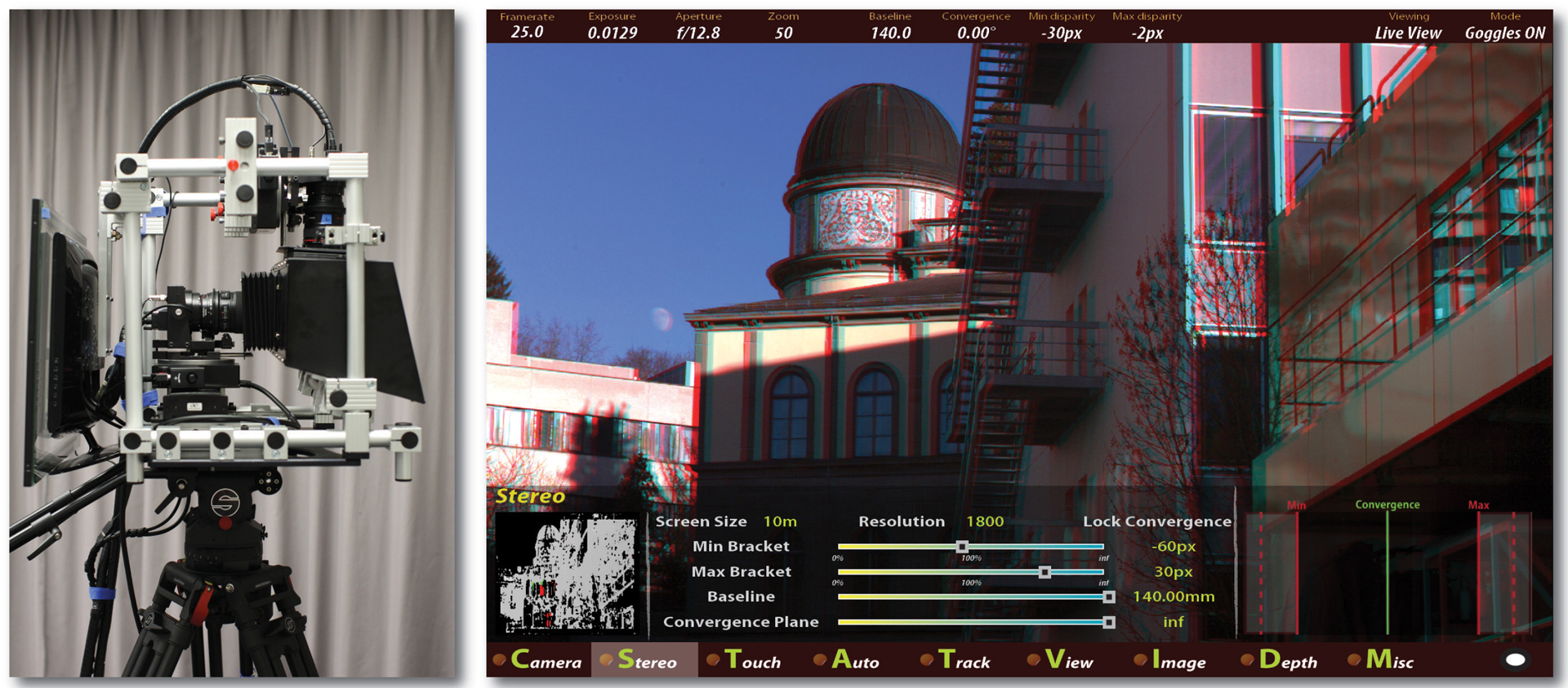
“Computational stereo camera system with programmable control loop” by Heinzle, Greisen, Gallup, Chen, Saner, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Computational stereo camera system with programmable control loop
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
Stereoscopic 3D has gained significant importance in the entertainment industry. However, production of high quality stereoscopic content is still a challenging art that requires mastering the complex interplay of human perception, 3D display properties, and artistic intent. In this paper, we present a computational stereo camera system that closes the control loop from capture and analysis to automatic adjustment of physical parameters. Intuitive interaction metaphors are developed that replace cumbersome handling of rig parameters using a touch screen interface with 3D visualization. Our system is designed to make stereoscopic 3D production as easy, intuitive, flexible, and reliable as possible. Captured signals are processed and analyzed in real-time on a stream processor. Stereoscopy and user settings define programmable control functionalities, which are executed in real-time on a control processor. Computational power and flexibility is enabled by a dedicated software and hardware architecture. We show that even traditionally difficult shots can be easily captured using our system.
References:
1. 3ality Digital, 2011. Beam splitter rigs and stereoscopic image processors. http://www.3alitydigital.com/.Google Scholar
2. Adams, A., Talvala, E.-V., Park, S. H., Jacobs, D. E., Ajdin, B., Gelfand, N., Dolson, J., Vaquero, D., Baek, J., Tico, M., Lensch, H. P. A., Matusik, W., Pulli, K., Horowitz, M., and Levoy, M. 2010. The Frankencamera: an experimental platform for computational photography. ACM Transactions of Graphics 29, 29:1–29:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Babenko, B., Yang, M., and Belongie, S. 2009. Visual tracking with online multiple instance learning. In Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 983–990.Google Scholar
4. Bouguet, J.-Y., 2010. Camera calibration toolbox for Matlab. http://www.vision.caltech.edu/bouguetj/calib_doc/.Google Scholar
5. Brown, D. C. 1966. Decentering distortion of lenses. Photogram-matric Engineering 32, 444–462.Google Scholar
6. Fraser, C. S., and Al-Ajlouni, S. 2006. Zoom-dependent camera calibration in digital close-range photogrammetry. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing 72, 1017–1026.Google ScholarCross Ref
7. Hoffman, D., Girshick, A., Akeley, K., and Banks, M. 2008. Vergence-accommodation conflicts hinder visual performance and cause visual fatigue. Journal of Vision 8, 3, 33.Google ScholarCross Ref
8. Howard, I. P., and Rogers, B. J. 2002. Seeing in Depth. Oxford University Press.Google Scholar
9. Jones, G., Lee, D., Holliman, N., and Ezra, D. 2001. Controlling perceived depth in stereoscopic images. SPIE, vol. 4297 of Stereoscopic Displays and Virtual Reality Systems, 42–53.Google Scholar
10. Kawai, T., Shibata, T., Inoue, T., Sakaguchi, Y., Okabe, K., and Kuno, Y. 2002. Development of software for editing of stereoscopic 3D movies. SPIE, vol. 4660 of Stereoscopic Displays and Virtual Reality Systems, 58–65.Google Scholar
11. Koppal, S., Zitnick, C. L., Cohen, M., Kang, S. B., Ressler, B., and Colburn, A. 2011. A viewer-centric editor for 3D movies. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications 31, 1, 20–35. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Lang, M., Hornung, A., Wang, O., Poulakos, S., Smolic, A., and Gross, M. H. 2010. Nonlinear disparity mapping for stereoscopic 3D. ACM Transactions on Graphics 29, 4. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Maier, F., 2010. Stereotec stereoscopic calculator. http://stereotec.com/.Google Scholar
14. Mallon, J., and Whelan, P. F. 2005. Projective rectification from the fundamental matrix. Image Vision Computing 23, 643–650. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Malvar, H., He, L.-W., and Cutler, R. 2004. High-quality linear interpolation for demosaicing of bayer-patterned color images. In International Conference of Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing, IEEE.Google Scholar
16. Masaoka, K., Hanazato, A., Emoto, M., Yamanoue, H., Nojiri, Y., and Okano, F. 2006. Spatial distortion prediction system for stereoscopic images. Electronic Imaging 15, 1, 013002:1–12.Google Scholar
17. Mendiburu, B. 2008. 3D Movie Making – Stereoscopic Digital Cinema from Script to Screen. Elsevier.Google Scholar
18. Mueller, R., Ward, C., and Husak, M. 2008. A systematized WYSIWYG pipeline for digital stereoscopic 3D filmmaking. SPIE, vol. 6803 of Stereoscopic Displays and Applications.Google Scholar
19. Pitié, F., Kokaram, A., and Dahyot, R. 2007. Automated colour grading using colour distribution transfer. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 107, 1-2, 123–137. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Ramanath, R., Snyder, W., Yoo, Y., and Drew, M. 2005. Color image processing pipeline. Signal Processing Magazine, IEEE 22, 1, 34–43.Google ScholarCross Ref
21. Sony, 2011. MPE200 multi image processor and software. http://pro.sony.com/.Google Scholar
22. Sun, G., and Holliman, N. 2009. Evaluating methods for controlling depth perception in stereoscopic cinematography. SPIE, vol. 7237 of Stereoscopic Displays and Virtual Reality Systems.Google Scholar
23. The Foundry, 2010. Ocula stereoscopic post-production plug-ins for Nuke. http://www.thefoundry.co.uk/.Google Scholar
24. Wang, C., and Sawchuk, A. A. 2008. Disparity manipulation for stereo images and video. SPIE, vol. 6803 of Stereoscopic displays and applications.Google Scholar
25. Zach, C., Karner, K., and Bischof, H. 2004. Hierarchical disparity estimation with programmable 3D hardware. In Short communications of WSCG, 275–282.Google Scholar
26. Zilly, F., Eisert, P., and Kauff, P. 2009. Real-time analysis and correction of stereoscopic HDTV sequences. In Proceedings of Visual Media Production.Google Scholar
27. Zilly, F., Mueller, M., Eisert, P., and Kauff, P. 2010. Joint estimation of epipolar geometry and rectification parameters using point correspondences for stereoscopic TV sequences. In Proceedings of 3DPVT.Google Scholar
28. Zilly, F., Mueller, M., Eisert, P., and Kauff, P. 2010. The stereoscopic analyzer – an image-based assistance tool for stereo shooting and 3D production. In IEEE International Conference on Image Processing.Google Scholar