, Thomas Auzinger, Bernd Bickel, and Moritz Bächer. 2019. X-CAD: optimizing CAD models with extended finite elements. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 6 (2019), 1–15.Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Yixin Hu, Teseo Schneider, Bolun Wang, Denis Zorin, and Daniele Panozzo. 2020. Fast Tetrahedral Meshing in the Wild. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 4, Article 117 (2020).Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Yixin Hu, Qingnan Zhou, Xifeng Gao, Alec Jacobson, Denis Zorin, and Daniele Panozzo. 2018. Tetrahedral Meshing in the Wild. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 60 (2018).Google ScholarDigital Library
17. John D Jakeman and Akil Narayan. 2018. Generation and application of multivariate polynomial quadrature rules. Comp. Methods in Applied Mech. and Eng. 338 (2018).Google Scholar
18. Doug L James, Jernej Barbič, and Christopher D Twigg. 2004. Squashing cubes: Automating deformable model construction for graphics. In ACM SIGGRAPH Sketches.Google Scholar
19. John N Jomo, Frits de Prenter, Mohamed Elhaddad, Davide D’Angella, Clemens V Verhoosel, Stefan Kollmannsberger, Jan S Kirschke, Vera Nübel, EH van Brummelen, and Ernst Rank. 2019. Robust and parallel scalable iterative solutions for large-scale finite cell analyses. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design 163 (2019), 14–30.Google ScholarCross Ref
20. Peter Kaufmann, Sebastian Martin, Mario Botsch, Eitan Grinspun, and Markus Gross. 2009. Enrichment Textures for Detailed Cutting of Shells. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3 (2009), 50:1–50:10.Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Peter Kaufmann, Sebastian Martin, Mario Botsch, and Markus Gross. 2008. Flexible Simulation of Deformable Models Using Discontinuous Galerkin FEM. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. 105–115.Google Scholar
22. Vahid Keshavarzzadeh, Robert M Kirby, and Akil Narayan. 2018. Numerical integration in multiple dimensions with designed quadrature. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 40, 4 (2018), A2033–A2061.Google ScholarCross Ref
23. Lily Kharevych, Patrick Mullen, Houman Owhadi, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2009. Numerical Coarsening of Inhomogeneous Elastic Materials. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3, Article 51 (2009), 8 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Dan Koschier, Jan Bender, and Nils Thuerey. 2017. Robust EXtended Finite Elements for Complex Cutting of Deformables. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4, Article 55 (2017).Google ScholarDigital Library
25. László Kudela, Nils Zander, Stefan Kollmannsberger, and Ernst Rank. 2016. Smart octrees: Accurately integrating discontinuous functions in 3D. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 306 (2016), 406–426.Google ScholarCross Ref
26. Tassilo Kugelstadt, Dan Koschier, and Jan Bender. 2018. Fast Corotated FEM using Operator Splitting. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 37.Google ScholarCross Ref
27. Johannes Mezger, Bernhard Thomaszewski, Simon Pabst, and Wolfgang Straßer. 2009. Interactive physically-based shape editing. Comp. Aided Geom. Design 26, 6 (2009).Google Scholar
28. Neil Molino, Zhaosheng Bao, and Ron Fedkiw. 2004. A Virtual Node Algorithm for Changing Mesh Topology During Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (2004).Google ScholarDigital Library
29. M. Müller, M. Teschner, and M. Gross. 2004. Physically-based simulation of objects represented by surface meshes. In Computer Graphics International. 26–33.Google Scholar
30. B. Müller, F. Kummer, and M. Oberlack. 2013. Highly accurate surface and volume integration on implicit domains by means of moment-fitting. Internat. J. Numer. Methods Engrg. 96, 8 (2013), 512–528.Google ScholarCross Ref
31. Andrew Nealen, Matthias Müller, Richard Keiser, Eddy Boxerman, and Mark Carlson. 2006. Physically Based Deformable Models in Computer Graphics. Computer Graphics Forum 25, 4 (2006), 809–836.Google ScholarCross Ref
32. Matthieu Nesme, Paul G. Kry, Lenka Jeřábková, and François Faure. 2009. Preserving Topology and Elasticity for Embedded Deformable Models. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3, Article 52 (2009), 9 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
33. Matthieu Nesme, Yohan Payan, and François Faure. 2006. Animating shapes at arbitrary resolution with non-uniform stiffness. In Proc. VRIPHYS.Google Scholar
34. Jorge Nocedal and Stephen Wright. 2006. Numerical optimization. Springer Science & Business Media.Google Scholar
35. Christopher C Paige and Michael A Saunders. 1975. Solution of sparse indefinite systems of linear equations. SIAM journal on numerical analysis 12, 4 (1975), 617–629.Google Scholar
36. Jamshid Parvizian, Alexander Düster, and Ernst Rank. 2007. Finite cell method. Computational Mechanics 41, 1 (2007), 121–133.Google ScholarCross Ref
37. Taylor Patterson, Nathan Mitchell, and Eftychios Sifakis. 2012. Simulation of Complex Nonlinear Elastic Bodies using Lattice Deformers. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6 (2012).Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Olivier Rémillard and Paul G Kry. 2013. Embedded thin shells for wrinkle simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4 (2013), 1–8.Google ScholarDigital Library
39. Alec R. Rivers and Doug L. James. 2007. FastLSM: Fast Lattice Shape Matching for Robust Real-Time Deformation. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3 (2007), 82.Google ScholarDigital Library
40. SH Roth, Markus H Gross, Silvio Turello, and Friedrich R Carls. 1998. A Bernstein-Bézier Based Approach to Soft Tissue Simulation. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 17.Google ScholarCross Ref
41. Ernest Ryu and Stephen Boyd. 2014. Extensions of Gauss Quadrature Via Linear Programming. Foundations of Computational Mathematics 15 (2014).Google Scholar
42. Leonardo Sacht, Etienne Vouga, and Alec Jacobson. 2015. Nested cages. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6 (2015), 1–14.Google ScholarDigital Library
43. Dominik Schillinger and Martin Ruess. 2015. The Finite Cell Method: A review in the context of higher-order structural analysis of CAD and image-based geometric models. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering 22, 3 (2015), 391–455.Google ScholarCross Ref
44. Eftychios Sifakis and Jernej Barbic. 2012. FEM Simulation of 3D Deformable Solids. In ACM SIGGRAPH Courses. 1–50.Google Scholar
45. Eftychios Sifakis, Kevin G Der, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2007. Arbitrary cutting of deformable tetrahedralized objects. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. 73–80.Google Scholar
46. Breannan Smith, Fernando De Goes, and Theodore Kim. 2018. Stable neo-hookean flesh simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 2 (2018), 12.Google ScholarDigital Library
47. Daniel Weber, Jan Bender, Markus Schnoes, André Stork, and Dieter Fellner. 2013. Efficient GPU Data Structures and methods to Solve Sparse Linear Systems in Dynamics Applications. Computer Graphics Forum 32, 1 (2013), 16–26.Google ScholarCross Ref
48. Daniel Weber, Johannes Mueller-Roemer, Christian Altenhofen, André Stork, and Dieter Fellner. 2015. Deformation simulation using cubic finite elements and efficient p-multigrid methods. Computers & graphics 53 (2015), 185–195.Google Scholar
49. Freddie D Witherden and Peter E Vincent. 2015. On the identification of symmetric quadrature rules for finite element methods. Computers & Mathematics with Applications 69, 10 (2015), 1232–1241.Google ScholarDigital Library
50. Yuan Xu. 1997. On orthogonal polynomials in several variables. Special functions, q-series and related topics, The Fields Institute for Research in Mathematical Sciences, Communications Series 14 (1997), 247–270.Google Scholar