“Fluid-Measurement Technology using Flow Birefringence of Nanocellulose” by Yamashita, Miyaki, Kasuga, Nogi, Suwa, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Fluid-Measurement Technology using Flow Birefringence of Nanocellulose
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Entry Number:
- 56
Abstract:
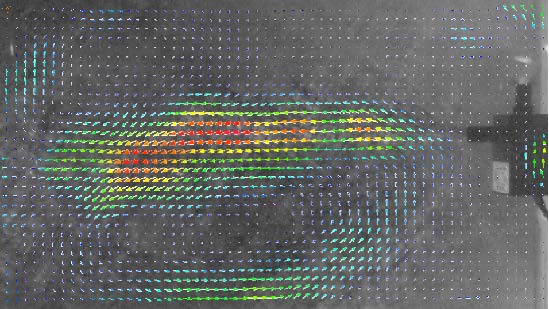
We propose a potential fluid-measurement technology aimed at supporting biomechanics research of water sports using fluid simulation and motion analysis. Cellulose nanofibers introduced into the water as tracer particles to visualize the movement of water. An optical property of nanofibers, called flow birefringence, makes water flows brighter than their surroundings when placed between right and left circularly polarized plates. We tested the capability of the technology in a water tank and succeeded in using an existing particle-tracking method-particle image velocimetry (PIV)-to measure the flows from a pump in the tank.
References:
- A Mtibe, Linda Z Linganiso, Aji P Mathew, Kristiina Oksman, Maya J John, and Rajesh D Anandjiwala. 2015. A comparative study on properties of micro and nanopapers produced from cellulose and cellulose nanofibres. Carbohydrate Polymers 118 (2015), 1–8.
- Kenzo Narita, Motomu Nakashima, and Hideki Takagi. 2018. Effect of leg kick on active drag in front-crawl swimming: comparison of whole stroke and arms-only stroke during front-crawl and the streamlined position. Journal of Biomechanics (2018).
- Markus Raffel, Christian E Willert, Jürgen Kompenhans, et al. 2007. Particle image velocimetry: a practical guide. Springer Science & Business Media.
- Weiguang Si, Sung-Hee Lee, Eftychios Sifakis, and Demetri Terzopoulos. 2014. Realistic biomechanical simulation and control of human swimming. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 1 (2014), 10.
- Timothy Wei, Russell Mark, and Sean Hutchison. 2014. The fluid dynamics of competitive swimming. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics 46 (2014), 547–565.