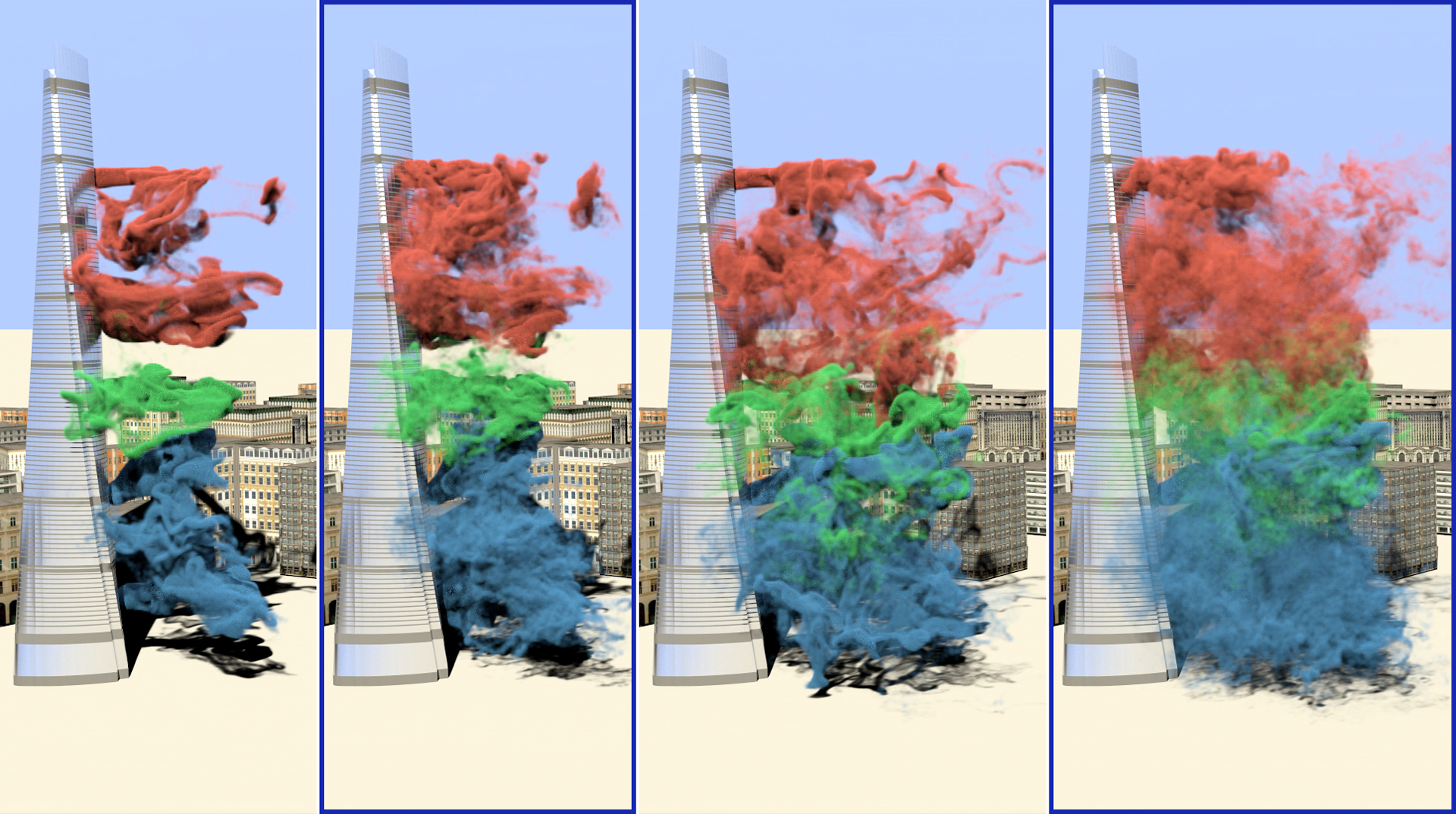
“Predicting high-resolution turbulence details in space and time” by Bai, Wang, Desbrun and Liu
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Predicting high-resolution turbulence details in space and time
Session/Category Title: Turbulence and Fluids
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
Predicting the fine and intricate details of a turbulent flow field in both space and time from a coarse input remains a major challenge despite the availability of modern machine learning tools. In this paper, we present a simple and effective dictionary-based approach to spatio-temporal upsampling of fluid simulation. We demonstrate that our neural network approach can reproduce the visual complexity of turbulent flows from spatially and temporally coarse velocity fields even when using a generic training set. Moreover, since our method generates finer spatial and/or temporal details through embarrassingly-parallel upsampling of small local patches, it can efficiently predict high-resolution turbulence details across a variety of grid resolutions. As a consequence, our method offers a whole range of applications varying from fluid flow upsampling to fluid data compression. We demonstrate the efficiency and generalizability of our method for synthesizing turbulent flows on a series of complex examples, highlighting dramatically better results in spatio-temporal upsampling and flow data compression than existing methods as assessed by both qualitative and quantitative comparisons.
References:
1. Martín Abadi, Paul Barham, Jianmin Chen, Zhifeng Chen, Andy Davis, Jeffrey Dean, Matthieu Devin, Sanjay Ghemawat, Geoffrey Irving, Michael Isard, et al. 2016. Tensorflow: a system for large-scale machine learning.. In OSDI, Vol. 16. 265–283.
2. Giancarlo Alfonsi. 2009. Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes equations for turbulence modeling. Applied Mechanics Reviews 62, 4 (2009).
3. Kai Bai, Wei Li, Mathieu Desbrun, and Xiaopei Liu. 2020. Dynamic Upsampling of Smoke through Dictionary-Based Learning. ACM Trans. Graph. 40, 1, Article 4 (Sept. 2020), 19 pages.
4. Robert Bridson, Jim Houriham, and Marcus Nordenstam. 2007. Curl-Noise for Procedural Fluid Flow. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3.
5. René-Daniel Cécora, Rolf Radespiel, Bernhard Eisfeld, and Axel Probst. 2015. Differential Reynolds-stress modeling for aeronautics. AIAA Journal 53, 3 (2015), 739–755.
6. Yixin Chen, Wei Li, Rui Fan, and Xiaopei Liu. 2021. GPU Optimization for High-Quality Kinetic Fluid Simulation. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comp. Graph. (2021).
7. Jack Chessa and Ted Belytschko. 2003. An extended finite element method for two-phase fluids. J. Appl. Mech. 70, 1 (2003), 10–17.
8. Mengyu Chu and Nils Thuerey. 2017. Data-Driven Synthesis of Smoke Flows with CNN-Based Feature Descriptors. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4, Article 69 (July 2017), 14 pages.
9. P. Clark di Leoni, P. J. Cobelli, and P. D. Mininni. 2015. The spatio-temporal spectrum of turbulent flows. Eur. Phys. J. E 38, 136 (2015), 1–10.
10. Fernando de Goes, Corentin Wallez, Jin Huang, Dmitry Pavlov, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2015. Power Particles: An Incompressible Fluid Solver Based on Power Diagrams. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4, Article 50 (July 2015), 11 pages.
11. Alessandro De Rosis. 2017. Nonorthogonal central-moments-based lattice Boltzmann scheme in three dimensions. Physical Review E 95, 1 (2017), 013310.
12. Karthik Duraisamy, Gianluca Iaccarino, and Heng Xiao. 2019. Turbulence Modeling in the Age of Data. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics 51, 1 (2019), 357–377.
13. EA Fadlun, Roberto Verzicco, Paolo Orlandi, and J Mohd-Yusof. 2000. Combined immersed-boundary finite-difference methods for three-dimensional complex flow simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 161, 1 (2000), 35–60.
14. Ronald Fedkiw, Jos Stam, and Henrik Wann Jensen. 2001. Visual Simulation of Smoke. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques. 15–22.
15. Zahra Forootaninia and Rahul Narain. 2020. Frequency-Domain Smoke Guiding. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 6, Article 172 (Nov. 2020), 10 pages.
16. Kai Fukami, Koji Fukagata, and Kunihiko Taira. 2021. Machine-learning-based spatio-temporal super resolution reconstruction of turbulent flows. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 909 (2021).
17. M Geier, A Greiner, and JG Korvink. 2006. Cascaded digital lattice Boltzmann automata for high Reynolds number flow. Physical Review. E 73, 6.2 (2006), 066705–066705.
18. Abhinav Golas, Rahul Narain, Jason Sewall, Pavel Krajcevski, Pradeep Dubey, and Ming Lin. 2012. Large-Scale Fluid Simulation Using Velocity-Vorticity Domain Decomposition. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6, Article 148 (Nov. 2012), 9 pages.
19. Xiaoxiao Guo, Wei Li, and Francesco Iorio. 2016. Convolutional neural networks for steady flow approximation. In ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. 481–490.
20. SoHyeon Jeong, Barbara Solenthaler, Marc Pollefeys, Markus Gross, et al. 2015. Data-Driven Fluid Simulations Using Regression Forests. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6, Article 199 (Oct. 2015), 9 pages.
21. Huaizu Jiang, Deqing Sun, Varun Jampani, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Erik Learned-Miller, and Jan Kautz. 2018. Super slomo: High quality estimation of multiple intermediate frames for video interpolation. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 9000–9008.
22. Volker John. 2003. Large eddy simulation of turbulent incompressible flows: analytical and numerical results for a class of LES models. Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering, Vol. 34. Springer Science & Business Media.
23. Madhuri A Joshi, Mehul S Raval, Yogesh H Dandawate, Kalyani R Joshi, and Shilpa P Metkar. 2014. Image and video compression: Fundamentals, Techniques, and Applications. CRC press.
24. Hyungmin Kang, Dongho Lee, and Dohyung Lee. 2003. A study on CFD data compression using hybrid supercompact wavelets. KSME international journal 17, 11 (2003), 1784–1792.
25. Byungsoo Kim, Vinicius C. Azevedo, Markus Gross, and Barbara Solenthaler. 2020. Lagrangian Neural Style Transfer for Fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 4, Article 52 (July 2020), 10 pages.
26. Byungsoo Kim, Vinicius C. Azevedo, Nils Thuerey, Theodore Kim, Markus Gross, and Barbara Solenthaler. 2019. Deep Fluids: A Generative Network for Parameterized Fluid Simulations. Computer Graphics Forum 38, 2 (2019).
27. Jungwoo Kim, Dongjoo Kim, and Haecheon Choi. 2001. An immersed-boundary finite-volume method for simulations of flow in complex geometries. J. Comput. Phys. 171, 1 (2001), 132–150.
28. Theodore Kim and John Delaney. 2013. Subspace Fluid Re-Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4, Article 62 (July 2013), 9 pages.
29. Theodore Kim, Nils Thürey, Doug James, and Markus Gross. 2008. Wavelet Turbulence for Fluid Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3 (Aug. 2008), 1–6.
30. Diederik P Kingma and Jimmy Ba. 2014. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014).
31. Dmitrii Kochkov, Jamie A Smith, Ayya Alieva, Qing Wang, Michael P Brenner, and Stephan Hoyer. 2021. Machine learning-accelerated computational fluid dynamics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 118, 21 (2021).
32. Dmitry Kolomenskiy, Ryo Onishi, and Hitoshi Uehara. 2019. Wavelet-based Data Compression for Three-dimensional Fluid Flow Simulations on Regular Grids. Bulletin of the American Physical Society (2019).
33. Wei Li, Yixin Chen, Mathieu Desbrun, Changxi Zheng, and Xiaopei Liu. 2020. Fast and Scalable Turbulent Flow Simulation with Two-Way Coupling. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 4, Article 47 (July 2020), 20 pages.
34. P. Lindstrom. 2014. Fixed-Rate Compressed Floating-Point Arrays. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comp. Graph. 20, 12 (2014), 2674–2683.
35. P. Lindstrom and M. Isenburg. 2006. Fast and Efficient Compression of Floating-Point Data. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comp. Graph. 12, 5 (2006), 1245–1250.
36. Beibei Liu, Gemma Mason, Julian Hodgson, Yiying Tong, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2015. Model-Reduced Variational Fluid Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6, Article 244 (2015).
37. Zichao Long, Yiping Lu, and Bin Dong. 2019. PDE-Net 2.0: Learning PDEs from data with a numeric-symbolic hybrid deep network. J. Comput. Phys. 399 (2019), 108925.
38. Siwei Ma, Xinfeng Zhang, Chuanmin Jia, Zhenghui Zhao, Shiqi Wang, and Shanshe Wang. 2019. Image and video compression with neural networks: A review. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 30, 6 (2019), 1683–1698.
39. D. Marr, E. Hildreth, and Sydney Brenner. 1980. Theory of edge detection. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B. Biological Sciences 207, 1167 (1980), 187–217.
40. Maxon. 2021. Redshift renderer. (2021). https://www.redshift3d.com/product
41. Shilpa P Metkar and Sanjay N Talbar. 2010. Fast motion estimation using modified orthogonal search algorithm for video compression. Signal, Image and Video Processing 4, 1 (2010), 123–128.
42. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali. 1988. Reconstruction Filters in Computer-Graphics. In Proceedings of the 15th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH ’88). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 221–228.
43. Patrick Mullen, Keenan Crane, Dmitry Pavlov, Yiying Tong, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2009. Energy-Preserving Integrators for Fluid Animation. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3, Article 38 (July 2009), 8 pages.
44. Octavi Obiols-Sales, Abhinav Vishnu, Nicholas Malaya, and Aparna Chandramowliswharan. 2020. CFDNet: A deep learning-based accelerator for fluid simulations. In Proceedings of the 34th ACM International Conference on Supercomputing. 1–12.
45. Young Jin Oh and In-Kwon Lee. 2021. Two-step Temporal Interpolation Network Using Forward Advection for Efficient Smoke Simulation. Computer Graphics Forum 40, 2 (2021), 355–365. arXiv:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/cgf.142638
46. Sang Il Park and Myoung Jun Kim. 2005. Vortex Fluid for Gaseous Phenomena. In Symposium on Computer Animation. 261–270.
47. Tobias Pfaff, Nils Thuerey, Jonathan Cohen, Sarah Tariq, and Markus Gross. 2010. Scalable Fluid Simulation Using Anisotropic Turbulence Particles. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 6, Article 174 (Dec. 2010), 8 pages.
48. Tobias Pfaff, Nils Thuerey, and Markus Gross. 2012. Lagrangian Vortex Sheets for Animating Fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4, Article 112 (July 2012), 8 pages.
49. L Lo Presti. 2000. Efficient modified-sinc filters for sigma-delta A/D converters. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Analog and Digital Signal processing 47, 11 (2000), 1204–1213.
50. Ziyin Qu, Xinxin Zhang, Ming Gao, Chenfanfu Jiang, and Baoquan Chen. 2019. Efficient and Conservative Fluids Using Bidirectional Mapping. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 4, Article 128 (July 2019), 12 pages.
51. Ryotaro Sakai, Daisuke Sasaki, and Kazuhiro Nakahashi. 2013. Parallel implementation of large-scale CFD data compression toward aeroacoustic analysis. Computers & Fluids 80 (2013), 116–127.
52. Syuhei Sato, Yoshinori Dobashi, and Theodore Kim. 2021. Stream-Guided Smoke Simulations. ACM Trans. Graph. 40, 4, Article 161 (July 2021), 7 pages.
53. Syuhei Sato, Yoshinori Dobashi, Theodore Kim, and Tomoyuki Nishita. 2018. Example-Based Turbulence Style Transfer. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 84 (July 2018), 9 pages.
54. H. Schechter and R. Bridson. 2008. Evolving Sub-grid Turbulence for Smoke Animation. In Symposium on Computer Animation. 1–7.
55. Andrew Selle, Ronald Fedkiw, Byungmoon Kim, Yingjie Liu, and Jarek Rossignac. 2008. An Unconditionally Stable MacCormack Method. Journal of Scientific Computing 35, 2-3 (2008), 350–371.
56. Adam J Sierakowski and Andrea Prosperetti. 2016. Resolved-particle simulation by the Physalis method: enhancements and new capabilities. J. Comput. Phys. 309 (2016), 164–184.
57. Philippe R Spalart. 2009. Detached-eddy simulation. Annual review of fluid mechanics 41 (2009), 181–202.
58. John Steinhoff and David Underhill. 1994. Modification of the Euler equations for “vorticity confinement”: Application to the computation of interacting vortex rings. Physics of Fluids 6 (1994), 2738–2744.
59. Jonathan Tompson, Kristofer Schlachter, Pablo Sprechmann, and Ken Perlin. 2017. Accelerating Eulerian fluid simulation with convolutional networks. In International Conference on Machine Learning, Vol. 70. 3424–3433.
60. Kiwon Um, Robert Brand, Yun (Raymond) Fei, Philipp Holl, and Nils Thuerey. 2020. Solver-in-the-Loop: Learning from Differentiable Physics to Interact with Iterative PDE-Solvers. In NeurIPS, H. Larochelle, M. Ranzato, R. Hadsell, M. F. Balcan, and H. Lin (Eds.), Vol. 33. 6111–6122.
61. Kiwon Um, Xiangyu Hu, and Nils Thuerey. 2018. Liquid splash modeling with neural networks. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 37. 171–182.
62. Nobuyuki Umetani and Bernd Bickel. 2018. Learning Three-Dimensional Flow for Interactive Aerodynamic Design. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 89 (July 2018), 10 pages.
63. Henk Kaarle Versteeg and Weeratunge Malalasekera. 2007. An introduction to computational fluid dynamics: the finite volume method. Pearson education.
64. Steffen Weißmann and Ulrich Pinkall. 2010. Filament-based Smoke with Vortex Shedding and Variational Reconnection. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 4, Article 115 (July 2010), 12 pages.
65. Maximilian Werhahn, You Xie, Mengyu Chu, and Nils Thuerey. 2019. A Multi-Pass GAN for Fluid Flow Super-Resolution. Proc. ACM Comput. Graph. Interact. Tech. 2, 2, Article 10 (July 2019), 21 pages.
66. Martin Wicke, Matt Stanton, and Adrien Treuille. 2009. Modular Bases for Fluid Dynamics. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3, Article 39 (July 2009), 8 pages.
67. Steffen Wiewel, Moritz Becher, and Nils Thuerey. 2019. Latent space physics: Towards learning the temporal evolution of fluid flow. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 38. Wiley Online Library, 71–82.
68. David C Wilcox et al. 1998. Turbulence modeling for CFD. Vol. 2. DCW industries La Canada, CA.
69. You Xie, Erik Franz, Mengyu Chu, and Nils Thuerey. 2018. TempoGAN: A Temporally Coherent, Volumetric GAN for Super-Resolution Fluid Flow. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 95 (July 2018), 15 pages.
70. Jonas Zehnder, Rahul Narain, and Bernhard Thomaszewski. 2018. An Advection-Reflection Solver for Detail-Preserving Fluid Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 85 (July 2018), 8 pages.
71. Xinxin Zhang, Robert Bridson, and Chen Greif. 2015. Restoring the Missing Vorticity in Advection-projection Fluid Solvers. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4, Article 52 (July 2015), 8 pages.
72. Bo Zhu, Wenlong Lu, Matthew Cong, Byungmoon Kim, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2013. A New Grid Structure for Domain Extension. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4, Article 63 (July 2013), 12 pages.