“Data-Driven Suggestions for Portrait Posing” by Fu, Han and Phan
Conference:
Experience Type(s):
Title:
- Data-Driven Suggestions for Portrait Posing
Award:
Organizer(s)/Presenter(s):
Description:
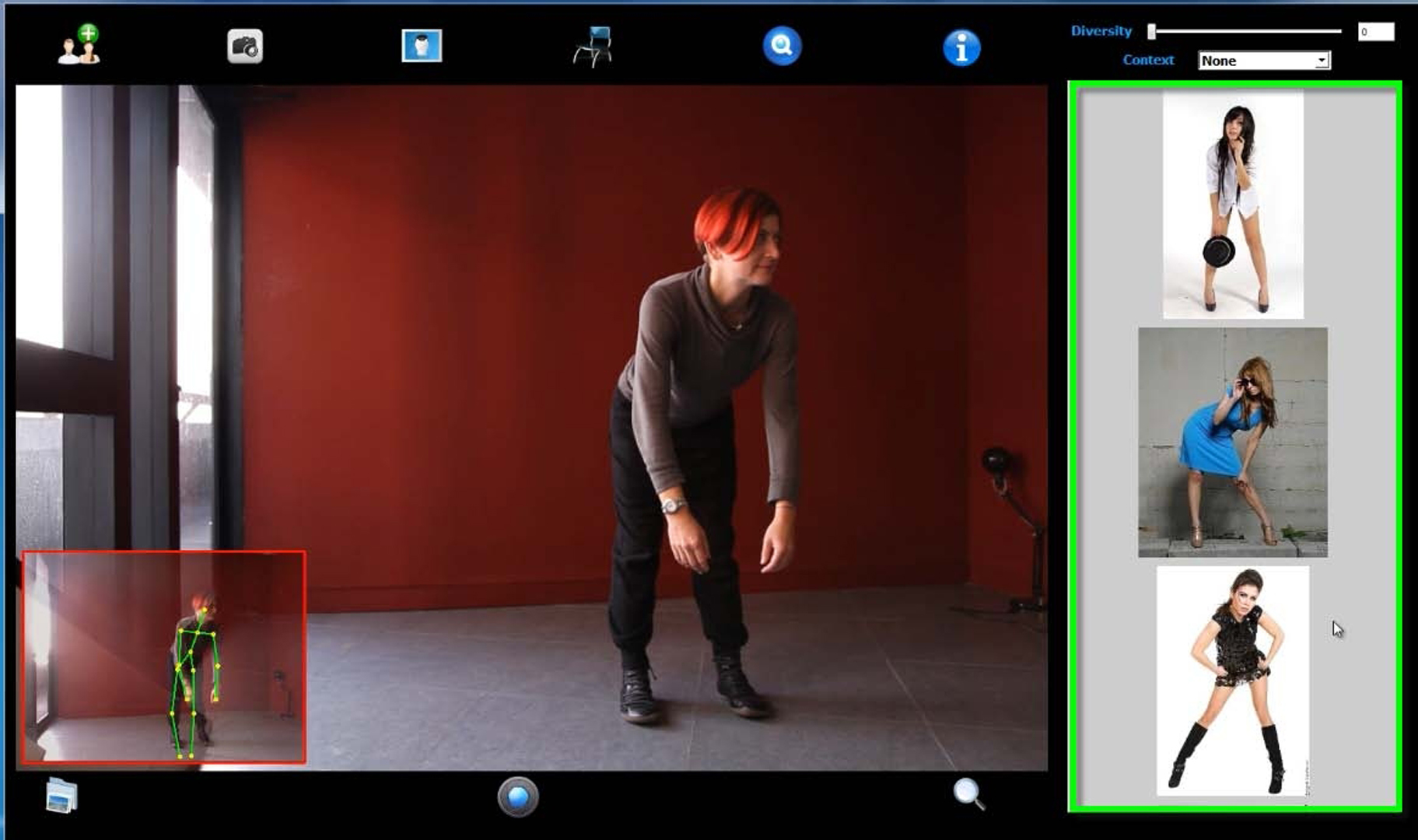
Next to lighting, posing is the most challenging aspect of portrait photography. A commonly adopted solution is to learn by example, which is beneficial for both trained photographers and novice users, especially when subjects have no clue about how to pose themselves. A collection of portrait images by professionals (e.g., [Perkins 2009]) provides a resource for photographers seeking inspiration for their own work. Such handful posing references (e.g., Posing App) have also been made available to smartphone platforms, which offer the unique possibility of directly overlaying camera view with a reference pose as visual guidance.
This work introduces an easy-to-use creativity support tool for portrait posing, which is an important but challenging problem in portrait photography. While it is well known that a collection of sample poses is a source of inspiration, manual browsing is the only option to identify a desired pose from a possibly large collection of poses. With our tool, a photographer is able to easily retrieve desired reference poses as guidance or stimulate creativity. We show how our data-driven suggestions can be effectively used to either refine the current pose of a subject or explore new poses. Our tool greatly helps unskilled photographers create aesthetically pleasing portraits with diversity. Our work takes the first step of using consumer-level depth sensors towards more intelligent cameras for computational photography.
References:
[1] Chaudhuri, S., and Koltun, V. 2010. Data-driven suggestions for creativity support in 3d modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 6, 183:1–183:10.
[2] Cheng, B., Ni, B., Yan, S., and Tian, Q. 2010. Learning to photograph. In MM ’10, ACM, 291–300.
[3] Choi, M. G., Yang, K., Igarashi, T., Mitani, J., and Lee, J. 2012. Retrieval and visualization of human motion data via stick figures. Computer Graphics Forum 21, 7, 2057–2065.
[4] Jammalamadaka, N., Zisserman, A., Eichner, M., Ferrari, V., and Jawahar, C. 2012. Video retrieval by mimicking poses. In ICMR, ACM, 34.
[5] Lee, Y. J., Zitnick, C. L., and Cohen, M. F. 2011. Shadowdraw: real-time user guidance for freehand drawing. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 27:1–27:10.
[6] Nara, Y., Fujimura, W., Koide, Y., Kunitomi, G., and Shirai, A. 2013. Kinemotion: context controllable emotional motion analysis method for interactive cartoon generator. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2013 Posters.
[7] Perkins, M. 2009. 500 Poses for Photographing Women: A Visual Sourcebook for Portrait Photographers. Amherst Media, Incorporated.
[8] Projects, L., 2013. Sculpture lens – strike a pose. Cleveland Museum of Art.
[9] Smith, J. 2004. Posing for Portrait Photography: A Head-to-Toe Guide. Amherst Media, Incorporated.
[10] Yeh, J.-S., Wen, C.-L., Chiang, J.-Y., Wang, L.-K., Huan, T.-H., Chen, D.-Y., Lin, L.-F., Chuang, Y.-Y., Yu, M.-Y., Chen, B.-Y., et al. 2006. Bodyrevolution: Hand-shadow illusions and 3d DDR based on efficient model retrieval. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2006 Emerging technologies, 13.
[11] Yin, W., Mei, T., and Chen, C. W. 2012. Crowdsourced learning to photograph via mobile devices. In ICME ’12, 812–817.
[12] Zhou, S., Fu, H., Liu, L., Cohen-Or, D., and Han, X. 2010. Parametric reshaping of human bodies in images. ACM Transactions on Computer Graphics 29, 4, Article No. 126.