“Functional optimization of fluidic devices with differentiable stokes flow” by Du, Wu, Spielberg, Matusik, Zhu, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Functional optimization of fluidic devices with differentiable stokes flow
Session/Category Title:
- Differentiable Graphics
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
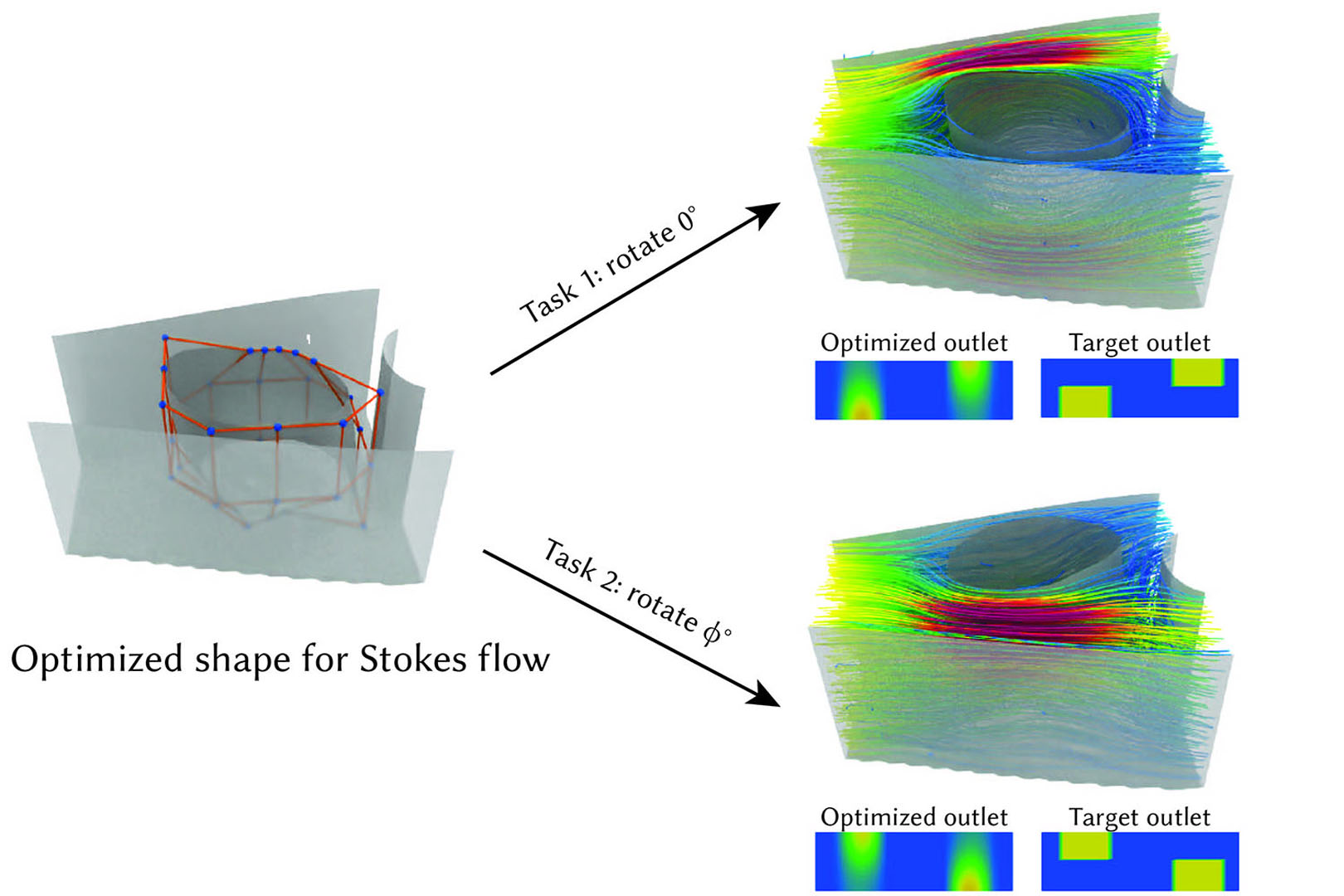
We present a method for performance-driven optimization of fluidic devices. In our approach, engineers provide a high-level specification of a device using parametric surfaces for the fluid-solid boundaries. They also specify desired flow properties for inlets and outlets of the device. Our computational approach optimizes the boundary of the fluidic device such that its steady-state flow matches desired flow at outlets. In order to deal with computational challenges of this task, we propose an efficient, differentiable Stokes flow solver. Our solver provides explicit access to gradients of performance metrics with respect to the parametric boundary representation. This key feature allows us to couple the solver with efficient gradient-based optimization methods. We demonstrate the efficacy of this approach on designs of five complex 3D fluidic systems. Our approach makes an important step towards practical computational design tools for high-performance fluidic devices.
References:
1. Niels Aage, Erik Andreassen, Boyan S. Lazarov, and Ole Sigmund. 2017. Giga-Voxel Computational Morphogenesis for Structural Design. Nature 550, 7674 (2017), 84–86.Google Scholar
2. Niels Aage, Thomas H. Poulsen, Allan Gersborg-Hansen, and Ole Sigmund. 2008. Topology Optimization of Large Scale Stokes Flow Problems. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 35, 2 (2008), 175–180.Google ScholarCross Ref
3. Joe Alexandersen and Casper Schousboe Andreasen. 2020. A Review of Topology Optimisation for Fluid-Based Problems. Fluids 5, 1 (2020), 29.Google ScholarCross Ref
4. Ryoichi Ando, Nils Thürey, and Chris Wojtan. 2013. Highly Adaptive Liquid Simulations on Tetrahedral Meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4, Article 103 (July 2013), 10 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Casper Schousboe Andreasen and Ole Sigmund. 2013. Topology Optimization of Fluid-Structure-Interaction Problems in Poroelasticity. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 258 (2013), 55–62.Google ScholarCross Ref
6. Vinicius C. Azevedo, Christopher Batty, and Manuel M. Oliveira. 2016. Preserving Geometry and Topology for Fluid Flows with Thin Obstacles and Narrow Gaps. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 4, Article 97 (July 2016), 12 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. David L. Barrow and Philip W. Smith. 1979. Spline Notation Applied to a Volume Problem. The American Mathematical Monthly 86, 1 (1979), 50–51.Google ScholarCross Ref
8. Christopher Batty, Florence Bertails, and Robert Bridson. 2007. A Fast Variational Framework for Accurate Solid-Fluid Coupling. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 Papers (San Diego, California) (SIGGRAPH ’07). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 100-es. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. William Baxter, Yuanxin Liu, and Ming C. Lin. 2004. A Viscous Paint Model for Interactive Applications. Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds 15, 3–4 (2004), 433–441.Google ScholarCross Ref
10. Jacob Bedrossian, James H. Von Brecht, Siwei Zhu, Eftychios Sifakis, and Joseph Teran. 2010. A Second Order Virtual Node Method for Elliptic Problems with Interfaces and Irregular Domains. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 18 (2010), 6405–6426.Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Reza Behrou, Ram Ranjan, and James K. Guest. 2019. Adaptive Topology Optimization for Incompressible Laminar Flow Problems with Mass Flow Constraints. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 346 (2019), 612–641.Google ScholarCross Ref
12. Martin Philip Bendsoe and Ole Sigmund. 2013. Topology Optimization: Theory, Methods, and Applications. Springer Science & Business Media.Google Scholar
13. Haimasree Bhattacharya, Michael Bang Nielsen, and Robert Bridson. 2012. Steady State Stokes Flow Interpolation for Fluid Control. In Eurographics (Short Papers). Citeseer, 57–60.Google Scholar
14. Thomas Borrvall and Joakim Petersson. 2003. Topology Optimization of Fluids in Stokes Flow. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids 41, 1 (2003), 77–107.Google ScholarCross Ref
15. Franco Brezzi and Michel Fortin. 2012. Mixed and Hybrid Finite Element Methods. Vol. 15. Springer Science & Business Media.Google Scholar
16. Robert Bridson. 2015. Fluid Simulation for Computer Graphics. CRC press.Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Walter Jesus Paucar Casas and Renato Pavanello. 2017. Optimization of Fluid-Structure Systems by Eigenvalues Gap Separation with Sensitivity Analysis. Applied Mathematical Modelling 42 (2017), 269–289.Google ScholarCross Ref
18. Vivien J. Challis and James K. Guest. 2009. Level Set Topology Optimization of Fluids in Stokes Flow. Internat. J. Numer. Methods Engrg. 79, 10 (2009), 1284–1308.Google ScholarCross Ref
19. Mengyu Chu and Nils Thürey. 2017. Data-Driven Synthesis of Smoke Flows with CNN-Based Feature Descriptors. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4, Article 69 (July 2017), 14 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Christophe Daux, Nicolas Moës, John Dolbow, Natarajan Sukumar, and Ted Belytschko. 2000. Arbitrary Branched and Intersecting Cracks with the Extended Finite Element Method. Internat. J. Numer. Methods Engrg. 48, 12 (2000), 1741–1760.Google ScholarCross Ref
21. Joshua D. Deaton and Ramana V. Grandhi. 2014. A Survey of Structural and Multidisciplinary Continuum Topology Optimization: Post 2000. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 49, 1 (2014), 1–38.Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Cetin B. Dilgen, Sumer B. Dilgen, David R. Fuhrman, Ole Sigmund, and Boyan S. Lazarov. 2018a. Topology Optimization of Turbulent Flows. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 331 (2018), 363–393.Google ScholarCross Ref
23. Sumer B. Dilgen, Cetin B. Dilgen, David R. Fuhrman, Ole Sigmund, and Boyan S. Lazarov. 2018b. Density Based Topology Optimization of Turbulent Flow Heat Transfer Systems. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 57, 5 (2018), 1905–1918.Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Marie-Lena Eckert, Kiwon Um, and Nils Thürey. 2019. ScalarFlow: A Large-Scale Volumetric Data Set of Real-World Scalar Transport Flows for Computer Animation and Machine Learning. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 6, Article 239 (Nov. 2019), 16 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Douglas Enright, Stephen Marschner, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2002. Animation and Rendering of Complex Water Surfaces. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques. 736–744.Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Anton Evgrafov. 2006. Topology Optimization of Slightly Compressible Fluids. ZAMM-Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics/Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik: Applied Mathematics and Mechanics 86, 1 (2006), 46–62.Google ScholarCross Ref
27. Ronald Fedkiw, Tariq Aslam, Barry Merriman, Stanley Osher, et al. 1999. A Non-Oscillatory Eulerian Approach to Interfaces in Multimaterial Flows (the Ghost Fluid Method). J. Comput. Phys. 152, 2 (1999), 457–492.Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Ronald Fedkiw, Jos Stam, and Henrik Wann Jensen. 2001. Visual Simulation of Smoke. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques. 15–22.Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Bryan E. Feldman, James F. O’Brien, Bryan M. Klingner, and Tolga G. Goktekin. 2005. Fluids in Deforming Meshes. In Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (Los Angeles, California) (SCA ’05). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 255–259. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Florian Ferstl, Rüdiger Westermann, and Christian Dick. 2014. Large-Scale Liquid Simulation on Adaptive Hexahedral Grids. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 20, 10 (2014), 1405–1417.Google ScholarCross Ref
31. Francisco. J. Gaspar, José L. Gracia, Francisco J. Lisbona, and Cornelis W. Oosterlee. 2008. Distributive Smoothers in Multigrid for Problems with Dominating Grad-Div Operators. Numerical Linear Algebra with Applications 15, 8 (2008), 661–683. arXiv:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/nla.587 Google ScholarCross Ref
32. Allan Gersborg-Hansen, Ole Sigmund, and Robert B. Haber. 2005. Topology Optimization of Channel Flow Problems. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 30, 3 (2005), 181–192.Google ScholarCross Ref
33. James K. Guest and Jean H. Prévost. 2006. Topology Optimization of Creeping Fluid Flows Using a Darcy-Stokes Finite Element. Internat. J. Numer. Methods Engrg. 66, 3 (2006), 461–484.Google ScholarCross Ref
34. Jeffrey Lee Hellrung, Luming Wang, Eftychios Sifakis, and Joseph Teran. 2012. A Second Order Virtual Node Method for Elliptic Problems with Interfaces and Irregular Domains in Three Dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 4 (2012), 2015–2048.Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Philipp Holl, Vladlen Koltun, and Nils Thürey. 2020. Learning to Control PDEs with Differentiable Physics. In International Conference on Learning Representations.Google Scholar
36. Yuanming Hu, Jiancheng Liu, Andrew Spielberg, Joshua B. Tenenbaum, William T. Freeman, Jiajun Wu, Daniela Rus, and Wojciech Matusik. 2019. ChainQueen: A Real-Time Differentiable Physical Simulator for Soft Robotics. In International Conference on Robotics and Automation. IEEE, 6265–6271.Google Scholar
37. Thomas J. R. Hughes. 2012. The Finite Element Method: Linear Static and Dynamic Finite Element Analysis. Courier Corporation.Google Scholar
38. Hikaru Ibayashi, Chris Wojtan, Nils Thürey, Takeo Igarashi, and Ryoichi Ando. 2018. Simulating Liquids on Dynamically Warping Grids. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (2018).Google Scholar
39. Byungsoo Kim, Vinicius C. Azevedo, Nils Thürey, Theodore Kim, Markus Gross, and Barbara Solenthaler. 2019. Deep Fluids: A Generative Network for Parameterized Fluid Simulations. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 38. Wiley Online Library, 59–70.Google Scholar
40. Nipun Kwatra, Jonathan Su, Jón T. Grétarsson, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2009. A Method for Avoiding the Acoustic Time Step Restriction in Compressible Flow. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 11 (2009), 4146–4161.Google ScholarDigital Library
41. Egor Larionov, Christopher Batty, and Robert Bridson. 2017. Variational Stokes: A Unified Pressure-Viscosity Solver for Accurate Viscous Liquids. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4, Article 101 (July 2017), 11 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
42. Benny Lautrup. 2004. Physics of Continuous Matter: Exotic and Everyday Phenomena in the Macroscopic World. CRC press.Google Scholar
43. Sung-Hee Lee, Eftychios Sifakis, and Demetri Terzopoulos. 2009. Comprehensive Biomechanical Modeling and Simulation of the Upper Body. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 4, Article 99 (Sept. 2009), 17 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
44. Yunzhu Li, Jiajun Wu, Russ Tedrake, Joshua B. Tenenbaum, and Antonio Torralba. 2019. Learning Particle Dynamics for Manipulating Rigid Bodies, Deformable Objects, and Fluids. (2019).Google Scholar
45. Junbang Liang, Ming C. Lin, and Vladlen Koltun. 2019. Differentiable Cloth Simulation for Inverse Problems. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 771–780.Google Scholar
46. Sen Lin, Longyu Zhao, James K. Guest, Timothy P. Weihs, and Zhenyu Liu. 2015. Topology Optimization of Fixed-Geometry Fluid Diodes. Journal of Mechanical Design 137, 8 (2015).Google ScholarCross Ref
47. Haixiang Liu, Yuanming Hu, Bo Zhu, Wojciech Matusik, and Eftychios Sifakis. 2018. Narrow-Band Topology Optimization on a Sparsely Populated Grid. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 6, Article 251 (Dec. 2018), 14 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
48. Kurt Maute and Matthew Allen. 2004. Conceptual Design of Aeroelastic Structures by Topology Optimization. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 27, 1–2 (2004), 27–42.Google ScholarCross Ref
49. Aleka McAdams, Yongning Zhu, Andrew Selle, Mark Empey, Rasmus Tamstorf, Joseph Teran, and Eftychios Sifakis. 2011. Efficient Elasticity for Character Skinning with Contact and Collisions. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4, Article 37 (July 2011), 12 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
50. Antoine McNamara, Adrien Treuille, Zoran Popović, and Jos Stam. 2004. Fluid Control Using the Adjoint Method. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (Aug. 2004), 449–456. Google ScholarDigital Library
51. Nicolas Moës, John Dolbow, and Ted Belytschko. 1999. A Finite Element Method for Crack Growth without Remeshing. Internat. J. Numer. Methods Engrg. 46, 1 (1999), 131–150.Google ScholarCross Ref
52. Maxim Olshanskii, Gert Lube, Timo Heister, and Johannes Löwe. 2009. Grad-Div Stabilization and Subgrid Pressure Models for the Incompressible Navier-Stokes Equations. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 198, 49–52 (2009), 3975–3988.Google ScholarCross Ref
53. Stanley Osher and Ronald Fedkiw. 2003. Level Set Methods and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces. Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 153. Springer. I–XIII, 1–273 pages.Google Scholar
54. Matthew Overby, George E Brown, Jie Li, and Rahul Narain. 2017. ADMM ⊇ Projective Dynamics: Fast Simulation of Hyperelastic Models with Dynamic Constraints. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 23, 10 (2017), 2222–2234.Google ScholarDigital Library
55. Zherong Pan, Jin Huang, Yiying Tong, Changxi Zheng, and Hujun Bao. 2013. Interactive Localized Liquid Motion Editing. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 6, Article 184 (Nov. 2013), 10 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
56. Evangelos M. Papoutsis-Kiachagias and Kyriakos C. Giannakoglou. 2016. Continuous Adjoint Methods for Turbulent Flows, Applied to Shape and Topology Optimization: Industrial Applications. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering 23, 2 (2016), 255–299.Google ScholarCross Ref
57. Taylor Patterson, Nathan Mitchell, and Eftychios Sifakis. 2012. Simulation of Complex Nonlinear Elastic Bodies Using Lattice Deformers. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6, Article 197 (Nov. 2012), 10 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
58. Karthik Raveendran, Nils Thürey, Chris Wojtan, and Greg Turk. 2012. Controlling Liquids Using Meshes. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (Lausanne, Switzerland) (SCA ’12). Eurographics Association, Goslar, DEU, 255–264.Google ScholarDigital Library
59. George I. N. Rozvany. 2009. A Critical Review of Established Methods of Structural Topology Optimization. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 37, 3 (2009), 217–237.Google ScholarCross Ref
60. Connor Schenck and Dieter Fox. 2018. SPNets: Differentiable Fluid Dynamics for Deep Neural Networks (Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, Vol. 87). PMLR, 317–335. http://proceedings.mlr.press/v87/schenck18a.htmlGoogle Scholar
61. Olaf Schenk and Klaus Gärtner. 2004. Solving Unsymmetric Sparse Systems of Linear Equations with PARDISO. Future Generation Computer Systems 20, 3 (2004), 475–487.Google ScholarDigital Library
62. Craig Schroeder, Wen Zheng, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2012. Semi-Implicit Surface Tension Formulation with a Lagrangian Surface Mesh on an Eulerian Simulation Grid. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 4 (2012), 2092–2115.Google ScholarDigital Library
63. Eftychios Sifakis and Jernej Barbic. 2012. FEM Simulation of 3D Deformable Solids: A Practitioner’s Guide to Theory, Discretization and Model Reduction. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2012 Courses (Los Angeles, California) (SIGGRAPH ’12). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 20, 50 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
64. Eftychios Sifakis, Tamar Shinar, Geoffrey Irving, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2007. Hybrid Simulation of Deformable Solids. In Proceedings of the 2007 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (San Diego, California) (SCA ’07). Eurographics Association, Goslar, DEU, 81–90.Google ScholarDigital Library
65. Ole Sigmund and Kurt Maute. 2013. Topology Optimization Approaches. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 48, 6 (2013), 1031–1055.Google ScholarCross Ref
66. Jos Stam. 1999. Stable Fluids. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH ’99). ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., USA, 121–128. Google ScholarDigital Library
67. Alexey Stomakhin, Craig Schroeder, Chenfanfu Jiang, Lawrence Chai, Joseph Teran, and Andrew Selle. 2014. Augmented MPM for Phase-Change and Varied Materials. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4, Article 138 (July 2014), 11 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
68. Nobuyuki Umetani and Bernd Bickel. 2018. Learning Three-Dimensional Flow for Interactive Aerodynamic Design. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 89 (July 2018), 10 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
69. Carlos H. Villanueva and Kurt Maute. 2017. CutFEM Topology Optimization of 3D Laminar Incompressible Flow Problems. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 320 (2017), 444–473.Google ScholarCross Ref
70. Gil Ho Yoon. 2010. Topology Optimization for Stationary Fluid-Structure Interaction Problems Using a New Monolithic Formulation. Internat. J. Numer. Methods Engrg. 82, 5 (2010), 591–616.Google ScholarCross Ref
71. Mingdong Zhou, Haojie Lian, Ole Sigmund, and Niels Aage. 2018. Shape Morphing and Topology Optimization of Fluid Channels by Explicit Boundary Tracking. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids 88, 6 (2018), 296–313.Google ScholarCross Ref
72. Shiwei Zhou and Qing Li. 2008. A Variational Level Set Method for the Topology Optimization of Steady-State Navier-Stokes Flow. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 24 (2008), 10178–10195.Google ScholarDigital Library
73. Yongning Zhu, Eftychios Sifakis, Joseph Teran, and Achi Brandt. 2010. An Efficient Multigrid Method for the Simulation of High-Resolution Elastic Solids. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 2, Article 16 (April 2010), 18 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
74. Yongning Zhu, Yuting Wang, Jeffrey Hellrung, Alejandro Cantarero, Eftychios Sifakis, and Joseph Teran. 2012. A Second-Order Virtual Node Algorithm for Nearly Incompressible Linear Elasticity in Irregular Domains. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 21 (2012), 7092–7117.Google ScholarDigital Library