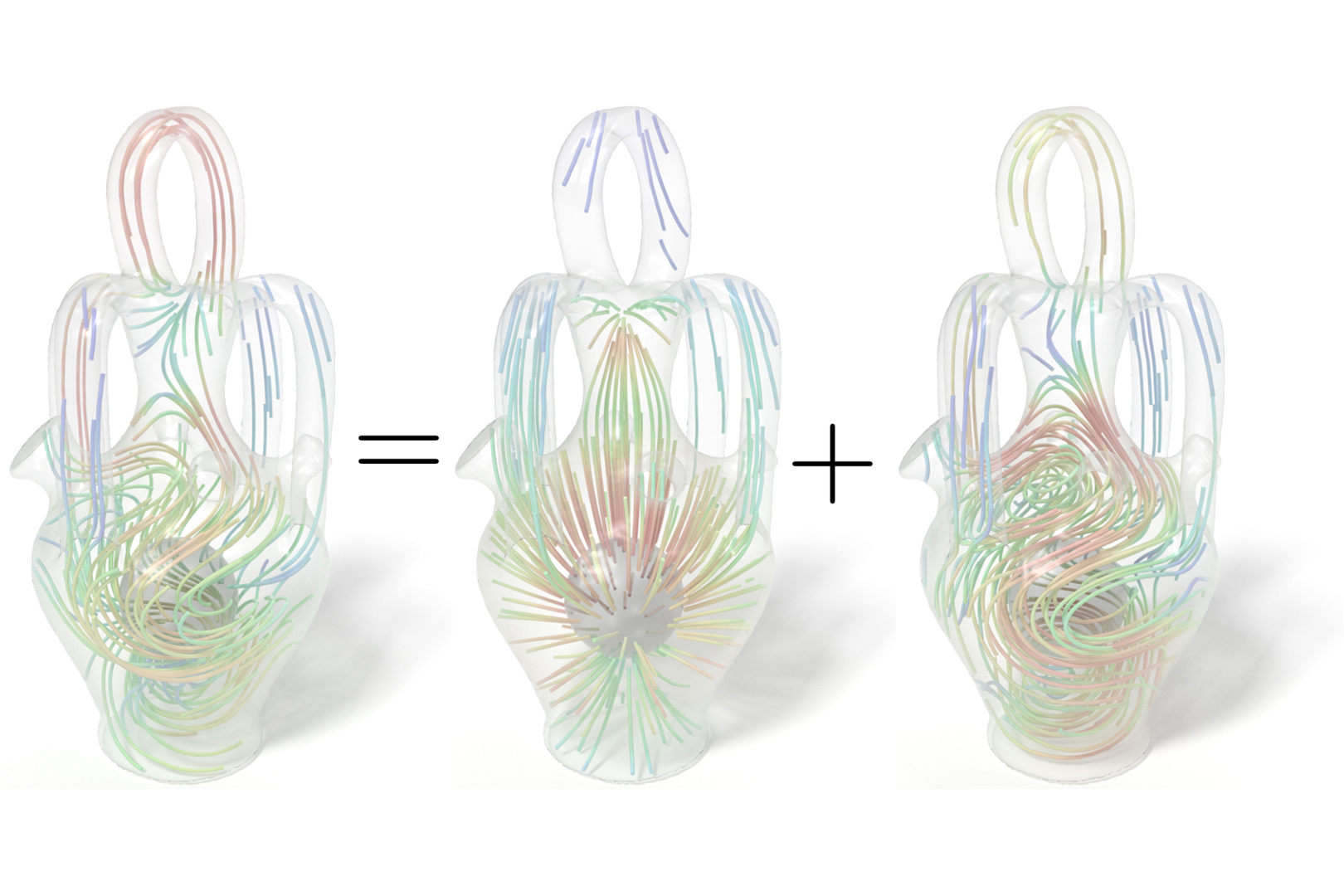“3D hodge decompositions of edge- and face-based vector fields” by Zhao, Desbrun, Wei and Tong
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- 3D hodge decompositions of edge- and face-based vector fields
Session/Category Title:
- Composing & Decomposing Geometry
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
We present a compendium of Hodge decompositions of vector fields on tetrahedral meshes embedded in the 3D Euclidean space. After describing the foundations of the Hodge decomposition in the continuous setting, we describe how to implement a five-component orthogonal decomposition that generically splits, for a variety of boundary conditions, any given discrete vector field expressed as discrete differential forms into two potential fields, as well as three additional harmonic components that arise from the topology or boundary of the domain. The resulting decomposition is proper and mimetic, in the sense that the theoretical dualities on the kernel spaces of vector Laplacians valid in the continuous case (including correspondences to cohomology and homology groups) are exactly preserved in the discrete realm. Such a decomposition only involves simple linear algebra with symmetric matrices, and can thus serve as a basic computational tool for vector field analysis in graphics, electromagnetics, fluid dynamics and elasticity.
References:
1. Ralph Abraham, Jerrold E. Marsden, and Tudor Ratiu. 1988. Manifolds, Tensor Analysis, and Applications. Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 75. Springer-Verlag.Google Scholar
2. Cherif Amrouche, Christine Bernardi, Monique Dauge, and Vivette Girault. 1998. Vector potentials in three-dimensional non-smooth domains. Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences 21, 9 (1998), 823–864.Google ScholarCross Ref
3. Douglas Arnold. 2018. Finite Element Exterior Calculus. SIAM.Google Scholar
4. Douglas N Arnold and Richard S Falk. 1989. A uniformly accurate finite element method for the Reissner-Mindlin plate. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 26, 6 (1989), 1276–1290.Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Harsh Bhatia, Gregory Norgard, Valerio Pascucci, and Peer-Timo Bremer. 2013. The Helmholtz-Hodge decomposition-a survey. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comp. Graph. 19, 8 (2013), 1386–1404.Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Harsh Bhatia, Valerio Pascucci, and Peer-Timo Bremer. 2014. The natural Helmholtz-Hodge decomposition for open-boundary flow analysis. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comp. Graph. 20, 11 (2014), 1566–1578.Google ScholarCross Ref
7. Alain Bossavit. 2000. Computational electromagnetism and geometry. (5): The ‘Galerkin Hodge’. J. Japan Soc. Appl. Electromagn. & Mech. 8, 2 (2000), 203–209.Google Scholar
8. Alain Bossavit and Lauri Kettunen. 1999. Yee-like schemes on a tetrahedral mesh, with diagonal lumping. Int. J. Num. Model. Elec. Net. Dev. Fields 12, 1–2 (1999), 129–142.Google Scholar
9. Jason Cantarella, Dennis DeTurck, and Herman Gluck. 2002. Vector calculus and the topology of domains in 3-space. American math. monthly 109, 5 (2002), 409–442.Google Scholar
10. Salvatore Caorsi, Paolo Fernandes, and Mirco Raffetto. 2001. On the Convergence of Galerkin Finite Element Approximations of Electromagnetic Eigenproblems. SIAM J. Numerical Analysis 38, 2 (2001), 580–607.Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Albert Chern. 2017. Fluid dynamics with incompressible Schrödinger flow. Ph.D. Dissertation. California Institute of Technology.Google Scholar
12. Fabrice Colin, Richard Egli, and Feng Ying Lin. 2006. Computing a null divergence velocity field using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J. Comp. Phys. 217, 2 (2006), 680–692.Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Keenan Crane, Fernando de Goes, Mathieu Desbrun, and Peter Schröder. 2013. Digital Geometry Processing with Discrete Exterior Calculus. In SIGGRAPH Course #7.Google Scholar
14. Fernando de Goes, Mathieu Desbrun, Mark Meyer, and Tony DeRose. 2016b. Subdivision Exterior Calculus for Geometry Processing. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 4, Article 133 (2016).Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Fernando de Goes, Mathieu Desbrun, and Yiying Tong. 2016a. Vector Field Processing on Triangle Meshes. In SIGGRAPH Course #27.Google Scholar
16. Alan Demlow and Anil N. Hirani. 2014. A posteriori error estimates for finite element exterior calculus: the de Rham complex. Found. Comput. Math. 14, 6 (2014), 1337–1371.Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Mathieu Desbrun, Anil N. Hirani, and Jerrold E. Marsden. 2003. Discrete Exterior Calculus for variational problems in computer vision and graphics. In Inter. Conf. on Decision and Control, Vol. 5. 4902–4907.Google Scholar
18. Mathieu Desbrun, Eva Kanso, and Yiying Tong. 2008. Discrete differential forms for computational modeling. In Discrete Differential Geometry, Alexander I. Bobenko et al. (Ed.). Birkhäuser Basel, 287–324.Google Scholar
19. Sharif Elcott, Yiying Tong, Eva Kanso, Peter Schröder, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2007. Stable, circulation-preserving, simplicial fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 1, Article 4 (2007).Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Kurt O. Friedrichs. 1955. Differential forms on Riemannian manifolds. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics 8, 4 (1955), 551–590.Google ScholarCross Ref
21. William V. D. Hodge. 1941. The theory and applications of harmonic integrals. Cambridge U. Press.Google Scholar
22. Christian Lessig. 2012. A primer on differential forms. (2012). arXiv:1206.3323.Google Scholar
23. Mamdouh S. Mohamed, Anil N. Hirani, and Ravi Samtaney. 2016. Comparison of discrete Hodge star operators for surfaces. Comput. Aided Des. 78 (2016), 118–125.Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Peter B Monk. 1991. A mixed method for approximating Maxwell’s equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 28, 6 (1991), 1610–1634.Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Charles B. Morrey. 1956. A Variational Method in the Theory of Harmonic Integrals, II. American Journal of Mathematics 78, 1 (1956), 137–170.Google ScholarCross Ref
26. Konstantin Poelke. 2017. Hodge-type decompositions for piecewise constant vector fields on simplicial surfaces and solids with boundary. Ph.D. Dissertation. FU Berlin.Google Scholar
27. Konstantin Poelke and Konrad Polthier. 2016. Boundary-aware hodge decompositions for piecewise constant vector fields. Computer-Aided Design 78 (2016), 126–136.Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Konrad Polthier and Eike Preuß. 2000. Variational approach to vector field decomposition. In Data Visualization. Springer, 147–155.Google Scholar
29. Faniry Razafindrazaka, Pavlov Yevtushenko, Konstantin Poelke, Konrad Polthier, and Leonid Goubergrits. 2018. Hodge decomposition of wall shear stress vector fields characterizing biological flows. (2018).Google Scholar
30. Günter Schwarz. 1995. Hodge decomposition: a method for solving boundary value problems. Springer-Verlag.Google Scholar
31. Clayton Shonkwiler. 2009. Poincaré duality angles for Riemannian manifolds with boundary. arXiv preprint arXiv:0909.1967 (2009).Google Scholar
32. Jos Stam. 1999. Stable fluids. In ACM SIGGRAPH proceedings. 121–128.Google ScholarDigital Library
33. Yiying Tong, Pierre Alliez, David Cohen-Steiner, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2006. Designing Quadrangulations with Discrete Harmonic Forms. In Symp. Geo. Proc. 201–210.Google Scholar
34. Yiying Tong, Santiago Lombeyda, Anil N. Hirani, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2003. Discrete Multiscale Vector Field Decomposition. ACM Trans. Graph. 22, 3 (2003), 445–452.Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Joel A. Tropp. 2009. Column Subset Selection, Matrix Factorization, and Eigenvalue Optimization. In Symp. Disc. Algo. 978–986.Google ScholarCross Ref
36. Amir Vaxman, Marcel Campen, Olga Diamanti, Daniele Panozzo, David Bommes, Klaus Hildebrandt, and Mirela Ben-Chen. 2016. Directional Field Synthesis, Design, and Processing (STAR). Computer Graphics Forum (2016).Google Scholar
37. Ke Wang, Weiwei, Yiying Tong, Mathieu Desbrun, and Peter Schröder. 2006. Edge subdivision schemes and the construction of smooth vector fields. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 3 (2006), 1041–1048.Google ScholarDigital Library