“A Versatile High-Resolution Scanning System and its Application to Statistical Analysis of Lizards’ Skin Colour Time-Evolution” by Manukyan, Martins, Montandon, Bessant and Milinkovitch
Conference:
Type(s):
Entry Number: 06
Title:
- A Versatile High-Resolution Scanning System and its Application to Statistical Analysis of Lizards’ Skin Colour Time-Evolution
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
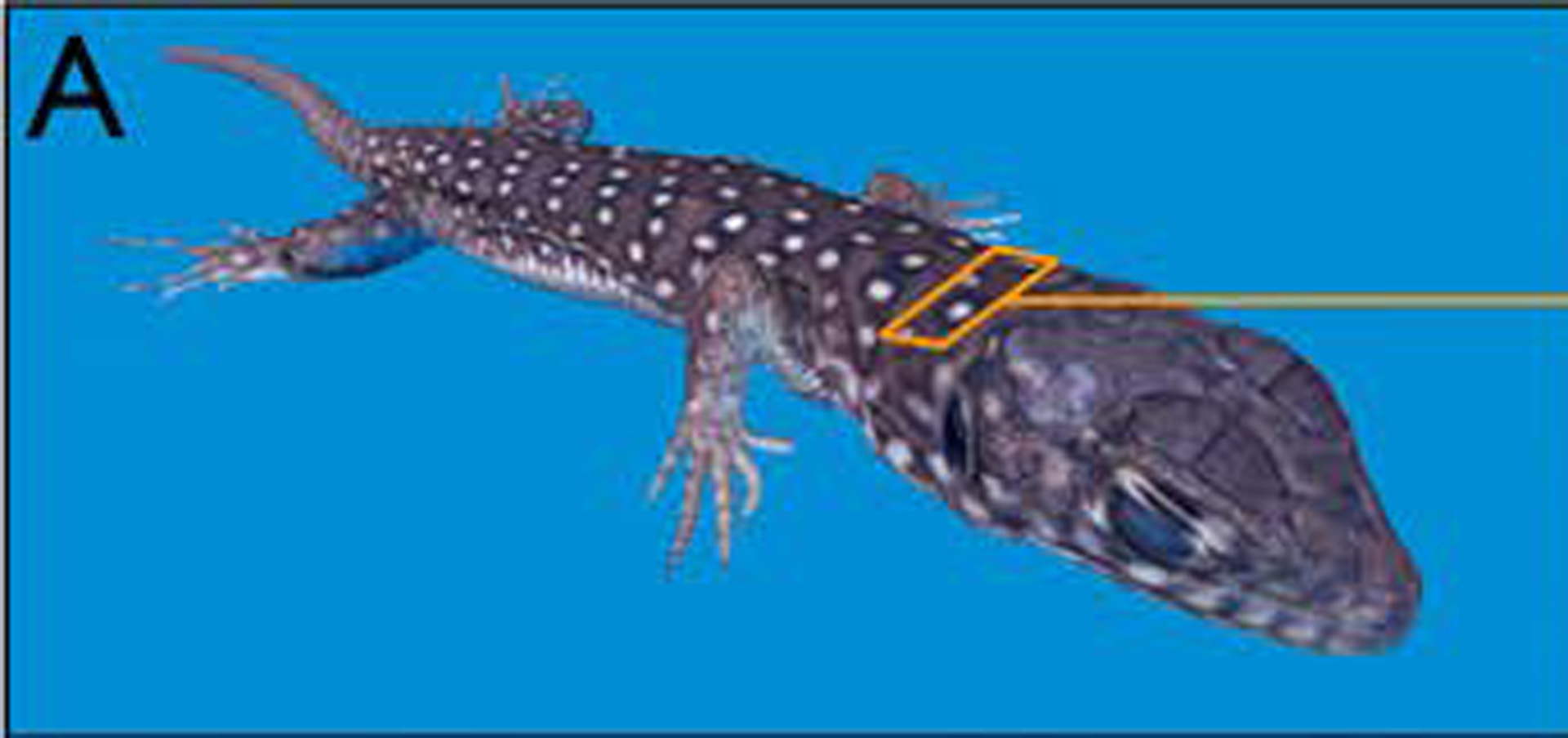
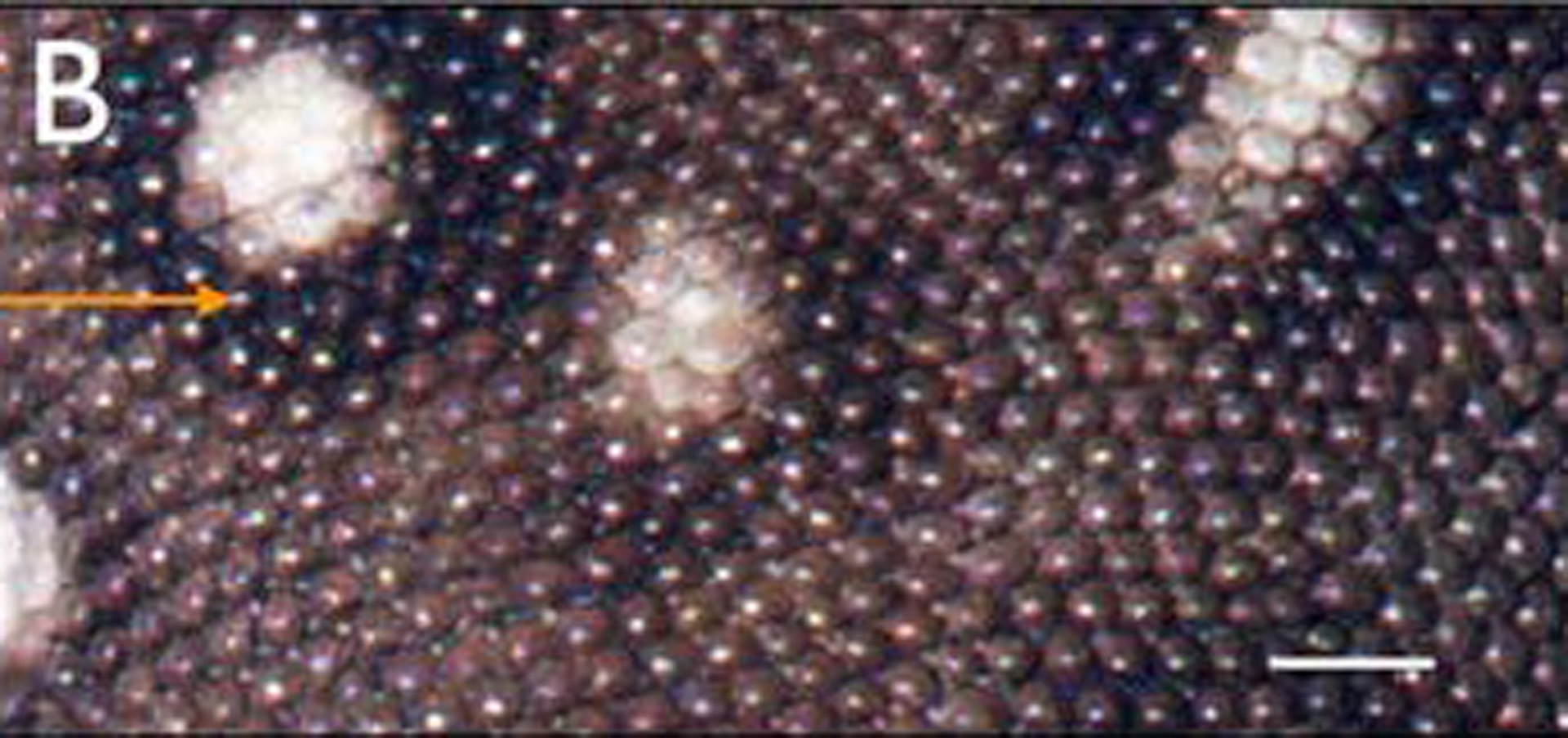
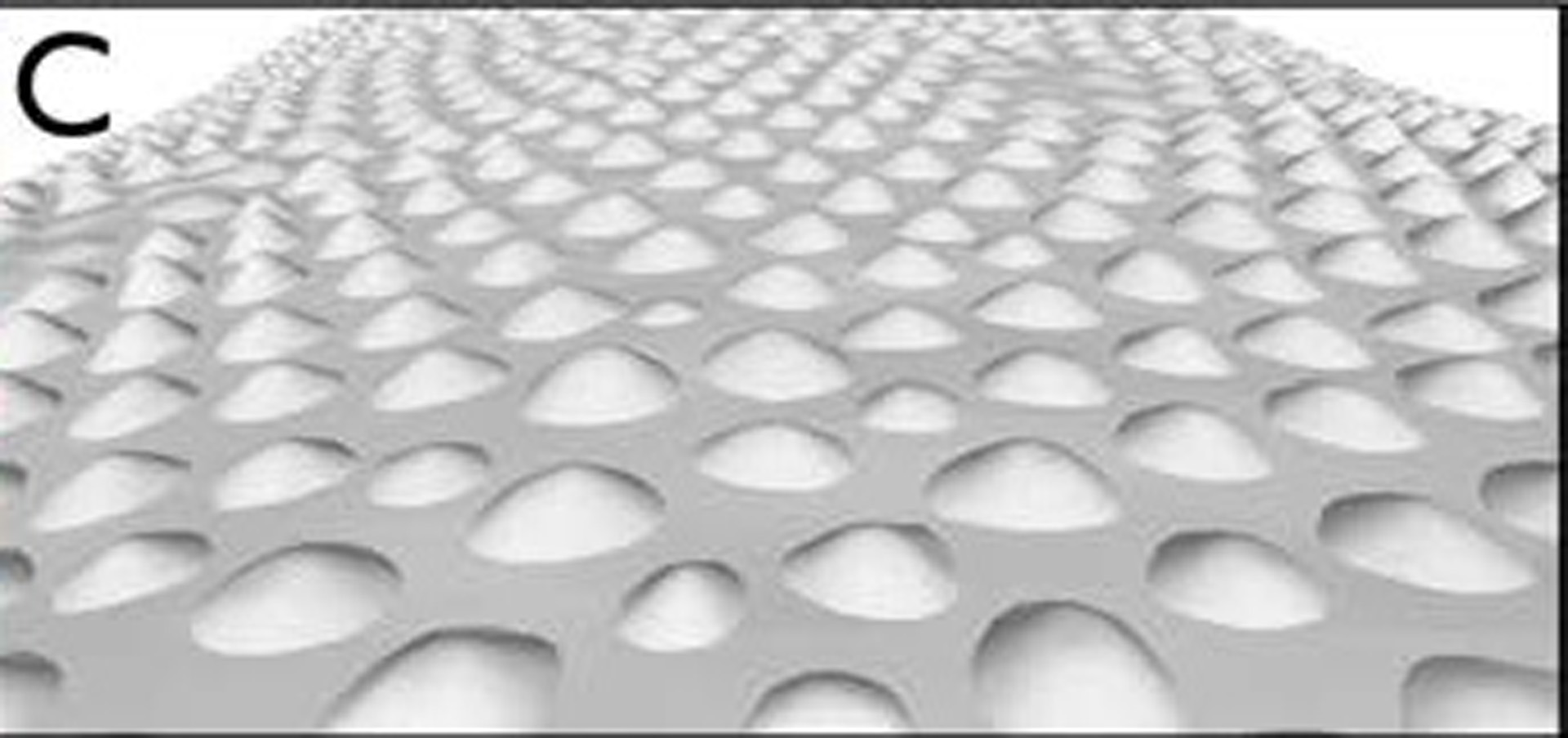
Numerous methods and systems exist for 3D objects scanning. Each application area uses different types of hardware and software setups, requiring application-specific fine-tuning. Robotic scanning systems are usually used in manufacturing and reverseengineering (e.g., for inspection of parts in a production line). For safety reasons, robotic systems are complicated to use. However the aim of our project was to develop high-quality, fast and versatile hardware for automated scanning small-sized (from 2cm to 100cm long) living animals under anaesthesia for investigating the evolution and development of morphological features. Two reconstruction approaches, Structure from Motion (SfM; [Furukawa and Ponce 2010]) and Photometric Stereo (PS; [Papadhimitri and Favaro 2014]) are of particular interest to us, as they can be performed fast, do not require additional complicated hardware and are scalable. PS acquires high-frequency micro-geometry information, but often generates a low-frequency bias, while SFM provides low frequency unbiased geometry. Our robotic system allows combining the two methods, yielding enough resolution and completeness to investigate the time-evolution of single skin appendage (scales) colour change during animal growth (see Fig. 1.)
References:
- Furukawa, Y., and Ponce, J. 2010. Accurate, dense, and robust multiview stereopsis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32, 8 (Aug.), 1362–1376.
- Nehab, D., Rusinkiewicz, S., Davis, J., and Ramamoorthi, R. 2005. Efficiently combining positions and normals for precise 3D geometry. ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proc. of ACM SIGGRAPH 2005) 24, 3 (Aug.).
- Papadhimitri, T., and Favaro, P. 2014. A closed-form, consistent and robust solution to uncalibrated photometric stereo via local diffuse reflectance maxima. International Journal of Computer Vision 107, 2, 139–154.