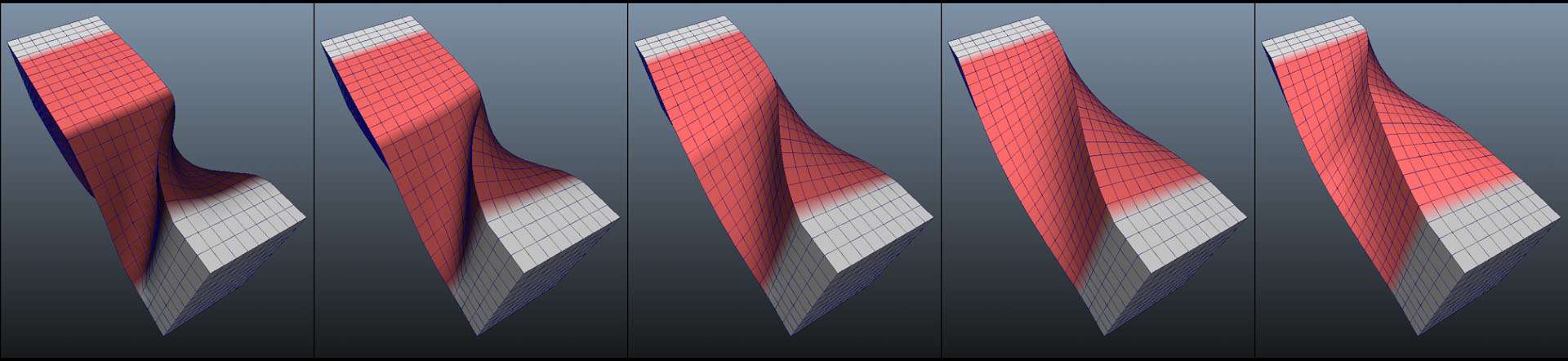
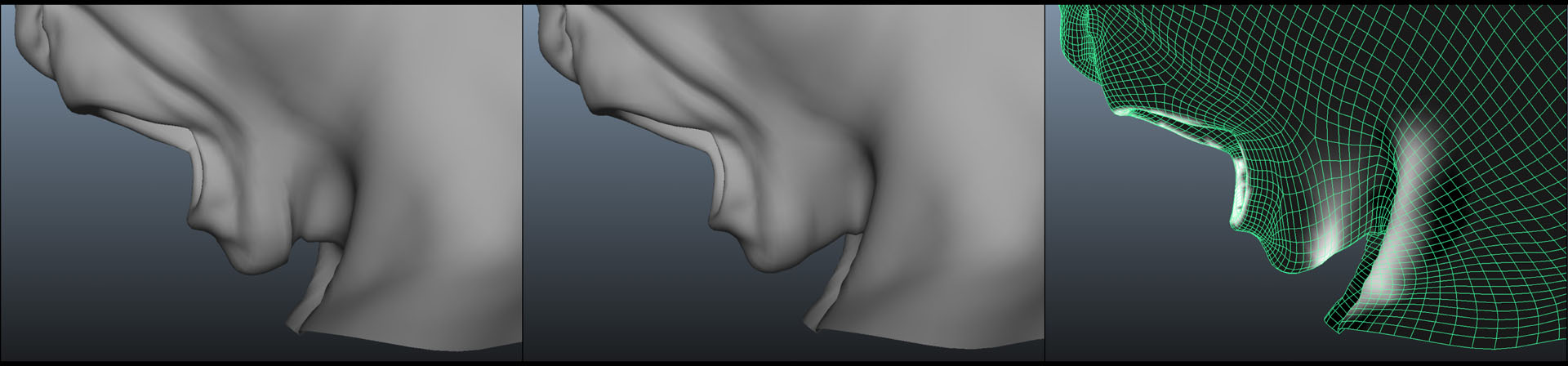
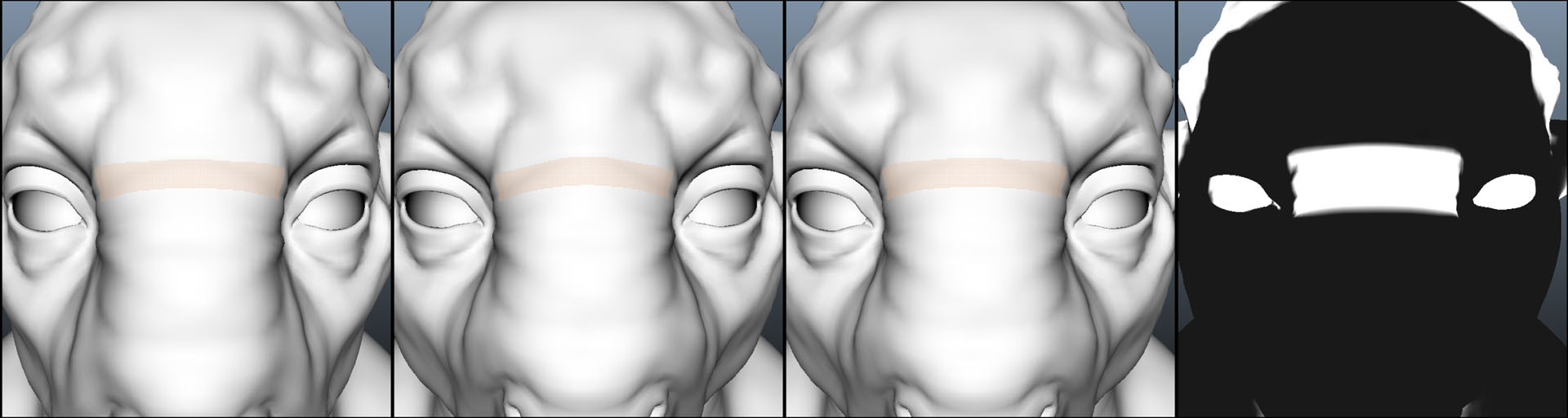
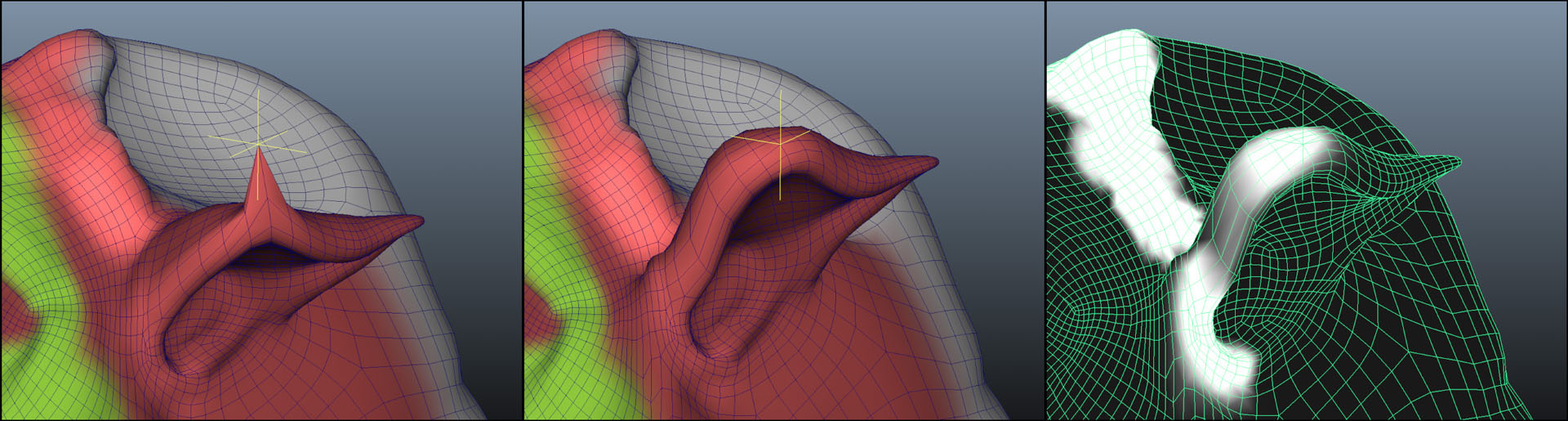
“As-Rigid-As-Possible Deformation Transfer for Facial Animation” by Corral, Roble and Moser
Conference:
Title:
- As-Rigid-As-Possible Deformation Transfer for Facial Animation
Session/Category Title:
- Face Off
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Entry Number:
- 29
Abstract:
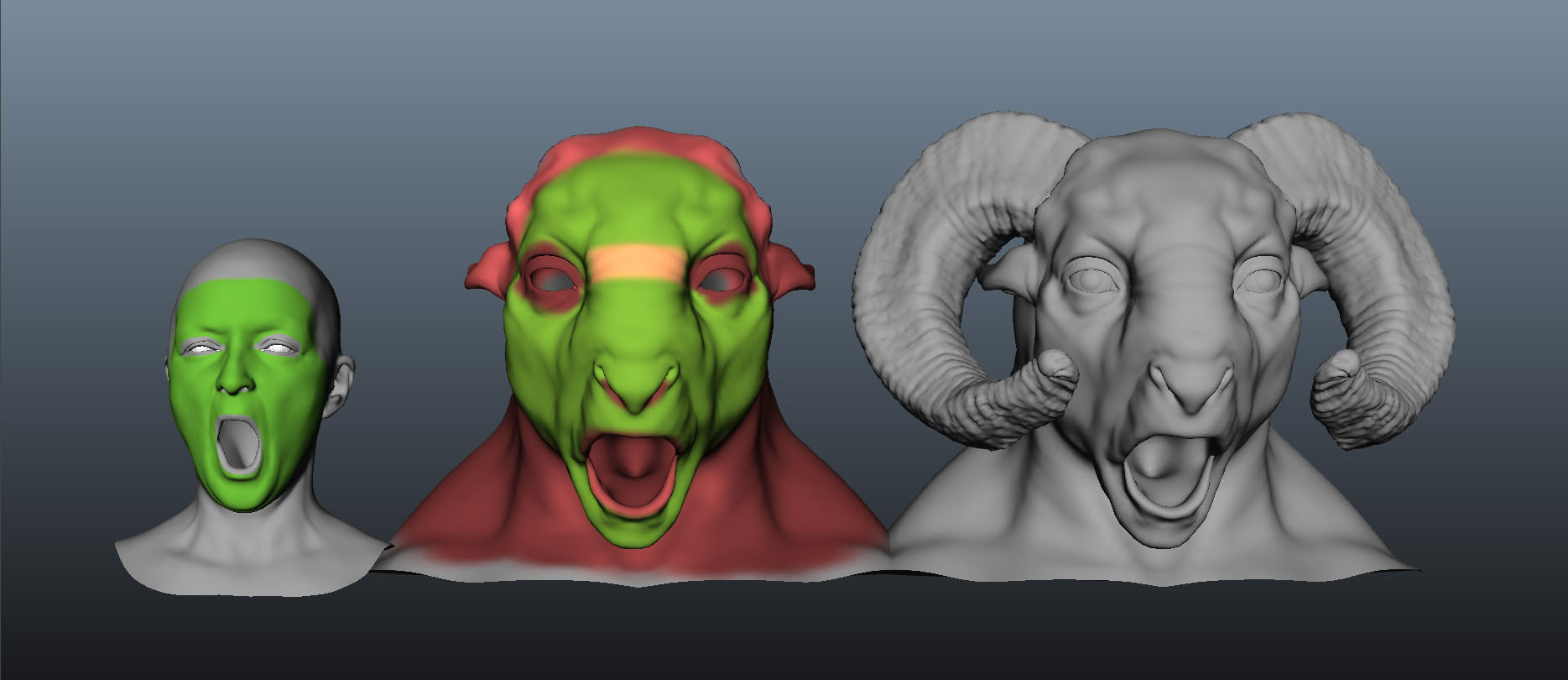
We present a novel tool for transferring facial motion capture performance between significantly different characters. This work combines the shape deformation techniques of Deformation Transfer (DT) and As-Rigid-As-Possible (ARAP) into a single formulation by defining rigidity over triangle edge sets as opposed to spokes. Further, it improves them by adding non-uniform rigidity using paintable weights. We examine three important use cases for the tool: adding physically plausible behavior where animation is not available; fixing animation transfer artifacts; and providing plausible deformation around manipulated vertices. By combining Deformation Transfer and As-Rigid-As-Possible, this tool allows users to control the balance between animation fidelity and physically plausible deformation.
References:
Botsch, M., Sumner, R., Pauly, M., and Gross, M. 2006. Deformation Transfer for Detail-Preserving Surface Editing. In Vision, Modeling & Visualization, 357–364.Google Scholar
Chao, I., Pinkall, U., Sanan, P., and Schröder, P. 2010. A simple geometric model for elastic deformations. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 4 (July), 38:1–38:6. Google ScholarDigital Library
Levi, Z., and Gotsman, C. 2015. Smooth rotation enhanced as-rigid-as-possible mesh animation. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 21, 2, 264–277.Google ScholarCross Ref
Sorkine, O., and Alexa, M. 2007. As-rigid-as-possible surface modeling. In Proceedings of the Fifth Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing, Eurographics Association, Airela-Ville, Switzerland, Switzerland, SGP ’07, 109–116. Google ScholarDigital Library
Sumner, R. W., and Popović, J. 2004. Deformation transfer for triangle meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (Aug.), 399–405.